Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Army with our comprehensive guide to Army Officer Ranks. Learn to decipher insignia, symbols, and rank structures, from Second Lieutenant to General. Understand the differences between Commissioned, Warrant, and Non-Commissioned Officers, and how they contribute to the militarys chain of command and leadership.
The rank structure of the army is a complex system that can be confusing for those who are not familiar with it. Army officer ranks are a crucial part of this system, and understanding the insignia and symbols associated with each rank is essential for anyone who wants to navigate the military hierarchy.
Army officer ranks are divided into several categories, including commissioned officers, warrant officers, and non-commissioned officers. Commissioned officers are the highest-ranking officers in the army, and they hold positions of authority and leadership. Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, and they often serve as advisors to commissioned officers. Non-commissioned officers are enlisted personnel who have risen through the ranks and hold positions of leadership and responsibility.
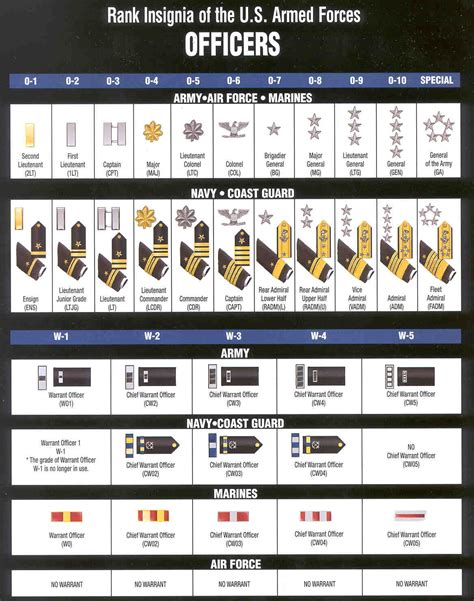
Commissioned Officer Ranks
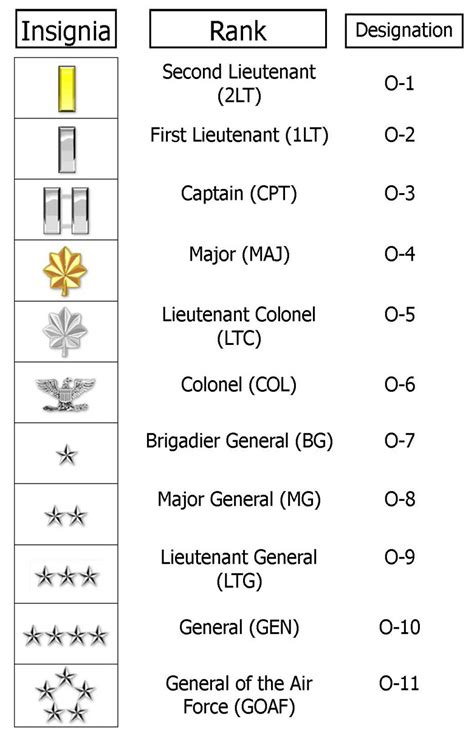
Commissioned officer ranks are the highest-ranking officer ranks in the army. These ranks are divided into several categories, including company-grade officers, field-grade officers, and general officers.
Company-Grade Officers
Company-grade officers are the lowest-ranking commissioned officers in the army. These ranks include:
- Second Lieutenant (2LT)
- First Lieutenant (1LT)
- Captain (CPT)
Company-grade officers typically serve as platoon leaders or company commanders. They are responsible for leading small units of soldiers and carrying out the day-to-day tasks of the army.

Field-Grade Officers
Field-grade officers are higher-ranking than company-grade officers. These ranks include:
- Major (MAJ)
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC)
- Colonel (COL)
Field-grade officers typically serve as battalion or brigade commanders. They are responsible for leading larger units of soldiers and making strategic decisions.

General Officers
General officers are the highest-ranking officers in the army. These ranks include:
- Brigadier General (BG)
- Major General (MG)
- Lieutenant General (LTG)
- General (GEN)
General officers typically serve as corps or division commanders. They are responsible for leading large units of soldiers and making strategic decisions at the highest level.

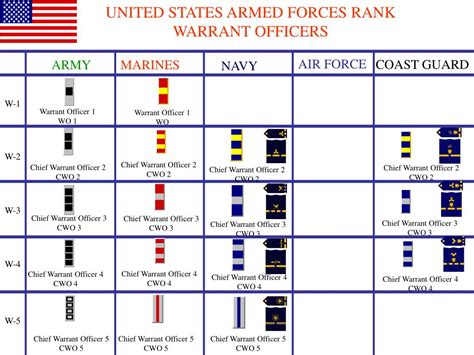
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field. They serve as advisors to commissioned officers and are responsible for providing technical guidance and expertise.
Warrant officer ranks include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
Non-commissioned officers are enlisted personnel who have risen through the ranks and hold positions of leadership and responsibility.
Non-commissioned officer ranks include:
- Corporal (CPL)
- Sergeant (SGT)
- Staff Sergeant (SSG)
- Sergeant First Class (SFC)
- Master Sergeant (MSG)
- Sergeant Major (SGM)
- Command Sergeant Major (CSM)
- Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA)
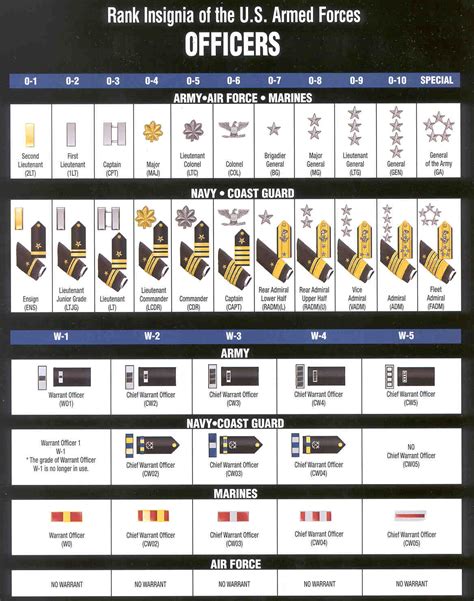
Insignia and Symbols
Each rank in the army has its own unique insignia and symbols. These insignia and symbols are used to identify an officer's rank and to distinguish them from other officers.
Commissioned officers wear rank insignia on their uniforms, which consists of bars, oak leaves, or stars. Warrant officers wear a distinctive insignia on their uniforms, which consists of a bar and a wreath. Non-commissioned officers wear rank insignia on their uniforms, which consists of stripes or chevrons.
Gallery of Army Officer Ranks
Army Officer Ranks Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the highest rank in the army?
+The highest rank in the army is General (GEN).
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+A commissioned officer is a leader who has completed officer candidate school, while a warrant officer is a technical expert who has completed warrant officer candidate school.
How do I become a non-commissioned officer?
+To become a non-commissioned officer, you must enlist in the army and work your way up through the ranks.
We hope this article has helped you understand the different ranks in the army and the insignia and symbols associated with each rank. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or just starting out, it's essential to know the rank structure and how it works.
