Intro
Uncover the history of the US militarys oldest branch, tracing its roots back to the American Revolution. Discover the evolution of the Continental Army, its role in shaping the nation, and the significance of its legacy. Learn about the brave men and women who served, and how their sacrifices continue to inspire patriotism and pride today.
The United States Armed Forces have a rich history, with each branch playing a unique and vital role in defending the country. Among the five branches, one stands out as the oldest, with a history dating back to the early days of the American Revolution.
The Continental Army, the precursor to the modern-day United States Army, was formed on June 14, 1775, during the Second Continental Congress. This marks the beginning of the US Army's long and storied history, making it the oldest branch of the US military.

In this article, we will delve into the history of the US Army, its evolution, and its role in shaping the country's military. We will also explore the Army's structure, its various components, and its contributions to national defense.
A Brief History of the US Army
The US Army's history is closely tied to the American Revolution. In June 1775, the Continental Congress authorized the formation of the Continental Army, with George Washington as its commander-in-chief. The Army played a crucial role in the Revolutionary War, fighting against the British and their allies.
After the war, the Continental Army was disbanded, but in 1784, the US Army was officially established as a professional military force. Over the years, the Army has undergone significant transformations, adapting to new technologies, tactics, and threats.

The American Civil War and the Expansion of the US Army
The American Civil War marked a significant turning point in the US Army's history. The conflict saw the Army expand rapidly, with the number of soldiers increasing from 16,000 in 1861 to over 1 million by 1865. The war also led to the introduction of new technologies, such as railroads and telegraphs, which revolutionized military logistics and communication.
The US Army continued to grow and modernize in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, playing a key role in both World War I and World War II. The Army's performance in these conflicts cemented its position as a dominant force in global military affairs.
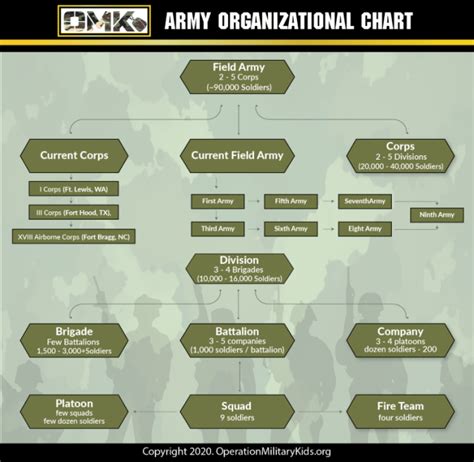
The Structure of the US Army
The US Army is divided into several components, each with its unique mission and responsibilities. The main components include:
- Active Duty: The full-time, professional force of the US Army.
- Army National Guard: A reserve component that can be called upon to support state and federal missions.
- Army Reserve: A part-time force that supports the Active Duty and National Guard components.
The US Army is also organized into various branches, including:
- Infantry: The largest branch, responsible for ground combat operations.
- Armor: Specializes in armored warfare, using tanks and other armored vehicles.
- Artillery: Provides indirect fire support to ground units.
- Engineers: Responsible for constructing and maintaining infrastructure, as well as conducting combat engineering operations.
The US Army's Contributions to National Defense
The US Army has played a vital role in defending the country and its interests. From the Revolutionary War to the present day, the Army has been involved in numerous conflicts, peacekeeping missions, and humanitarian operations.
Some of the US Army's most notable contributions include:
- World War I: The Army played a key role in the Allied victory, suffering over 115,000 casualties.
- World War II: The Army was instrumental in the defeat of Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan, with over 318,000 soldiers killed or wounded.
- Korean War: The Army fought against North Korean and Chinese forces, suffering over 36,000 casualties.
- Vietnam War: The Army was involved in the conflict from 1955 to 1973, suffering over 47,000 casualties.

Modernization and the Future of the US Army
The US Army is currently undergoing significant modernization efforts, with a focus on adapting to emerging threats and technologies. Some of the key areas of modernization include:
- Cybersecurity: The Army is investing heavily in cybersecurity, recognizing the growing threat of cyber attacks.
- Artificial Intelligence: The Army is exploring the use of AI in various areas, including logistics, intelligence, and operations.
- Hypersonic Missiles: The Army is developing hypersonic missiles, capable of traveling at speeds over Mach 5.
The US Army is also placing a greater emphasis on soldier lethality, with the introduction of new technologies such as the Next Generation Squad Weapon (NGSW) and the Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS).

Challenges Facing the US Army
Despite its many successes, the US Army faces numerous challenges, including:
- Budget constraints: The Army's budget has been subject to fluctuations, affecting its ability to modernize and maintain readiness.
- Recruitment and retention: The Army faces challenges in recruiting and retaining high-quality soldiers, particularly in certain specialties.
- Changing nature of warfare: The Army must adapt to emerging threats, such as cyber attacks and asymmetric warfare.
US Army Image Gallery






What is the oldest branch of the US military?
+The US Army is the oldest branch of the US military, with a history dating back to June 14, 1775.
What are the main components of the US Army?
+The US Army is divided into Active Duty, Army National Guard, and Army Reserve components.
What are some of the US Army's most notable contributions to national defense?
+The US Army has played a vital role in numerous conflicts, including World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War.
As we reflect on the US Army's rich history, it is clear that the branch has played a vital role in shaping the country's military and defending its interests. From its humble beginnings in the Continental Army to its current status as a dominant force in global military affairs, the US Army continues to adapt and evolve to meet emerging threats and challenges.
