Intro
Unlock the structure of the US Army with our in-depth guide to its 6 key parts. From Combat Arms to Combat Support and Combat Service Support, discover the essential branches and specialties that work together to defend the nation. Learn about Military Occupational Specialties, ranks, and more in this comprehensive Army breakdown.
The Army is a vital institution in many countries, responsible for defending national interests and maintaining peace and security. While the Army's overall mission is clear, its internal structure and organization can be complex and confusing. In this article, we will break down the six key parts of the Army, explaining their roles, responsibilities, and importance.
The Army is a large and complex organization, comprising various branches, divisions, and units. Understanding the six key parts of the Army can help you appreciate its inner workings and the roles that different personnel play.
1. The Infantry
The Backbone of the Army
The Infantry is the largest and most well-known branch of the Army. Infantrymen are responsible for fighting on foot, using a range of weapons and tactics to engage enemy forces. They are the backbone of the Army, providing the ground troops that are essential for securing territory and completing missions.
The Infantry is divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Light Infantry: These units are designed to be fast and agile, using speed and surprise to outmaneuver enemy forces.
- Heavy Infantry: These units are equipped with heavy armor and artillery, providing a strong defensive presence on the battlefield.
- Mechanized Infantry: These units use armored vehicles to transport troops and equipment, providing a mobile and flexible force.
2. The Artillery
Providing Firepower on the Battlefield
The Artillery is responsible for providing firepower on the battlefield, using a range of guns, howitzers, and rockets to attack enemy positions. Artillery units are equipped with heavy guns and equipment, and are trained to deliver precise and accurate firepower.
The Artillery is divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Field Artillery: These units use towed guns and howitzers to provide firepower on the battlefield.
- Air Defense Artillery: These units use surface-to-air missiles to defend against enemy aircraft.
- Missile Artillery: These units use guided missiles to attack enemy positions.

3. The Armor
The Army's Tank Forces
The Armor is responsible for providing the Army's tank forces, using armored vehicles to break through enemy lines and secure territory. Armor units are equipped with tanks, armored personnel carriers, and other vehicles, and are trained to operate in a range of environments.
The Armor is divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Tank Units: These units use tanks to break through enemy lines and provide mobile firepower.
- Cavalry Units: These units use armored vehicles to conduct reconnaissance and provide security.
- Armor Infantry Units: These units use armored vehicles to transport troops and equipment.
4. The Aviation
The Army's Air Power
The Aviation is responsible for providing the Army's air power, using helicopters and airplanes to transport troops and equipment, and to provide firepower on the battlefield. Aviation units are equipped with a range of aircraft, including attack helicopters, transport helicopters, and fixed-wing planes.
The Aviation is divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Attack Aviation: These units use helicopters and airplanes to attack enemy positions.
- Transport Aviation: These units use helicopters and airplanes to transport troops and equipment.
- Reconnaissance Aviation: These units use aircraft to conduct reconnaissance and provide intelligence.

5. The Engineers
Building and Maintaining Infrastructure
The Engineers are responsible for building and maintaining infrastructure, using a range of skills and equipment to construct roads, bridges, and buildings. Engineers are also responsible for demolishing enemy infrastructure, using explosives and other techniques to disrupt enemy operations.
The Engineers are divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Combat Engineers: These units use explosives and other techniques to demolish enemy infrastructure.
- Construction Engineers: These units use heavy equipment and construction techniques to build roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Topographic Engineers: These units use mapping and surveying techniques to provide intelligence and support military operations.
6. The Signals
Communicating on the Battlefield
The Signals are responsible for communicating on the battlefield, using a range of techniques and equipment to transmit information between units. Signals units are equipped with radios, satellites, and other communication equipment, and are trained to operate in a range of environments.
The Signals are divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Communication Units: These units use radios and other communication equipment to transmit information between units.
- Signal Intelligence Units: These units use intercepts and other techniques to gather intelligence on enemy communications.
- Cyber Units: These units use computer networks and other cyber techniques to disrupt enemy operations.
In conclusion, the six key parts of the Army play critical roles in maintaining national security and defending against threats. Each branch has its own unique responsibilities and specializations, and together they form a powerful and effective fighting force.
Army Structure Image Gallery






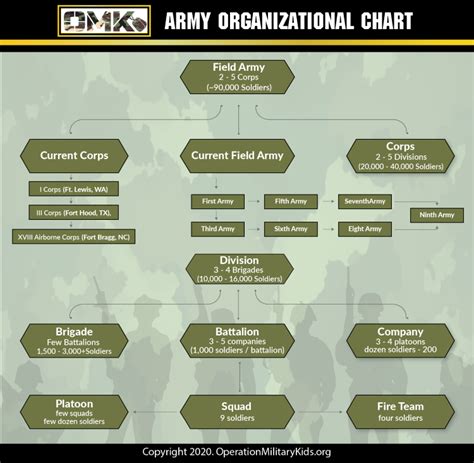



What is the role of the Infantry in the Army?
+The Infantry is the largest and most well-known branch of the Army, responsible for fighting on foot and using a range of weapons and tactics to engage enemy forces.
What is the difference between the Artillery and the Armor?
+The Artillery is responsible for providing firepower on the battlefield, using guns, howitzers, and rockets to attack enemy positions. The Armor is responsible for providing the Army's tank forces, using armored vehicles to break through enemy lines and secure territory.
What is the role of the Signals in the Army?
+The Signals are responsible for communicating on the battlefield, using a range of techniques and equipment to transmit information between units.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the six key parts of the Army and their roles in maintaining national security. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
