Intro
Discover the unsung heroes behind diagnostic ultrasounds. Sonographers play a crucial role in medical imaging, using specialized equipment to capture high-quality images. Learn about the skills, training, and expertise required to become a sonographer, and how they work with radiologists to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, including cardiovascular, obstetric, and musculoskeletal disorders.
Medical imaging technology has revolutionized the field of healthcare, enabling doctors to diagnose and treat diseases more effectively. Among the various medical imaging modalities, ultrasound technology stands out for its non-invasive nature, safety, and cost-effectiveness. But have you ever wondered who are the professionals behind these diagnostic ultrasounds? Let's take a closer look at the role of sonographers in the medical imaging field.

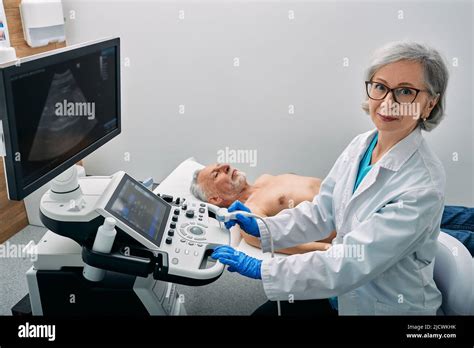
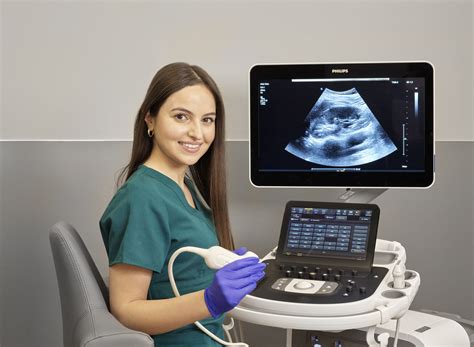
Sonographers, also known as ultrasound technologists or diagnostic medical sonographers, are trained healthcare professionals responsible for performing diagnostic ultrasound examinations. They use specialized equipment to produce images of the internal structures of the body, which helps doctors diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
What Do Sonographers Do?
Sonographers play a crucial role in the medical imaging process. Their primary responsibilities include:
- Preparing patients for ultrasound examinations by explaining the procedure, answering questions, and positioning them correctly.
- Operating ultrasound equipment to produce high-quality images of the internal structures of the body.
- Adjusting equipment settings and using various techniques to optimize image quality.
- Analyzing images to identify potential abnormalities or diseases.
- Maintaining accurate records of patient data and test results.
- Collaborating with radiologists and other healthcare professionals to ensure accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Types of Sonographers
Sonographers can specialize in various areas, including:
- Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer: Specializes in imaging the heart and blood vessels.
- Vascular Sonographer: Focuses on imaging blood vessels and diagnosing vascular diseases.
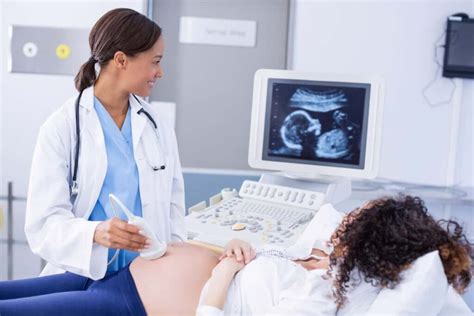
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Sonographer: Concentrates on imaging the female reproductive system and fetus during pregnancy.
- Abdominal Sonographer: Examines organs in the abdominal cavity, such as the liver, kidneys, and gallbladder.
- Musculoskeletal Sonographer: Specializes in imaging muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Education and Training
To become a sonographer, one typically needs to complete a formal education program in diagnostic medical sonography. These programs are usually offered at colleges, universities, or vocational schools and can lead to an associate's degree or a postsecondary certificate.

In addition to formal education, sonographers must also obtain professional certification to demonstrate their expertise. The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) offers various certifications for sonographers, such as the Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer (RDMS) credential.
Skills and Qualities
Sonographers need to possess a combination of technical, communication, and interpersonal skills to excel in their role. Some essential qualities include:
- Strong technical knowledge of ultrasound equipment and imaging techniques.
- Excellent communication skills to interact with patients, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals.
- Ability to work independently and as part of a team.
- Compassion and empathy when dealing with patients who may be anxious or in pain.
- Strong analytical skills to interpret images and identify potential abnormalities.
Work Environment and Salary
Sonographers typically work in hospitals, clinics, or medical imaging centers. They may work irregular hours, including evenings, weekends, or on-call shifts. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for diagnostic medical sonographers in the United States was around $68,000 in May 2020.

Growth Prospects and Job Outlook
The demand for sonographers is expected to grow significantly due to the increasing use of ultrasound technology in medical imaging. The BLS projects a 14% growth in employment opportunities for diagnostic medical sonographers from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Gallery of Sonographers at Work



Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a sonographer in medical imaging?
+Sonographers play a crucial role in medical imaging by using ultrasound technology to produce images of the internal structures of the body. They prepare patients for examinations, operate equipment, analyze images, and maintain accurate records.
What education and training do sonographers need?
+Sonographers typically need to complete a formal education program in diagnostic medical sonography, which can lead to an associate's degree or a postsecondary certificate. They must also obtain professional certification to demonstrate their expertise.
What are the different types of sonographers?
+Sonographers can specialize in various areas, including diagnostic cardiac sonography, vascular sonography, obstetric and gynecologic sonography, abdominal sonography, and musculoskeletal sonography.
In conclusion, sonographers play a vital role in medical imaging, using their technical expertise and communication skills to produce high-quality images that help doctors diagnose and treat diseases. With the increasing demand for ultrasound technology, the job outlook for sonographers is promising, making it an attractive career option for those interested in healthcare and medical imaging.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the role of sonographers in medical imaging. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences as a sonographer, please leave a comment below.
