Intro
Discover the strategic Persian Gulf location on the world map, bordered by eight countries including Iran, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia. Learn about its geographical significance, economic importance, and historical relevance. Explore the gulfs role in global trade, oil production, and cultural exchange, and get an insiders look at its position in the Middle East region.
The Persian Gulf, also known as the Arabian Gulf, is a vital body of water located in the Middle East, playing a crucial role in global trade, economy, and politics. Understanding its location on the world map is essential to grasp its significance and the impact it has on the surrounding regions.
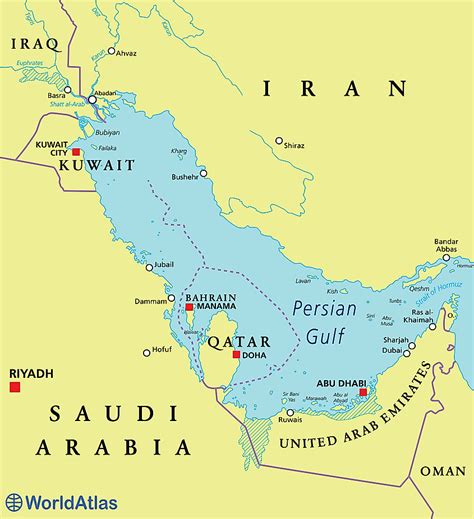
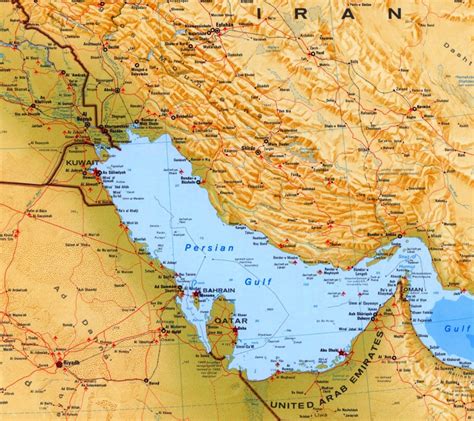
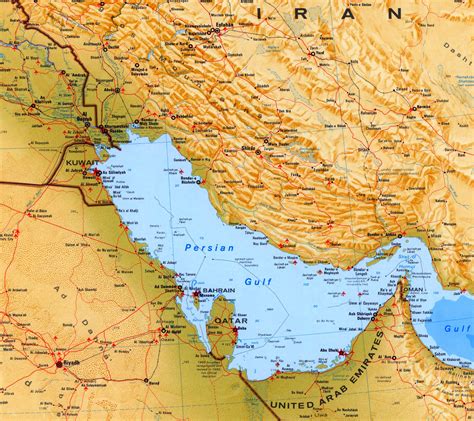
Geographically, the Persian Gulf is situated in the southwestern part of Asia, bordering several countries, including Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Oman. It connects to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea, ultimately leading to the Indian Ocean. The gulf's unique location makes it a vital waterway for international trade, with many major shipping lanes passing through it.
Significance of the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf holds immense strategic importance due to its:
- Crude oil reserves: The region is home to some of the world's largest oil reserves, making it a critical player in the global energy market.
- Trade routes: The gulf's location allows for easy access to international markets, facilitating the transportation of goods, including oil, natural gas, and other commodities.
- Economic importance: The Persian Gulf is a significant contributor to the global economy, with many countries relying heavily on its oil and gas exports.
Historical Background
The Persian Gulf has a rich history, dating back thousands of years. It has been an important center for trade and commerce, with ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Persians utilizing its waters for transportation and cultural exchange. The gulf's strategic location has also made it a coveted prize for various empires and colonial powers throughout history.
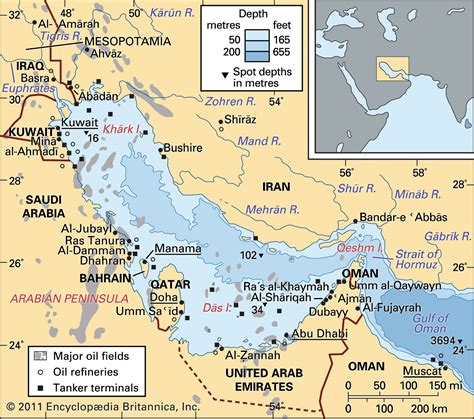
Countries Bordering the Persian Gulf
Eight countries border the Persian Gulf, each with its unique culture, economy, and history:
- Iran: Located on the gulf's northern coast, Iran is a significant player in regional politics and economy.
- Iraq: Bordering the gulf to the northwest, Iraq is a major oil producer and a key player in regional trade.
- Kuwait: A small, oil-rich country situated on the gulf's western coast, Kuwait is a major contributor to the global energy market.
- Saudi Arabia: The largest country bordering the gulf, Saudi Arabia is a dominant player in regional politics and economy.
- Qatar: A small, gas-rich country located on the gulf's eastern coast, Qatar is a significant player in regional trade and diplomacy.
- United Arab Emirates: A federation of seven emirates, the UAE is a major economic hub, with Dubai and Abu Dhabi being significant centers for trade and commerce.
- Oman: Located on the gulf's southeastern coast, Oman is a strategically important country, with a strong focus on trade and tourism.
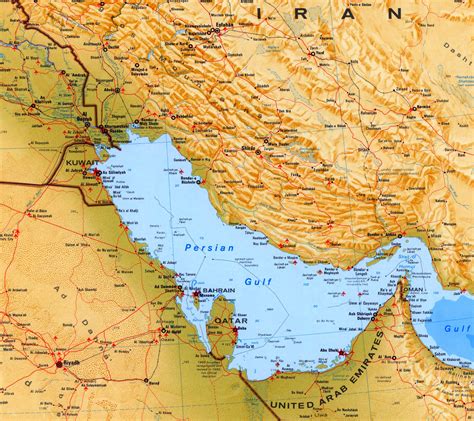
Environmental Concerns
The Persian Gulf faces several environmental challenges, including:
- Pollution: The gulf's waters are heavily polluted due to oil spills, industrial waste, and other human activities.
- Climate change: Rising temperatures and sea levels pose a significant threat to the gulf's ecosystem and the countries bordering it.
- Overfishing: The gulf's fisheries are under threat due to overfishing and destructive fishing practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Persian Gulf is a vital region, playing a significant role in global trade, economy, and politics. Its unique location, rich history, and strategic importance make it a crucial player in international relations. However, the region also faces several environmental challenges, which need to be addressed to ensure its long-term sustainability.
Persian Gulf Image Gallery




What is the strategic importance of the Persian Gulf?
+The Persian Gulf is strategically important due to its unique location, which allows for easy access to international markets, facilitating the transportation of goods, including oil, natural gas, and other commodities.
Which countries border the Persian Gulf?
+Eight countries border the Persian Gulf: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Oman.
What are the environmental concerns facing the Persian Gulf?
+The Persian Gulf faces several environmental challenges, including pollution, climate change, and overfishing, which pose a significant threat to the gulf's ecosystem and the countries bordering it.
