Intro
Unlock the secrets of potential energy from force and discover how it can be harnessed to transform our world. Explore the scientific principles behind this phenomenon, including kinetic energy, work, and force fields. Learn how potential energy is stored and converted, and its applications in fields like physics, engineering, and renewable energy.
The concept of force has been a cornerstone of physics for centuries, with Sir Isaac Newton's laws of motion providing the foundation for understanding the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. However, there is another fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in our understanding of the natural world: potential energy. Potential energy, often overlooked, is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration, waiting to be unleashed as kinetic energy. In this article, we will delve into the world of potential energy, exploring its relationship with force and the scientific principles that govern its behavior.

What is Potential Energy?
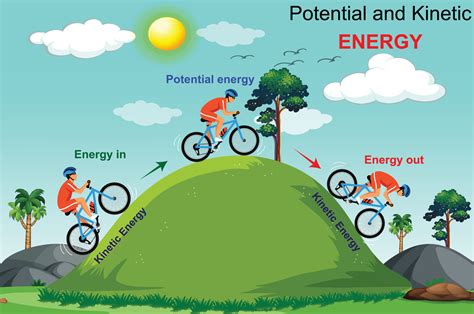
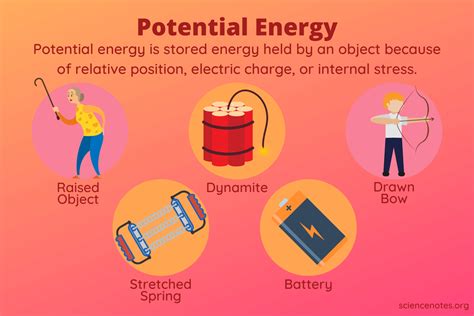
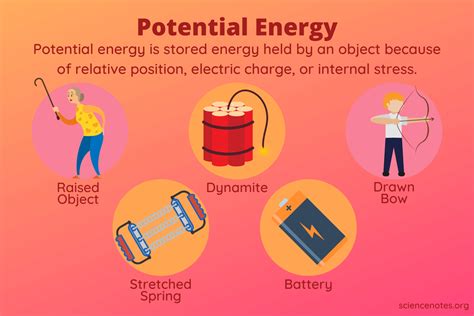
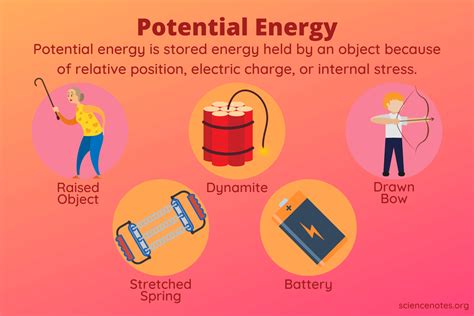
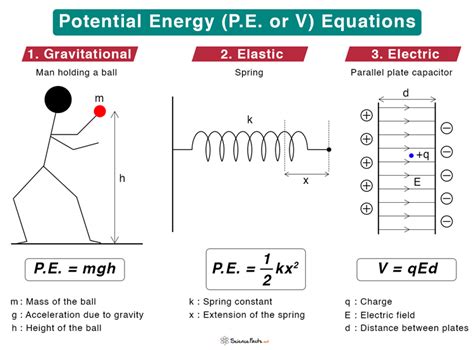
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration, such as being at a height or having a specific arrangement of particles. This energy is stored and waiting to be converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. There are several types of potential energy, including gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and electrical potential energy, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Gravitational Potential Energy
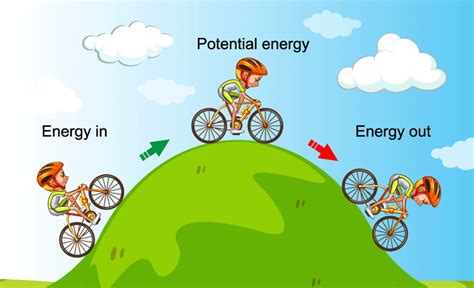
Gravitational potential energy is the most common type of potential energy, arising from the force of gravity acting on an object. The energy is stored in the object's position, with the amount of energy increasing with height. For example, a ball at the top of a hill possesses more gravitational potential energy than the same ball at the bottom of the hill. As the ball rolls down the hill, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, illustrating the fundamental principle of energy conservation.
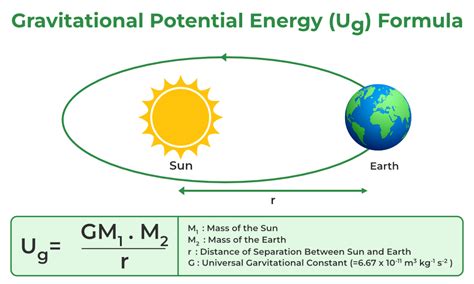
The Relationship Between Force and Potential Energy
Force and potential energy are intricately linked, with force playing a crucial role in the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy. When a force is applied to an object, it can cause the object to move, converting its potential energy into kinetic energy. The amount of force required to achieve this conversion depends on the object's mass and the distance over which the force is applied.
Hooke's Law and Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is another type of potential energy, arising from the force of elasticity in materials. Hooke's Law, which states that the force required to stretch or compress a material is proportional to the distance of stretching or compressing, governs the behavior of elastic potential energy. When a force is applied to a material, it stores energy in the form of elastic potential energy, which is released when the force is removed.
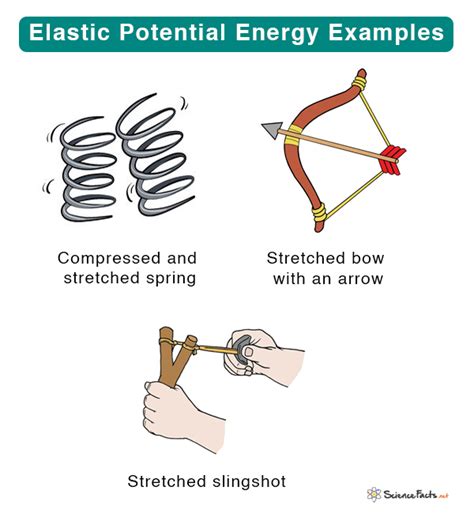
Applications of Potential Energy
Potential energy has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and chemistry. Understanding the principles of potential energy is essential for designing and optimizing systems, such as power plants, bridges, and machines.
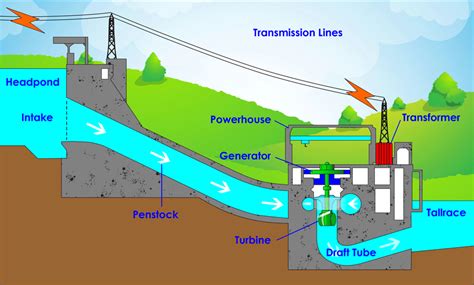
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Hydroelectric power plants harness the potential energy of water stored behind dams to generate electricity. As the water flows down through the turbines, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, driving the turbines to produce electricity.
Scientific Principles Governing Potential Energy
Several scientific principles govern the behavior of potential energy, including the law of conservation of energy, the law of universal gravitation, and Hooke's Law. Understanding these principles is crucial for predicting and analyzing the behavior of potential energy in various systems.
The Law of Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. This fundamental principle governs the behavior of potential energy, ensuring that the total energy of a closed system remains constant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, potential energy is a fundamental concept in physics, playing a crucial role in our understanding of the natural world. Its relationship with force, governed by scientific principles such as the law of conservation of energy and Hooke's Law, is essential for designing and optimizing systems. By unlocking the potential energy from force, we can harness the power of nature to generate electricity, build innovative machines, and advance our understanding of the universe.
Potential Energy Image Gallery


What is potential energy?
+Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration, such as being at a height or having a specific arrangement of particles.
How is potential energy related to force?
+Force and potential energy are intricately linked, with force playing a crucial role in the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy.
What are some applications of potential energy?
+Potential energy has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and chemistry, such as hydroelectric power plants and elastic materials.
