Intro
Boost your ASVAB score with our comprehensive Mechanical Comprehension practice test and study guide. Master essential concepts, including simple machines, mechanical advantage, and energy transfer. Get expert tips, detailed explanations, and realistic practice questions to ace the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension section and secure your military career goals.
The Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) Mechanical Comprehension test is a crucial part of the overall ASVAB exam, measuring a candidate's understanding of mechanical principles, concepts, and practices. As a future member of the US military, scoring well on this test can open up more career opportunities and give you a competitive edge in the enlistment process. To help you prepare, we've put together this comprehensive study guide and practice test for ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension.
Understanding the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Test

The ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test consists of 25 questions that must be completed within 19 minutes. The test assesses your knowledge of mechanical principles, including:
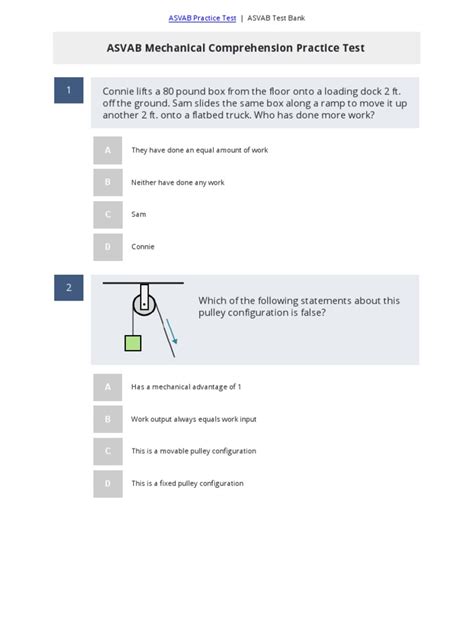
- Simple machines and mechanisms
- Levers, pulleys, and gears
- Fluid dynamics and hydraulics
- Thermodynamics and heat transfer
- Electric circuits and electronics
To succeed on this test, you'll need to demonstrate a solid understanding of these concepts and be able to apply them to real-world problems.
Key Concepts and Principles
Before diving into practice questions, it's essential to review the key concepts and principles that will be covered on the test. Here are some critical areas to focus on:
- Simple Machines: Understand the basic principles of simple machines, including levers, pulleys, and inclined planes.
- Mechanical Advantage: Learn how to calculate mechanical advantage and understand its applications in various mechanical systems.
- Fluid Dynamics: Study the basics of fluid dynamics, including pressure, flow rate, and Bernoulli's principle.
- Thermodynamics: Review the fundamental laws of thermodynamics, including heat transfer, temperature, and energy conversion.
- Electric Circuits: Understand the basics of electric circuits, including Ohm's law, series and parallel circuits, and circuit analysis.
Practice Questions and Study Guide

To help you assess your knowledge and identify areas for improvement, we've put together a set of practice questions and answers. Take your time to work through each question, and don't hesitate to review the explanations and solutions.
Practice Questions:
- A lever is used to lift a load of 100 pounds. If the effort arm is 2 feet long and the load arm is 4 feet long, what is the mechanical advantage of the lever?
A) 2:1 B) 4:1 C) 1:2 D) 1:4
- A hydraulic system consists of a cylinder with a diameter of 10 inches and a piston with a diameter of 5 inches. If the pressure on the piston is 100 psi, what is the pressure on the cylinder?
A) 50 psi B) 100 psi C) 200 psi D) 400 psi
- A thermodynamic system consists of a heat source at 200°F and a heat sink at 100°F. If the system is operating at a steady state, what is the heat transfer rate from the heat source to the heat sink?
A) 100 Btu/h B) 200 Btu/h C) 500 Btu/h D) 1000 Btu/h
- An electric circuit consists of a resistor with a resistance of 10 ohms and a voltage source of 12 volts. If the current flowing through the resistor is 2 amps, what is the power dissipated in the resistor?
A) 20 watts B) 40 watts C) 60 watts D) 80 watts
Answers and Explanations:
-
A) 2:1 The mechanical advantage of a lever is calculated by dividing the length of the effort arm by the length of the load arm. In this case, the mechanical advantage is 2:1.
-
C) 200 psi The pressure on the cylinder can be calculated by multiplying the pressure on the piston by the ratio of the piston diameter to the cylinder diameter. In this case, the pressure on the cylinder is 200 psi.
-
B) 200 Btu/h The heat transfer rate from the heat source to the heat sink can be calculated using the equation Q = m × Cp × ΔT, where Q is the heat transfer rate, m is the mass flow rate, Cp is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the temperature difference. In this case, the heat transfer rate is 200 Btu/h.
-
B) 40 watts The power dissipated in the resistor can be calculated using the equation P = V × I, where P is the power, V is the voltage, and I is the current. In this case, the power dissipated in the resistor is 40 watts.
Gallery of ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Images
ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test?
+The ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test is a part of the overall ASVAB exam, measuring a candidate's understanding of mechanical principles, concepts, and practices.
How many questions are on the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test?
+The ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test consists of 25 questions that must be completed within 19 minutes.
What topics are covered on the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test?
+The test assesses your knowledge of mechanical principles, including simple machines and mechanisms, levers, pulleys, and gears, fluid dynamics and hydraulics, thermodynamics and heat transfer, and electric circuits and electronics.
We hope this comprehensive study guide and practice test has helped you prepare for the ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension test. Remember to review the key concepts and principles, practice with sample questions, and stay focused on your goals. Good luck on your test!
