Intro
Discover the eligibility requirements for Army Reserve enlistment. Learn how to qualify for the Army Reserve through education, work experience, and physical fitness. Explore 5 ways to meet the Army Reserves enlistment standards, including prior military service, vocational training, and college credits. Start your journey to serving part-time and pursuing a civilian career.
Serving in the Army Reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering individuals the opportunity to serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers and personal goals. To qualify for the Army Reserve, candidates must meet specific requirements and follow a multi-step process. Here, we will outline five ways to qualify for the Army Reserve and provide detailed information on the eligibility criteria, application process, and benefits of serving in the Army Reserve.

1. Meet the Basic Eligibility Requirements
To qualify for the Army Reserve, candidates must meet the basic eligibility requirements, which include:
- Being a U.S. citizen or national
- Being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Meeting physical fitness standards
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Scoring a minimum of 31 on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Passing a background check and obtaining a security clearance
Understanding the Army Reserve Enlistment Process
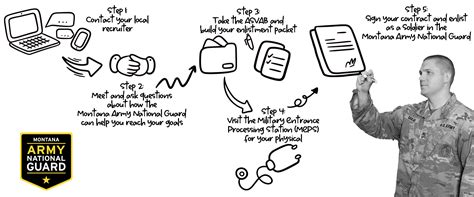
2. Choose a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS)
The Army Reserve offers over 150 different Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), ranging from administrative and technical roles to combat and healthcare positions. Candidates must choose an MOS that aligns with their skills, interests, and career goals.
- Research and explore different MOS options
- Consider factors such as job satisfaction, career advancement opportunities, and required training
- Consult with an Army Reserve recruiter or career counselor for guidance
Army Reserve MOS Options
- Administrative and support roles (e.g., human resources, finance, logistics)
- Technical and maintenance roles (e.g., mechanics, electricians, communications specialists)
- Combat and security roles (e.g., infantry, artillery, military police)
- Healthcare and medical roles (e.g., nursing, medicine, dental care)

3. Complete Basic Training and Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
Once candidates have chosen an MOS, they must complete Basic Training and Advanced Individual Training (AIT). Basic Training, also known as Basic Combat Training (BCT), is a 10-week program that teaches fundamental military skills, such as first aid, map reading, and combat techniques. AIT, on the other hand, is a specialized training program that teaches candidates the skills and knowledge required for their specific MOS.
- Complete Basic Training at a designated Army training facility
- Attend AIT at a designated Army training facility or through online/distance learning programs
Army Reserve Training and Education Benefits
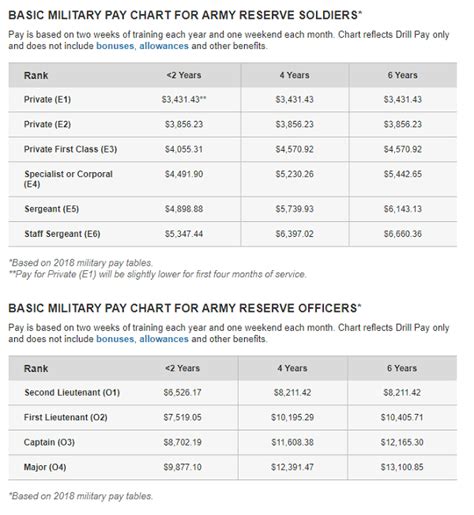
4. Meet the Physical Fitness Standards
The Army Reserve requires candidates to meet specific physical fitness standards, which include:
-
Passing the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT)
-
Meeting body fat percentage requirements
-
Completing a medical examination and obtaining a medical waiver (if necessary)
-
Prepare for the APFT by engaging in regular exercise and physical activity
-
Consult with an Army Reserve recruiter or fitness expert for guidance on meeting the physical fitness standards
Army Reserve Physical Fitness Standards
- Push-ups: 30-40 repetitions
- Sit-ups: 30-40 repetitions
- 2-mile run: 13-15 minutes
- Body fat percentage: 20-30%

5. Apply for Officer Candidate School (OCS)
For candidates who wish to become officers in the Army Reserve, they must apply for Officer Candidate School (OCS). OCS is a 12-week program that teaches leadership and officer skills, such as tactics, logistics, and personnel management.
- Meet the eligibility requirements for OCS, including a bachelor's degree and a minimum GPA of 2.5
- Apply for OCS through the Army Reserve website or by consulting with an Army Reserve recruiter
- Complete the OCS program and receive a commission as an Army Reserve officer
Army Reserve Officer Career Opportunities

In conclusion, qualifying for the Army Reserve requires meeting specific eligibility criteria, choosing an MOS, completing Basic Training and AIT, meeting physical fitness standards, and applying for OCS (for officer candidates). By following these steps, candidates can embark on a rewarding and challenging career in the Army Reserve, while also pursuing civilian careers and personal goals.
Gallery of Army Reserve Images
Army Reserve Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the basic eligibility requirements for the Army Reserve?
+The basic eligibility requirements for the Army Reserve include being a U.S. citizen or national, being between the ages of 17 and 35, meeting physical fitness standards, having a high school diploma or equivalent, scoring a minimum of 31 on the ASVAB test, and passing a background check and obtaining a security clearance.
How do I choose an MOS in the Army Reserve?
+Candidates can choose an MOS by researching and exploring different options, considering factors such as job satisfaction, career advancement opportunities, and required training, and consulting with an Army Reserve recruiter or career counselor for guidance.
What is the difference between Basic Training and Advanced Individual Training (AIT)?
+Basic Training is a 10-week program that teaches fundamental military skills, such as first aid, map reading, and combat techniques. AIT is a specialized training program that teaches candidates the skills and knowledge required for their specific MOS.
