Intro
Unlock the secrets of the military hierarchy with our comprehensive guide to Army Officer Ranks. Learn about the different ranks, from Second Lieutenant to General, and understand the responsibilities, insignia, and requirements for each. Discover the promotion process, rank structures, and the role of officers in the Armys chain of command.
The army is a highly structured institution, with a well-defined hierarchy of officer ranks. Understanding these ranks and their responsibilities is essential for anyone interested in military careers or simply wanting to learn more about the armed forces. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different army officer ranks, their insignia, and their roles within the military hierarchy.
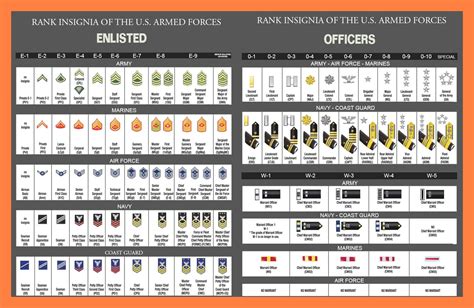
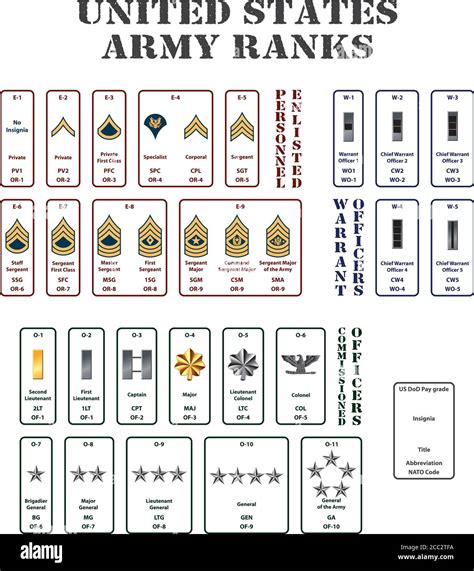
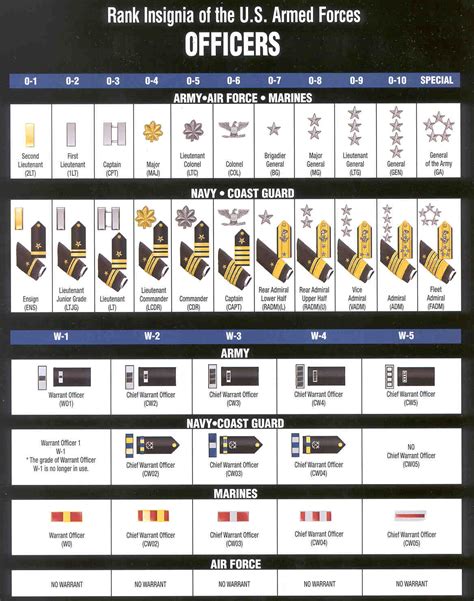
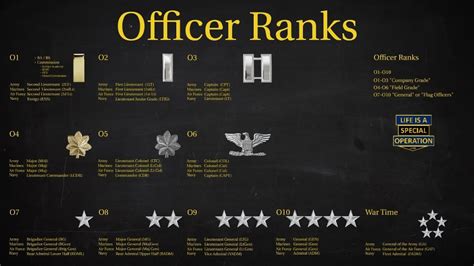
Commissioned Officer Ranks
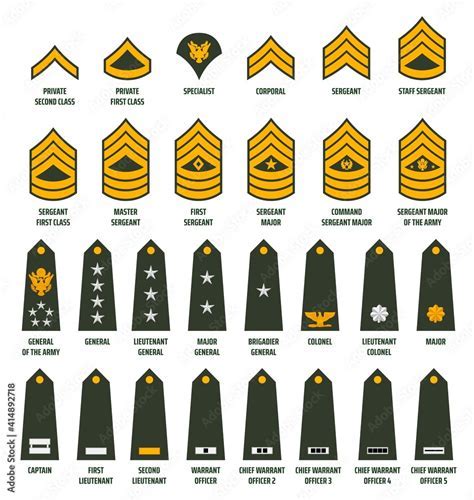
Commissioned officers are the leaders of the army, responsible for making strategic decisions and overseeing the enlisted personnel. The commissioned officer ranks are further divided into several categories, including company-grade officers, field-grade officers, and general officers.
Company-Grade Officers
Company-grade officers are the most junior commissioned officers in the army. They typically serve as platoon leaders or company commanders.
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The most junior commissioned officer rank, typically serving as a platoon leader.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A higher-ranking company-grade officer, often serving as a company executive officer or platoon leader.
- Captain (CPT): A senior company-grade officer, typically serving as a company commander or staff officer.

Field-Grade Officers
Field-grade officers are more senior than company-grade officers and typically serve in higher-level leadership positions.
- Major (MAJ): A mid-level field-grade officer, often serving as a battalion executive officer or staff officer.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A senior field-grade officer, typically serving as a battalion commander or staff officer.
- Colonel (COL): A high-ranking field-grade officer, often serving as a brigade commander or staff officer.
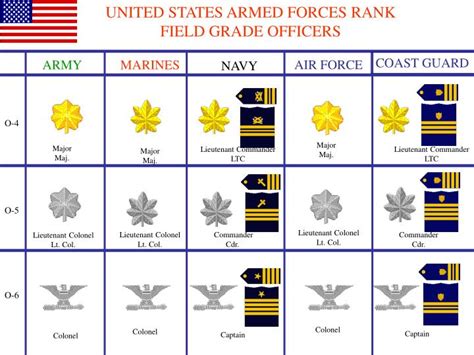
General Officers
General officers are the most senior commissioned officers in the army, holding high-level leadership positions.
- Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer, typically serving as a brigade commander or staff officer.
- Major General (MG): A two-star general officer, often serving as a division commander or staff officer.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer, typically serving as a corps commander or staff officer.
- General (GEN): A four-star general officer, the highest rank in the army, often serving as a senior staff officer or commander.
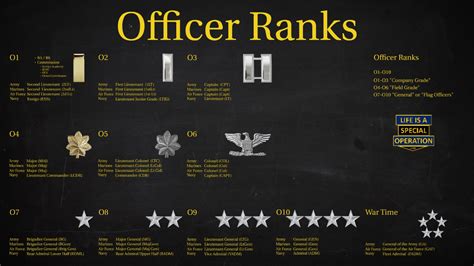
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, holding specialized skills and knowledge.
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The most junior warrant officer rank, typically serving as a technical expert.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A higher-ranking warrant officer, often serving as a technical expert or staff officer.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer, typically serving as a technical expert or staff officer.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A high-ranking warrant officer, often serving as a technical expert or staff officer.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The most senior warrant officer rank, typically serving as a technical expert or staff officer.
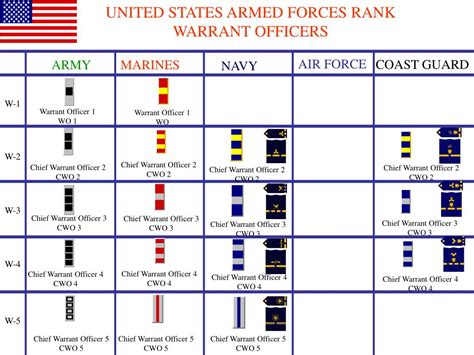
Enlisted Ranks
Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the army, performing a variety of tasks and supporting the commissioned officers.
- Private (PVT): The most junior enlisted rank, typically serving as a basic trainee.
- Private Second Class (PV2): A higher-ranking enlisted rank, often serving as a basic trainee or specialist.
- Private First Class (PFC): A senior enlisted rank, typically serving as a specialist or team leader.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): A mid-level enlisted rank, often serving as a specialist or team leader.
- Sergeant (SGT): A senior enlisted rank, typically serving as a team leader or squad leader.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): A high-ranking enlisted rank, often serving as a squad leader or platoon sergeant.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): A senior enlisted rank, typically serving as a platoon sergeant or section leader.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): A high-ranking enlisted rank, often serving as a section leader or first sergeant.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): The most senior enlisted rank, typically serving as a sergeant major or command sergeant major.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the army officer ranks and their responsibilities is essential for anyone interested in military careers or simply wanting to learn more about the armed forces. From commissioned officers to warrant officers and enlisted personnel, each rank plays a critical role in the military hierarchy. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or just starting your military journey, this comprehensive guide provides a valuable resource for navigating the complex world of army officer ranks.
Army Officer Ranks Image Gallery







What is the highest rank in the army?
+The highest rank in the army is General (GEN), a four-star general officer.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+Commissioned officers are leaders who hold a commission from the President, while warrant officers are technical experts who hold a warrant from the Secretary of the Army.
What is the lowest rank in the army?
+The lowest rank in the army is Private (PVT), the most junior enlisted rank.
How do I become an army officer?
+To become an army officer, you can attend a military academy, receive a commission through Officer Candidate School (OCS), or enlist and apply for Officer Candidate School (OCS) after serving as an enlisted soldier.
