Intro
Discover the esteemed Warrant Officer ranks, epitomizing authority and expertise in the military. Learn about the unique role, responsibilities, and requirements of Warrant Officers, as well as their pivotal position between enlisted and commissioned officers, and how they embody technical expertise and leadership in the armed forces.
Warrant officers hold a unique position in the military hierarchy, combining technical expertise with leadership authority. Their specialized knowledge and skills are essential to the effective operation of various military units and equipment. In this article, we will explore the world of warrant officer ranks, examining their history, roles, and responsibilities within the military.
History of Warrant Officer Ranks
The origins of warrant officer ranks date back to the early days of the British Royal Navy, where senior sailors and craftsmen were appointed as "warrant officers" to oversee specific shipboard operations. This concept was later adopted by the United States military, with the first warrant officers being appointed in the U.S. Army in 1941.
Over time, the role of warrant officers has evolved to reflect the changing needs of the military. Today, they play a vital part in the leadership and technical backbone of various military branches.
Warrant Officer Ranks Structure

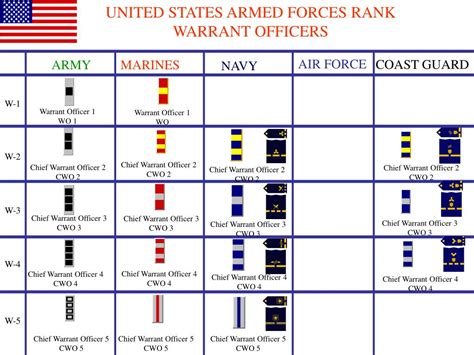
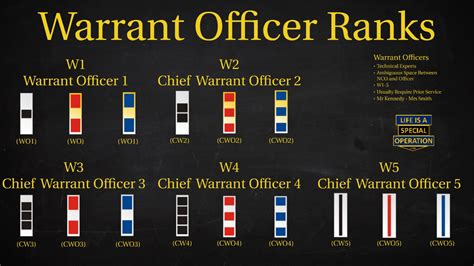
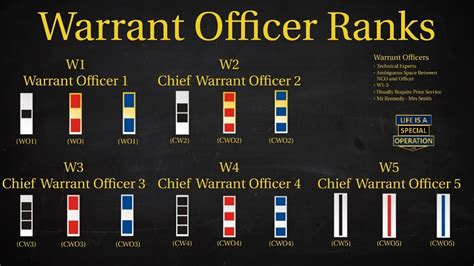
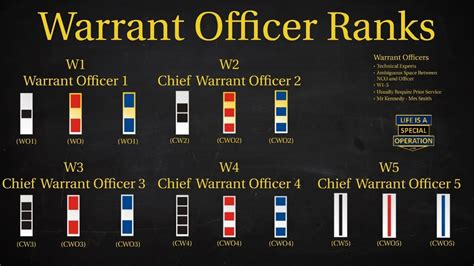
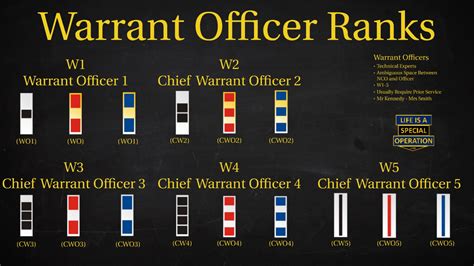
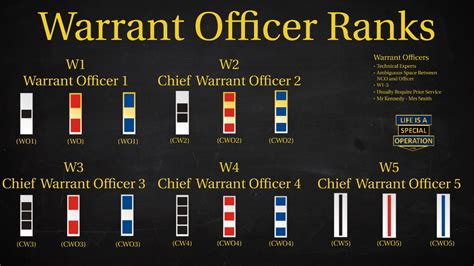
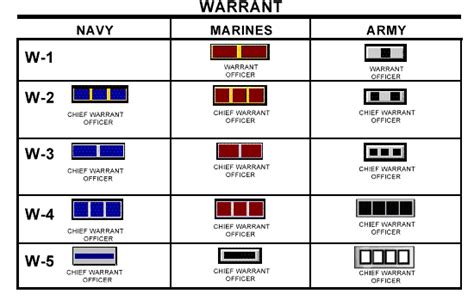
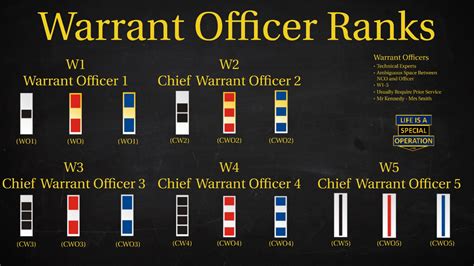
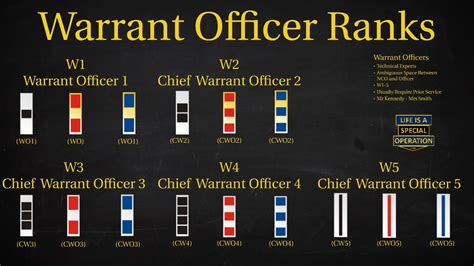
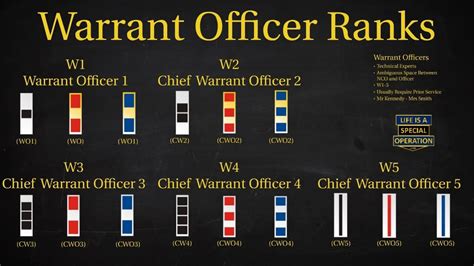
The structure of warrant officer ranks varies slightly between military branches. However, most branches use a similar framework, consisting of three to five distinct ranks:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The initial warrant officer rank, typically achieved after completing technical training and demonstrating exceptional technical expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A more senior rank, requiring significant experience and technical mastery.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A high-ranking warrant officer position, often involving leadership and mentorship responsibilities.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A senior rank, typically requiring advanced technical expertise and leadership abilities.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest warrant officer rank, reserved for exceptional leaders and technical experts.
Roles and Responsibilities

Warrant officers fulfill various roles, including:
- Technical Experts: Providing technical guidance and training to junior personnel.
- Leaders: Supervising and mentoring junior officers and enlisted personnel.
- Advisors: Offering technical advice to senior officers and commanders.
- Instructors: Teaching technical courses and developing training materials.
Some of the key responsibilities of warrant officers include:
- Equipment Maintenance: Overseeing the maintenance and repair of complex military equipment.
- Operational Planning: Participating in the planning and execution of military operations.
- Training and Development: Developing and delivering technical training programs.
- Leadership: Leading and mentoring junior personnel to achieve unit goals.
Benefits of Warrant Officer Ranks

The warrant officer ranks offer several benefits, including:
- Increased Authority: Warrant officers hold significant technical authority, enabling them to make decisions and take action.
- Improved Career Opportunities: The warrant officer ranks provide a clear career progression path, with opportunities for advancement and professional growth.
- Enhanced Leadership Skills: Warrant officers develop strong leadership skills, essential for effective unit management and technical guidance.
Challenges of Warrant Officer Ranks

Despite the benefits, warrant officers also face challenges, including:
- High Expectations: Warrant officers are expected to maintain exceptional technical expertise and leadership skills.
- Limited Career Flexibility: The warrant officer ranks can be highly specialized, limiting career flexibility and opportunities for lateral movement.
- Increased Responsibility: Warrant officers often bear significant responsibility for unit operations and equipment maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, warrant officer ranks play a vital role in the military, combining technical expertise with leadership authority. Their specialized knowledge and skills are essential to the effective operation of various military units and equipment. As the military continues to evolve, the importance of warrant officers will only continue to grow.
Gallery of Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant Officer Ranks Gallery
FAQs
What is the primary role of a warrant officer?
+The primary role of a warrant officer is to provide technical expertise and leadership in a specific area of specialty.
How do warrant officers differ from commissioned officers?
+Warrant officers differ from commissioned officers in that they hold technical authority and expertise, whereas commissioned officers hold command authority.
What is the typical career path for a warrant officer?
+The typical career path for a warrant officer involves technical training, followed by progressive leadership and technical responsibilities.
