Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US military with our comprehensive guide to the military ranking system. Learn about the structure, promotions, and ranks from Private to General, including enlisted, warrant, and officer ranks. Understand the insignia, pay grades, and requirements for advancement in the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard.
The United States Armed Forces is one of the most respected and formidable military organizations in the world. With a long history of protecting the nation and its interests, the US military is composed of five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its own unique culture, traditions, and ranking system. In this article, we will delve into the US military ranking system, exploring its structure, promotions, and what it takes to climb the ranks.

The US military ranking system is a hierarchical structure that reflects a service member's level of responsibility, experience, and authority. The system is divided into two main categories: enlisted personnel and officers. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the military, and they are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. Officers, on the other hand, are leaders who have completed a bachelor's degree and Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy.
Enlisted Personnel Rankings
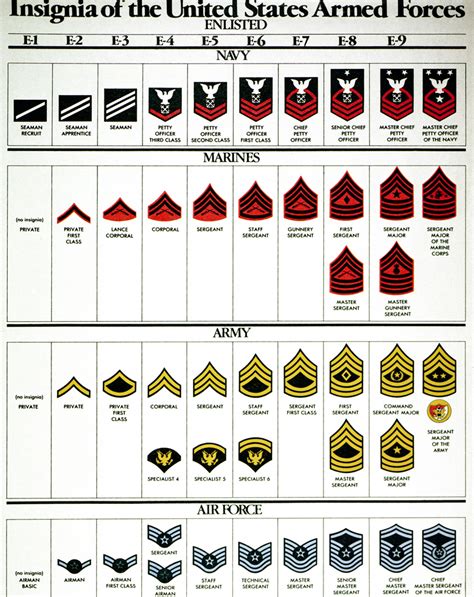
Enlisted personnel rankings are divided into nine grades, each with its own unique insignia and responsibilities.
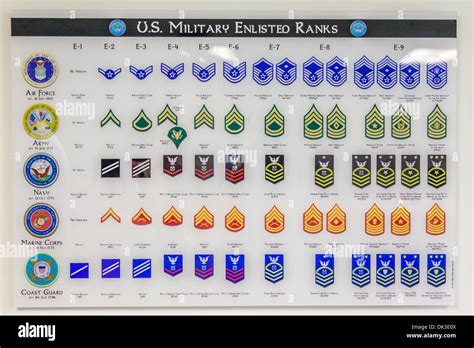
Here are the enlisted personnel rankings, from lowest to highest:
- Private (PVT) - E-1
- Private Second Class (PV2) - E-2
- Private First Class (PFC) - E-3
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - E-4
- Sergeant (SGT) - E-5
- Staff Sergeant (SSG) - E-6
- Sergeant First Class (SFC) - E-7
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) - E-8
- Sergeant Major (SGM) - E-9
Enlisted Personnel Promotion Process
The enlisted personnel promotion process is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and education. Service members can be promoted through a variety of methods, including:
- Time-in-grade (TIG) promotions, which occur after a certain amount of time in a particular rank
- Promotion boards, which consider a service member's performance evaluations and education
- Meritorious promotions, which recognize exceptional performance and contributions
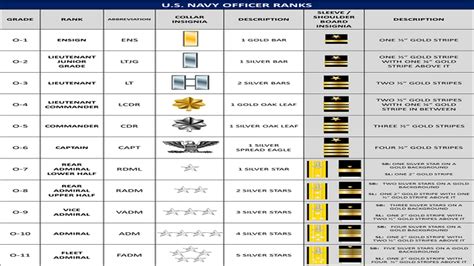
Officer Rankings
Officer rankings are divided into ten grades, each with its own unique insignia and responsibilities.
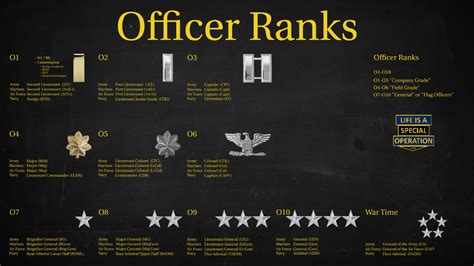
Here are the officer rankings, from lowest to highest:
- Second Lieutenant (2LT) - O-1
- First Lieutenant (1LT) - O-2
- Captain (CPT) - O-3
- Major (MAJ) - O-4
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) - O-5
- Colonel (COL) - O-6
- Brigadier General (BG) - O-7
- Major General (MG) - O-8
- Lieutenant General (LTG) - O-9
- General (GEN) - O-10
Officer Promotion Process
The officer promotion process is also based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and education. Officers can be promoted through a variety of methods, including:
- Time-in-grade (TIG) promotions, which occur after a certain amount of time in a particular rank
- Promotion boards, which consider an officer's performance evaluations and education
- Selection for advanced education and training, which can lead to promotion opportunities
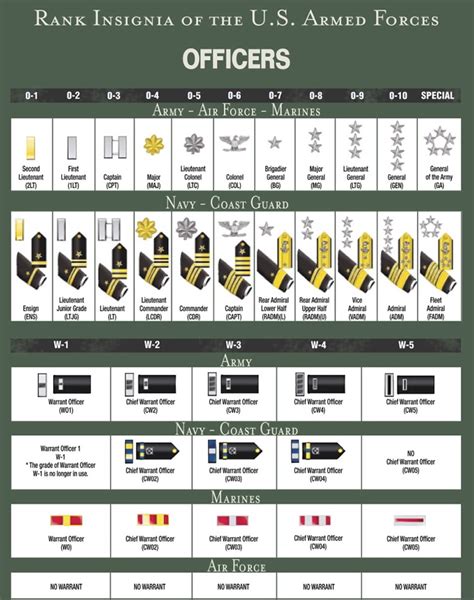
Warrant Officer Rankings
Warrant officers are technical experts in a particular field and hold a unique position in the military hierarchy. They are responsible for providing technical guidance and expertise to commanders and other service members.

Here are the warrant officer rankings, from lowest to highest:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) - W-1
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) - W-2
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) - W-3
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) - W-4
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) - W-5
Warrant Officer Promotion Process
The warrant officer promotion process is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and technical expertise. Warrant officers can be promoted through a variety of methods, including:
- Time-in-grade (TIG) promotions, which occur after a certain amount of time in a particular rank
- Technical expertise, which can lead to promotion opportunities
- Selection for advanced education and training, which can lead to promotion opportunities
Conclusion
The US military ranking system is a complex and nuanced hierarchy that reflects a service member's level of responsibility, experience, and authority. From enlisted personnel to officers and warrant officers, each rank has its own unique insignia and responsibilities. Understanding the ranking system is essential for anyone interested in joining the military or advancing their career. By providing a clear and concise overview of the ranking system, we hope to have shed light on the structure and promotions of the US military.
US Military Ranking System Image Gallery








What is the highest rank in the US military?
+The highest rank in the US military is General (GEN) - O-10.
How do military promotions work?
+Military promotions are based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and education.
What is the difference between enlisted personnel and officers?
+Enlisted personnel are responsible for carrying out day-to-day tasks and operations, while officers are leaders who have completed a bachelor's degree and Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the US military ranking system. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to ask.

