Intro
Discover the 7 Navy Ranks, from junior enlisted to senior officer, including enlisted ranks, warrant officer, and commissioned officer ranks, understanding navy rank structure and hierarchy.
The United States Navy is one of the most prestigious and respected naval forces in the world, with a rich history dating back to 1775. The Navy plays a critical role in maintaining the country's national security and protecting its interests abroad. One of the key factors that contribute to the Navy's success is its well-structured ranking system, which provides a clear chain of command and opportunities for advancement. In this article, we will explore the 7 Navy ranks, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the responsibilities, requirements, and benefits associated with each rank.
The Navy's ranking system is designed to recognize individual achievements, provide opportunities for career advancement, and ensure that personnel are adequately trained and prepared to perform their duties. Understanding the different Navy ranks is essential for anyone considering a career in the Navy, as well as for those who are already serving. With its complex hierarchy and numerous specialties, the Navy offers a wide range of career paths and opportunities for advancement.
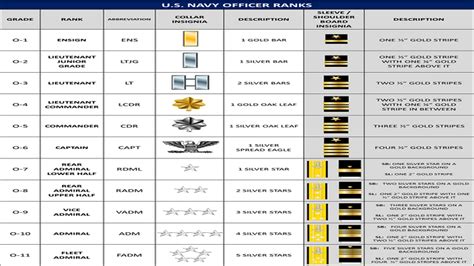
The Navy's ranking system is divided into three main categories: enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the Navy's workforce and are responsible for performing the day-to-day tasks necessary to keep the Navy running. Warrant officers are technical experts who have advanced knowledge and skills in a specific area, while commissioned officers are leaders who have completed a four-year college degree and have been commissioned as officers. Each category has its own set of ranks, with increasing levels of responsibility and authority.
Introduction to Navy Ranks
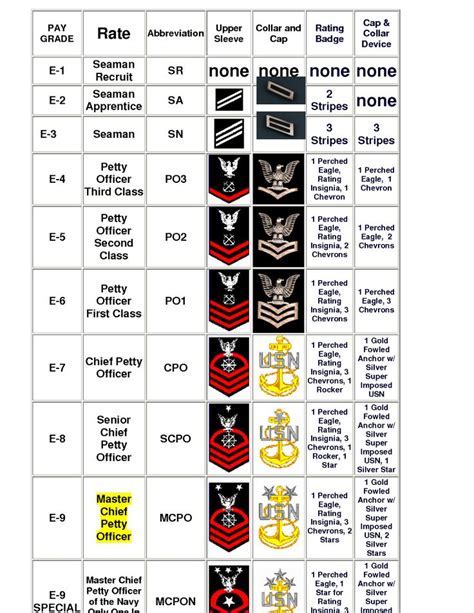
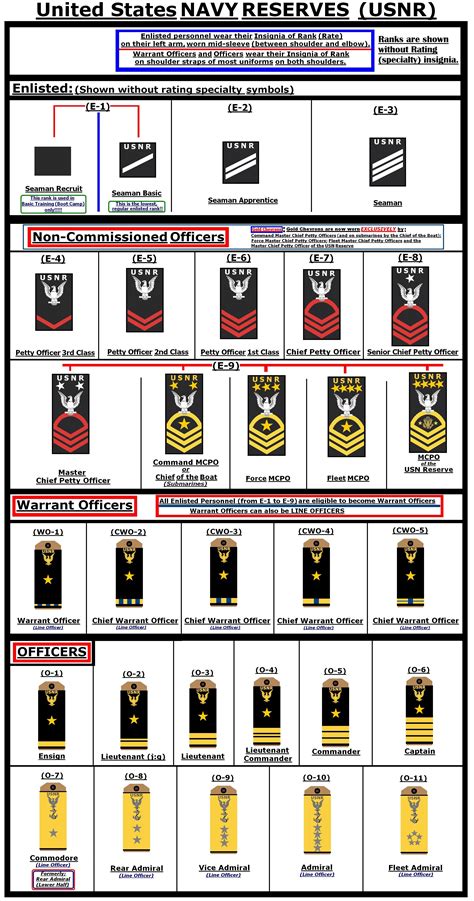
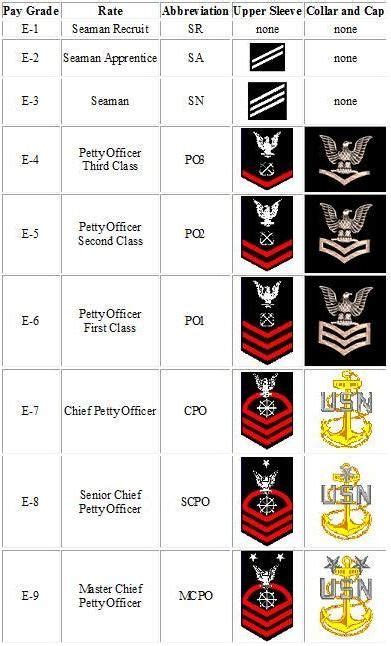
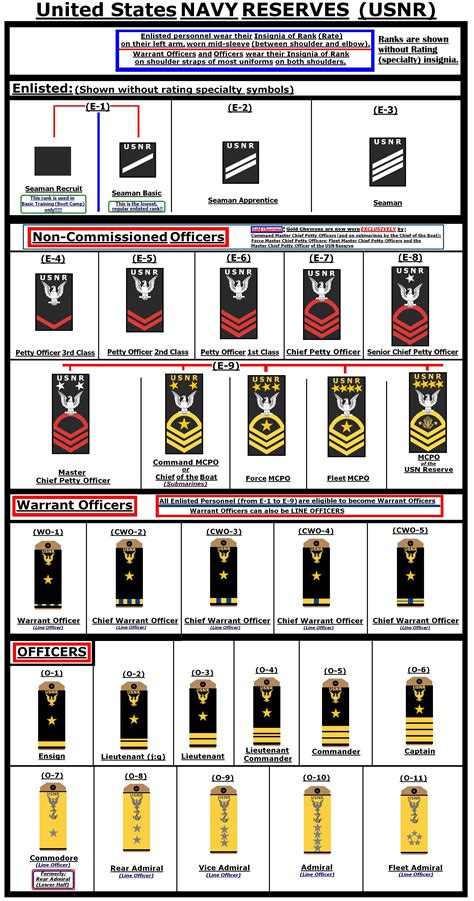
The 7 Navy ranks we will be discussing are part of the enlisted category, which is the largest and most diverse group in the Navy. These ranks are: Seaman Recruit (E-1), Seaman Apprentice (E-2), Seaman (E-3), Petty Officer Third Class (E-4), Petty Officer Second Class (E-5), Petty Officer First Class (E-6), and Chief Petty Officer (E-7). Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits, and personnel can advance through the ranks as they gain experience and complete training.
Seaman Recruit (E-1)

The lowest rank in the Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1), which is the entry-level rank for all new enlistees. Seaman Recruits are typically in their first year of service and are still in the process of completing their initial training. They are assigned to a specific ship or unit and are responsible for performing basic tasks such as cleaning, maintenance, and errands. Seaman Recruits are also required to complete a series of training courses, including basic seamanship, first aid, and naval history.
Seaman Apprentice (E-2)

After completing their initial training, Seaman Recruits are promoted to Seaman Apprentice (E-2). At this rank, personnel are considered to be in a learning phase, where they are acquiring new skills and knowledge in their specific rating (job specialty). Seaman Apprentices are responsible for performing more complex tasks, such as operating equipment, maintaining records, and assisting senior personnel. They are also required to complete additional training courses, including rating-specific training and leadership development.
Seaman (E-3)

The next rank is Seaman (E-3), which is considered to be a junior rank. Seamen are responsible for performing a variety of tasks, including operating equipment, maintaining records, and assisting senior personnel. They are also expected to take on more responsibility and demonstrate leadership skills. Seamen are typically assigned to a specific ship or unit and are responsible for performing tasks related to their rating.
Petty Officer Third Class (E-4)

Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) is the first rank in the petty officer category, which is considered to be a leadership rank. Petty Officers are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing more complex tasks related to their rating. They are also expected to demonstrate expertise in their field and take on additional responsibilities, such as training and evaluating junior personnel.
Petty Officer Second Class (E-5)

The next rank is Petty Officer Second Class (E-5), which is considered to be a senior rank. Petty Officers Second Class are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing complex tasks related to their rating. They are also expected to demonstrate advanced expertise in their field and take on additional responsibilities, such as supervising teams and projects.
Petty Officer First Class (E-6)

Petty Officer First Class (E-6) is the second-highest rank in the petty officer category. Petty Officers First Class are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing highly complex tasks related to their rating. They are also expected to demonstrate advanced expertise in their field and take on additional responsibilities, such as supervising teams and projects, and providing technical guidance to junior personnel.
Chief Petty Officer (E-7)

The highest rank in the enlisted category is Chief Petty Officer (E-7), which is considered to be a senior leadership rank. Chief Petty Officers are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel, as well as performing highly complex tasks related to their rating. They are also expected to demonstrate advanced expertise in their field and take on additional responsibilities, such as supervising teams and projects, providing technical guidance to junior personnel, and serving as a mentor and advisor to junior officers.
Gallery of Navy Ranks
Navy Ranks Image Gallery




What is the lowest rank in the Navy?
+The lowest rank in the Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1), which is the entry-level rank for all new enlistees.
How do I advance in rank in the Navy?
+To advance in rank in the Navy, you must meet the requirements for the next rank, which typically includes completing training courses, gaining experience, and demonstrating leadership skills.
What is the highest rank in the enlisted category?
+The highest rank in the enlisted category is Chief Petty Officer (E-7), which is considered to be a senior leadership rank.
In conclusion, the 7 Navy ranks are an essential part of the Navy's structure and organization. Understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities is crucial for anyone considering a career in the Navy, as well as for those who are already serving. By providing a clear chain of command and opportunities for advancement, the Navy's ranking system ensures that personnel are adequately trained and prepared to perform their duties. Whether you're just starting out as a Seaman Recruit or have reached the rank of Chief Petty Officer, the Navy offers a wide range of career paths and opportunities for advancement. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the Navy's ranking system, and to leave a comment below with any questions or feedback you may have.
