Intro
Discover the hierarchy of Air Force enlisted ranks, from Airman Basic to Command Chief Master Sergeant. Learn about the duties, responsibilities, and requirements for advancement in each rank, as well as the insignia, pay grade, and time-in-service needed to progress through the ranks.
The United States Air Force is one of the most prestigious and respected branches of the military, with a long history of excellence and service. For those looking to join the Air Force, understanding the enlisted rank structure is crucial. In this article, we will delve into the world of Air Force enlisted ranks, providing a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the complexities of this esteemed organization.
Understanding Air Force Enlisted Ranks
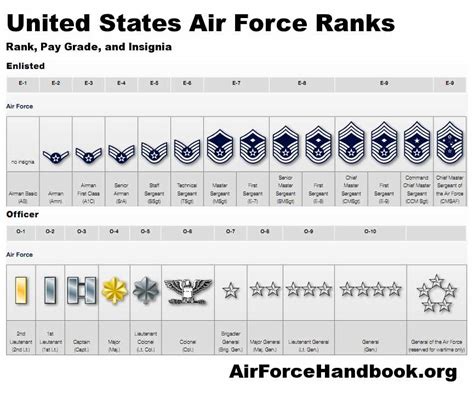
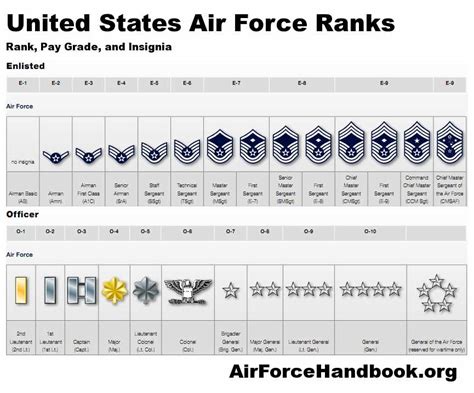
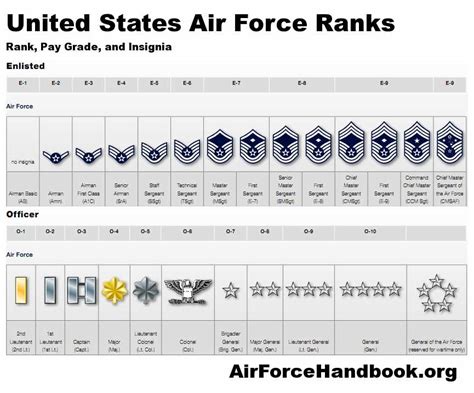
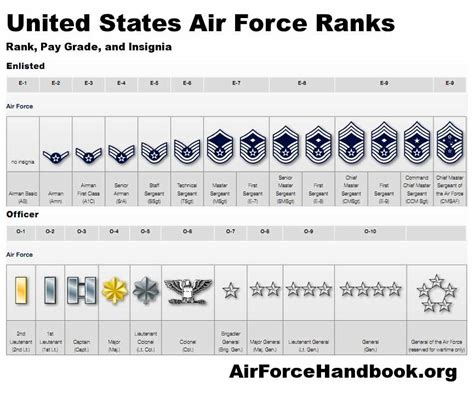
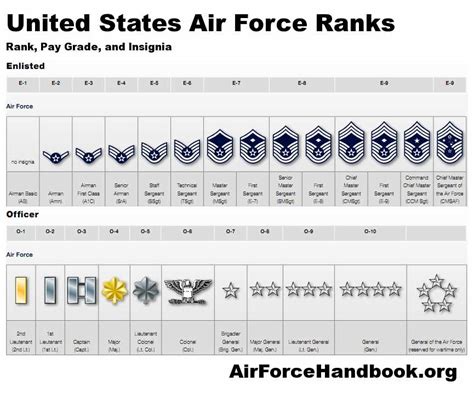
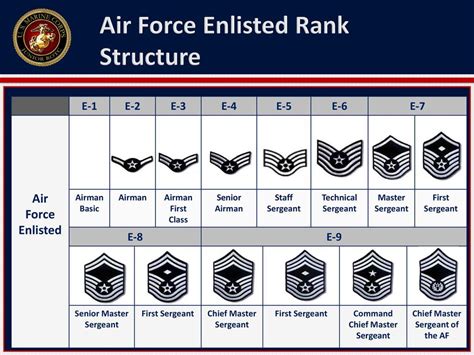
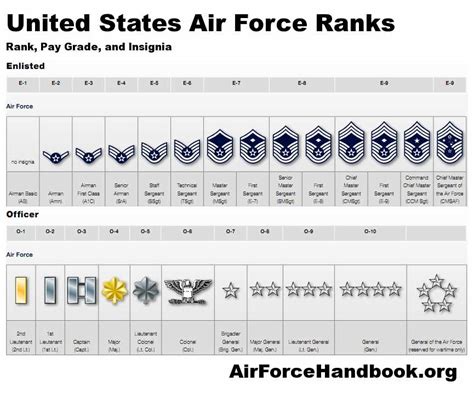
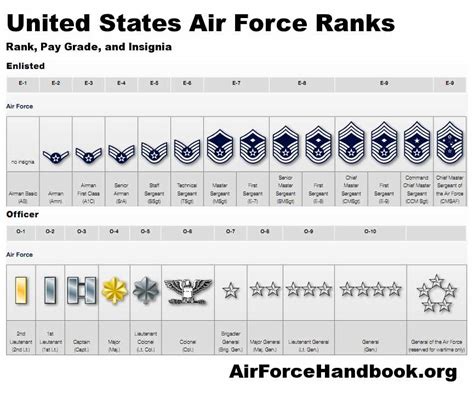
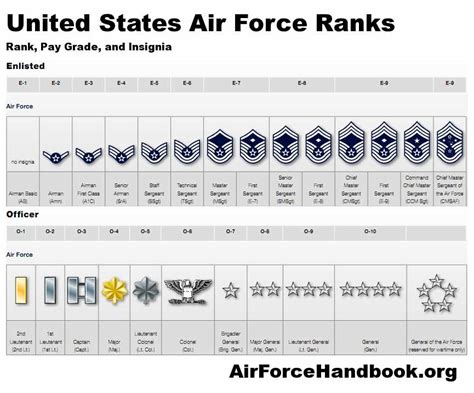
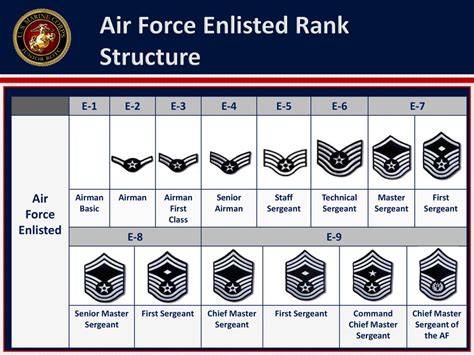
The Air Force enlisted rank structure is divided into nine distinct ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits. From the entry-level rank of Airman Basic (AB) to the highest rank of Command Chief Master Sergeant (CCM), understanding the different ranks and their corresponding roles is essential for success in the Air Force.
The Nine Enlisted Ranks of the Air Force
- Airman Basic (AB): The lowest rank in the Air Force, Airman Basic is the entry-level rank for new recruits. Airmen in this rank are typically in training and are learning the basics of Air Force life.
- Airman (AMN): After completing basic training, Airmen are promoted to the rank of Airman. This rank is typically held by Airmen who are still in training or are new to their career field.
- Airman First Class (A1C): Airmen who demonstrate exceptional performance and leadership potential are promoted to the rank of Airman First Class. This rank is a significant milestone in an Airman's career and comes with increased responsibilities.
- Senior Airman (SrA): With a minimum of 3-4 years of service, Airmen can be promoted to the rank of Senior Airman. This rank is characterized by increased leadership responsibilities and a higher level of expertise in their career field.
- Staff Sergeant (SSgt): The rank of Staff Sergeant is a significant step up in the Air Force enlisted rank structure. Airmen in this rank are typically in leadership positions and are responsible for mentoring and guiding junior Airmen.
- Technical Sergeant (TSgt): With a minimum of 8-10 years of service, Airmen can be promoted to the rank of Technical Sergeant. This rank is characterized by advanced technical expertise and leadership responsibilities.
- Master Sergeant (MSgt): Airmen who demonstrate exceptional leadership and technical expertise can be promoted to the rank of Master Sergeant. This rank is highly respected and comes with significant responsibilities.
- Senior Master Sergeant (SMSgt): With a minimum of 12-15 years of service, Airmen can be promoted to the rank of Senior Master Sergeant. This rank is characterized by advanced leadership and technical expertise.
- Command Chief Master Sergeant (CCM): The highest enlisted rank in the Air Force, Command Chief Master Sergeant is a rare and prestigious rank. Airmen in this rank are typically in senior leadership positions and are responsible for guiding the development of junior Airmen.
The Benefits of Air Force Enlisted Ranks
The Air Force enlisted rank structure offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Career Advancement: The Air Force offers a clear path for career advancement, with opportunities for promotion and professional development.
- Education Assistance: The Air Force offers education assistance programs, including the GI Bill and tuition assistance, to help Airmen pursue higher education.
- Healthcare Benefits: Airmen and their families are eligible for comprehensive healthcare benefits, including medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Housing Allowance: Airmen are eligible for a housing allowance, which helps to offset the cost of living expenses.
- Food Allowance: Airmen are eligible for a food allowance, which helps to offset the cost of food expenses.
The Responsibilities of Air Force Enlisted Ranks
The Air Force enlisted rank structure comes with a wide range of responsibilities, including:
- Leadership: Airmen in leadership positions are responsible for guiding and mentoring junior Airmen.
- Technical Expertise: Airmen are expected to develop advanced technical expertise in their career field.
- Career Development: Airmen are responsible for developing their careers, including pursuing education and training opportunities.
- Teamwork: Airmen are expected to work collaboratively as part of a team to achieve mission objectives.
- Discipline: Airmen are expected to adhere to a high level of discipline, including following rules and regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Air Force enlisted rank structure is a complex and multifaceted system that offers a wide range of benefits and opportunities for career advancement. Understanding the different ranks and their corresponding responsibilities is essential for success in the Air Force. Whether you're just starting your Air Force career or are a seasoned veteran, this comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge and insights you need to navigate the Air Force enlisted rank structure with confidence.
Air Force Enlisted Ranks Image Gallery



What is the highest enlisted rank in the Air Force?
+The highest enlisted rank in the Air Force is Command Chief Master Sergeant (CCM).
How long does it take to become a Senior Airman?
+Typically, it takes 3-4 years of service to become a Senior Airman.
What is the difference between a Technical Sergeant and a Master Sergeant?
+A Technical Sergeant is a senior enlisted rank that requires advanced technical expertise, while a Master Sergeant is a senior enlisted rank that requires advanced leadership and technical expertise.
Can I join the Air Force if I have a college degree?
+Yes, you can join the Air Force with a college degree. In fact, many Airmen have a college degree and can receive advanced pay and benefits.
How long does it take to become a Command Chief Master Sergeant?
+Typically, it takes 20-25 years of service to become a Command Chief Master Sergeant.
