Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the National Guard with our comprehensive guide to ranks. Discover the 13 enlisted and officer grades, from Private to General Officer, and learn about the responsibilities, requirements, and insignia for each. Understand the rank structure, promotion process, and career progression in the National Guard.
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces that consists of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in a variety of roles, from homeland security to overseas combat missions. Like the other branches of the military, the National Guard has its own system of ranks, which are used to denote a member's level of authority, responsibility, and experience.
Understanding the different ranks within the National Guard can be helpful for both members and non-members alike, as it can provide insight into the organization's structure and hierarchy. In this article, we will explore the 13 enlisted and officer grades that make up the National Guard ranks, including their responsibilities, requirements, and corresponding pay grades.
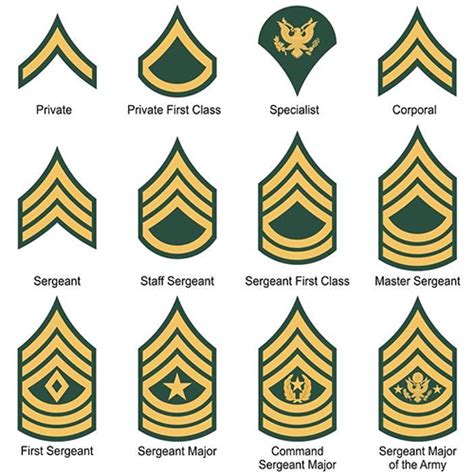
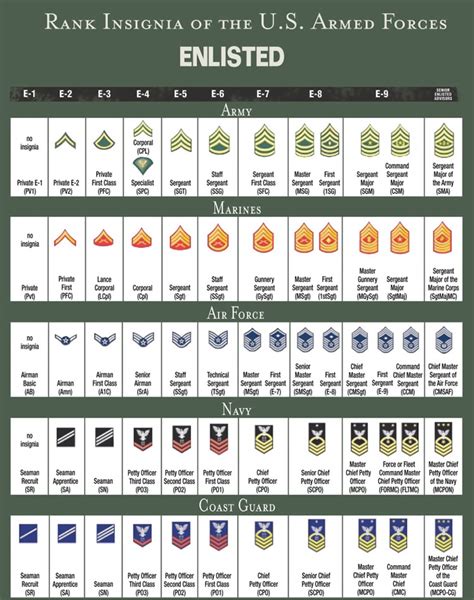
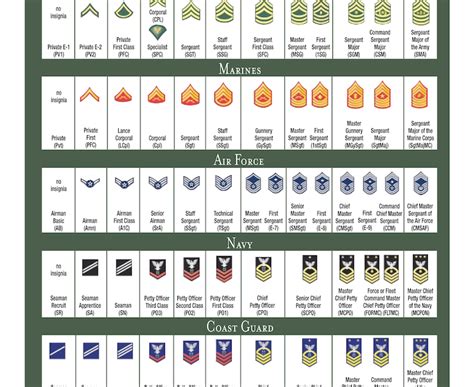
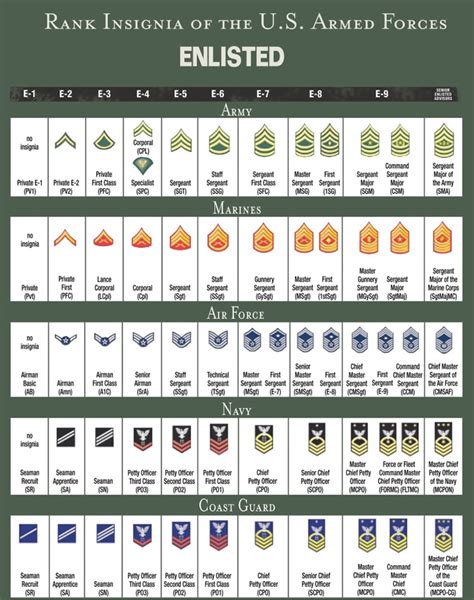
Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks within the National Guard are divided into three categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior NCOs.
Junior Enlisted Ranks

The junior enlisted ranks are the entry-level positions within the National Guard. These ranks are typically held by new recruits or those who are still in training.
- Private (PVT): The lowest rank in the National Guard, privates are typically new recruits who are still in training.
- Private Second Class (PV2): A step above private, privates second class have completed basic training and are beginning to take on more responsibilities.
- Private First Class (PFC): The third-lowest rank, privates first class have demonstrated leadership potential and are often tasked with leading small teams.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks

The NCO ranks are the backbone of the National Guard, providing leadership and guidance to junior enlisted members.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): The first NCO rank, specialists/corporals are responsible for leading small teams and providing technical expertise.
- Sergeant (SGT): A step above specialist/corporal, sergeants are experienced leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): The third NCO rank, staff sergeants are senior leaders who are responsible for planning and executing complex missions.
Senior Non-Commissioned Officer (SNCO) Ranks
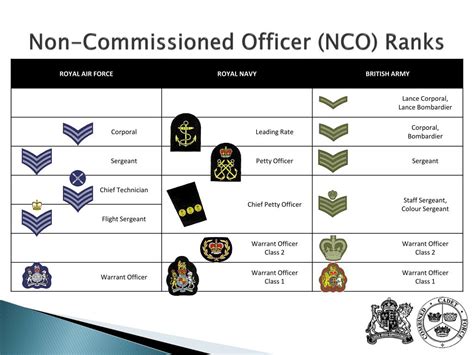
The SNCO ranks are the highest enlisted ranks within the National Guard, providing senior leadership and guidance to junior members.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): The first SNCO rank, sergeants first class are senior leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency and leadership ability.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG): A step above sergeant first class, master sergeants/first sergeants are senior leaders who are responsible for planning and executing complex missions.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): The highest enlisted rank, sergeants major are senior leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency and leadership ability.
Officer Ranks
The officer ranks within the National Guard are divided into two categories: company-grade officers and field-grade officers.
Company-Grade Officer Ranks

The company-grade officer ranks are the entry-level positions within the National Guard officer corps. These ranks are typically held by newly commissioned officers or those who are still in training.
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The lowest officer rank, second lieutenants are typically new officers who are still in training.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A step above second lieutenant, first lieutenants have completed officer training and are beginning to take on more responsibilities.
- Captain (CPT): The third company-grade officer rank, captains are experienced leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency.
Field-Grade Officer Ranks

The field-grade officer ranks are the senior leadership positions within the National Guard. These ranks are typically held by experienced officers who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency and leadership ability.
- Major (MAJ): The first field-grade officer rank, majors are senior leaders who are responsible for planning and executing complex missions.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A step above major, lieutenant colonels are senior leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency and leadership ability.
- Colonel (COL): The highest field-grade officer rank, colonels are senior leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical proficiency and leadership ability.
Gallery of National Guard Ranks
National Guard Ranks Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the highest rank in the National Guard?
+The highest rank in the National Guard is General (GEN).
How long does it take to become an officer in the National Guard?
+The time it takes to become an officer in the National Guard can vary depending on the individual's circumstances, but typically requires a minimum of a bachelor's degree and completion of Officer Candidate School (OCS).
What is the difference between a non-commissioned officer (NCO) and an officer?
+A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is an enlisted member who has advanced to a leadership position, while an officer is a member of the National Guard who has received a commission and holds a higher level of authority and responsibility.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the National Guard ranks and their corresponding responsibilities and requirements. Whether you are a member of the National Guard or simply interested in learning more about this important organization, we encourage you to share your thoughts and ask any questions you may have in the comments below.
