Intro
Explore the differences between Reserve and Active Duty military paths. Discover the pros and cons of each, including deployment frequencies, training requirements, and education benefits. Learn how to choose the right military career for you, whether youre looking for a full-time commitment or a part-time service option with civilian flexibility.
When considering a career in the military, one of the most significant decisions you'll make is whether to join the Reserve or Active Duty. Both paths offer unique benefits, challenges, and opportunities for service and personal growth. In this article, we'll delve into the differences between Reserve and Active Duty, exploring the pros and cons of each, to help you make an informed decision.
What is Active Duty?
Active Duty refers to full-time military service, where you'll be required to work on a daily basis, often for extended periods, including deployments and training exercises. As an Active Duty service member, you'll typically live on or near a military base, and your primary focus will be on your military career.
What is the Reserve?
The Reserve, also known as the Reserve Component, is a part-time military force that supports the Active Duty military. Reserve service members typically serve one weekend a month (known as a drill weekend) and two weeks a year (known as annual training or AT). They may also be called upon to deploy in times of war or national emergency.
Key Differences Between Reserve and Active Duty
While both Reserve and Active Duty service members are essential to the military's mission, there are significant differences between the two. Here are some key distinctions:
- Time Commitment: Active Duty requires a full-time commitment, while the Reserve is a part-time commitment.
- Deployment: Active Duty service members are more likely to be deployed, and for longer periods, than Reserve service members.
- Training: Active Duty service members receive more extensive training, including Basic Training, Advanced Individual Training (AIT), and ongoing professional development.
- Pay and Benefits: Active Duty service members typically receive higher pay and more comprehensive benefits, including housing and food allowances.
- Career Advancement: Active Duty service members may have more opportunities for career advancement and promotion.

Pros of Active Duty
- Camaraderie: Active Duty service members often develop strong bonds with their fellow service members, creating a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps.
- Career Advancement: Active Duty service members have more opportunities for career advancement and promotion.
- Education Benefits: Active Duty service members may be eligible for education benefits, including the GI Bill.
- Travel Opportunities: Active Duty service members may have the opportunity to travel and experience different cultures.
Cons of Active Duty
- Time Away from Family: Active Duty service members may spend extended periods away from family and friends.
- Deployment Risks: Active Duty service members are at risk of deployment, which can be stressful and dangerous.
- High Stress Levels: Active Duty service members may experience high levels of stress, particularly in combat situations.
Pros of the Reserve
- Flexibility: Reserve service members can maintain a civilian career and balance their military service with other responsibilities.
- Less Time Away from Family: Reserve service members typically spend less time away from family and friends.
- Lower Stress Levels: Reserve service members may experience lower stress levels, as they are not required to deploy as frequently.
- Community Involvement: Reserve service members can be involved in their local communities, participating in parades, ceremonies, and other events.
Cons of the Reserve
- Limited Career Advancement: Reserve service members may have limited opportunities for career advancement and promotion.
- Training Challenges: Reserve service members may face challenges in keeping their skills up-to-date, as they may not receive the same level of training as Active Duty service members.
- Deployment Uncertainty: Reserve service members may be called upon to deploy, which can be stressful and uncertain.
Which Military Path is Right for You?
Ultimately, the decision between Reserve and Active Duty depends on your individual circumstances, goals, and priorities. If you're looking for a full-time military career with opportunities for career advancement and education benefits, Active Duty may be the best choice. However, if you're seeking a part-time military commitment that allows you to balance your military service with civilian responsibilities, the Reserve may be the better option.
Consider the following questions to help you make your decision:
- What are your career goals, and which path aligns better with those goals?
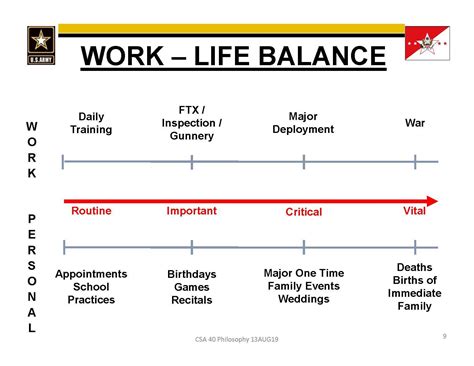
- How important is flexibility and work-life balance to you?
- Are you willing and able to deploy, and if so, for how long?
- What kind of training and education benefits are you looking for?

Conclusion
Choosing between Reserve and Active Duty is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of your goals, priorities, and circumstances. Both paths offer unique benefits and challenges, and it's essential to weigh these factors carefully before making a decision. By understanding the differences between Reserve and Active Duty, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your aspirations and supports your personal and professional growth.
Gallery of Military Life
Military Life Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Active Duty and Reserve?
+Active Duty requires a full-time commitment, while the Reserve is a part-time commitment. Active Duty service members typically work on a daily basis, while Reserve service members serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year.
How do I choose between Active Duty and Reserve?
+Consider your career goals, flexibility needs, and willingness to deploy. If you're looking for a full-time military career with opportunities for career advancement and education benefits, Active Duty may be the best choice. However, if you're seeking a part-time military commitment that allows you to balance your military service with civilian responsibilities, the Reserve may be the better option.
What kind of training and education benefits are available to Active Duty service members?
+Active Duty service members may be eligible for education benefits, including the GI Bill, which can help pay for college or vocational training. They may also receive extensive training, including Basic Training, Advanced Individual Training (AIT), and ongoing professional development.
