Intro
Unlock the secrets of military retirement pay with our simple guide. Learn how to calculate your pension using the military retirement pay chart, and discover the factors that affect your benefits, including years of service, retirement type, and pay grade. Maximize your post-military income with our expert insights.
Military retirement pay is a significant benefit for those who have dedicated their lives to serving their country. After years of service, military personnel can retire and receive a steady income to support themselves and their families. However, understanding the military retirement pay chart can be complex, especially for those who are new to the military or approaching retirement.
The military retirement pay chart is a tool used to calculate the amount of retirement pay a service member will receive based on their years of service and final pay grade. In this article, we will break down the military retirement pay chart and provide a simple guide to help you understand how it works.
Understanding the Military Retirement Pay Chart
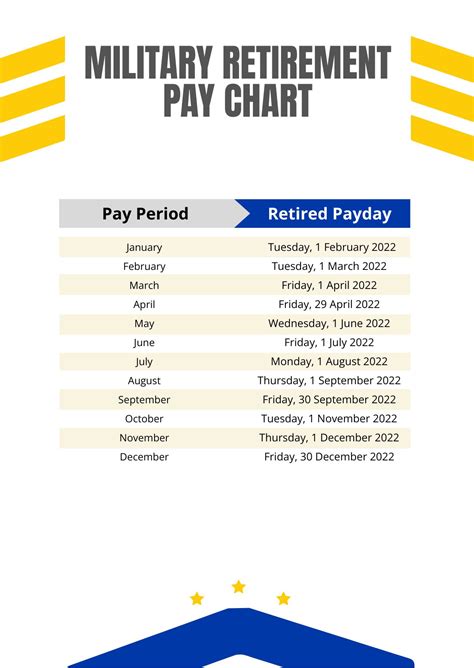
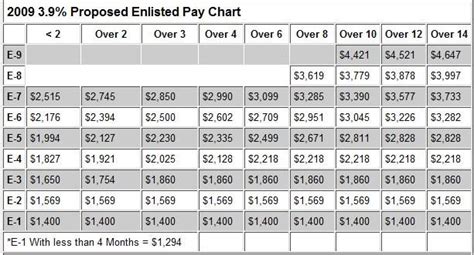
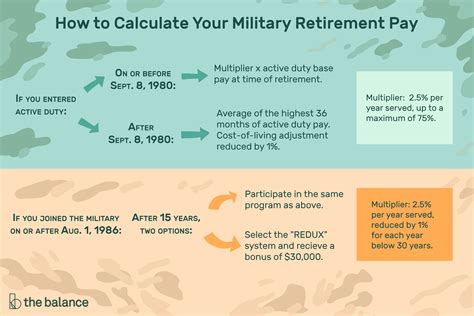
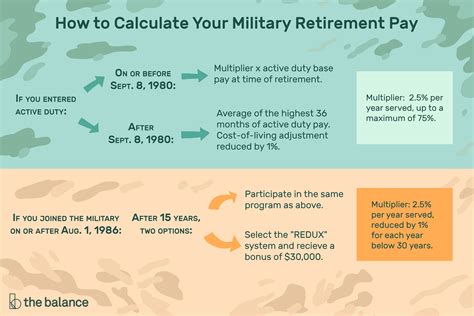
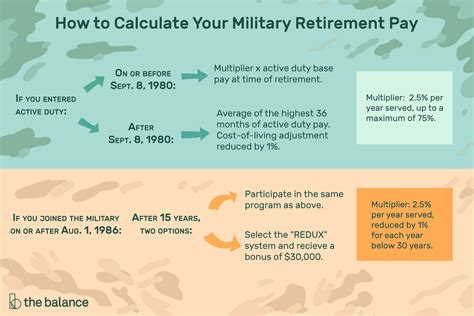
The military retirement pay chart is based on the High-3 system, which calculates retirement pay based on the average of the service member's highest 36 months of basic pay. The chart takes into account the service member's final pay grade and years of service to determine the percentage of basic pay they will receive as retirement pay.
How to Read the Military Retirement Pay Chart
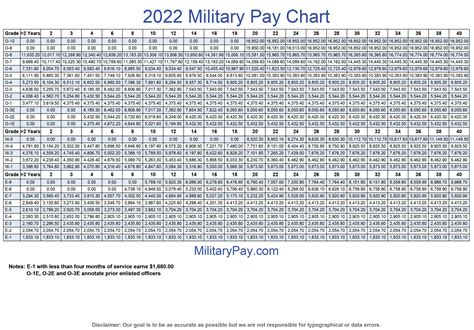
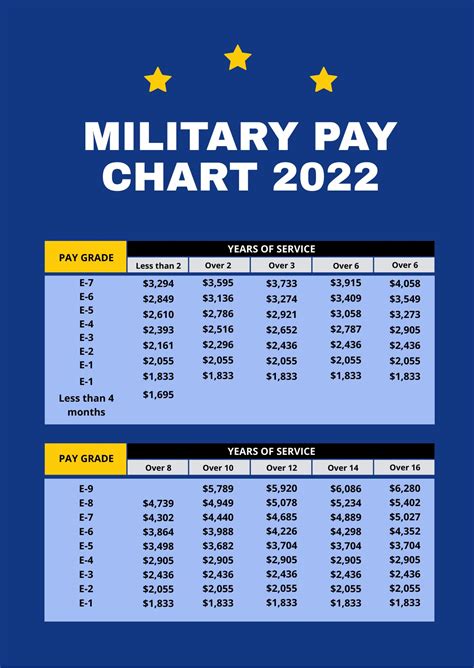
To read the military retirement pay chart, you need to know your final pay grade and years of service. The chart is divided into columns and rows, with the columns representing the years of service and the rows representing the pay grades.
- Find your pay grade on the left side of the chart and your years of service on the top of the chart.
- Where the column and row intersect, you will find the percentage of basic pay you will receive as retirement pay.
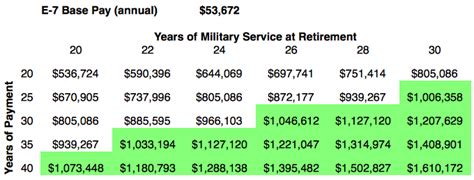
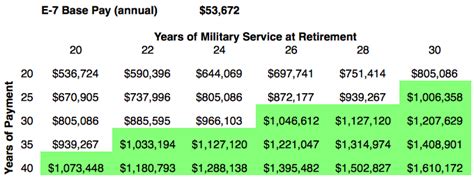
For example, if you are an E-7 with 20 years of service, you would find the intersection of the E-7 row and the 20-year column. According to the chart, you would receive 50% of your basic pay as retirement pay.
Military Retirement Pay Chart Rates

The military retirement pay chart rates vary based on the service member's years of service and final pay grade. Here are the current rates:
- 20 years of service: 50% of basic pay
- 21 years of service: 52% of basic pay
- 22 years of service: 54% of basic pay
- 23 years of service: 56% of basic pay
- 24 years of service: 58% of basic pay
- 25 years of service: 60% of basic pay
- 26 years of service: 62% of basic pay
- 27 years of service: 64% of basic pay
- 28 years of service: 66% of basic pay
- 29 years of service: 68% of basic pay
- 30 years of service: 70% of basic pay
Factors That Affect Military Retirement Pay
There are several factors that can affect military retirement pay, including:
- Years of service: The more years of service, the higher the percentage of basic pay.
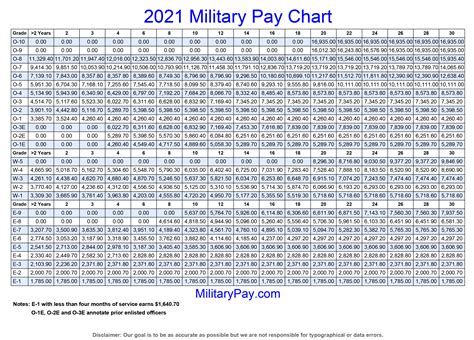
- Final pay grade: The higher the final pay grade, the higher the basic pay.
- Basic pay: The amount of basic pay is based on the service member's pay grade and years of service.
- Cost of living adjustments (COLAs): COLAs are annual increases to retirement pay to keep up with inflation.
How to Calculate Military Retirement Pay
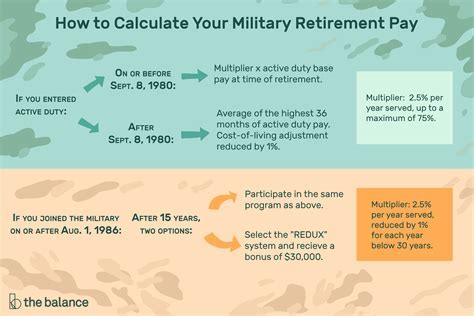
To calculate military retirement pay, you need to know your final pay grade, years of service, and basic pay. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Determine your final pay grade and years of service.
- Find your basic pay on the military pay chart.
- Use the military retirement pay chart to find the percentage of basic pay you will receive as retirement pay.
- Multiply your basic pay by the percentage to calculate your retirement pay.
For example, if you are an E-7 with 20 years of service and a basic pay of $5,000 per month, you would receive 50% of your basic pay as retirement pay. Your retirement pay would be $2,500 per month.
Military Retirement Pay Chart for Guard and Reserve
The military retirement pay chart for Guard and Reserve members is slightly different than the active duty chart. The chart is based on the number of qualifying years of service, which includes active duty and drill periods.
- 20 qualifying years of service: 50% of basic pay
- 21 qualifying years of service: 52% of basic pay
- 22 qualifying years of service: 54% of basic pay
- 23 qualifying years of service: 56% of basic pay
- 24 qualifying years of service: 58% of basic pay
- 25 qualifying years of service: 60% of basic pay
- 26 qualifying years of service: 62% of basic pay
- 27 qualifying years of service: 64% of basic pay
- 28 qualifying years of service: 66% of basic pay
- 29 qualifying years of service: 68% of basic pay
- 30 qualifying years of service: 70% of basic pay
Gallery of Military Retirement Pay Chart
Military Retirement Pay Chart Image Gallery
Frequently Asked Questions
How is military retirement pay calculated?
+Military retirement pay is calculated based on the service member's final pay grade and years of service. The High-3 system calculates retirement pay based on the average of the service member's highest 36 months of basic pay.
What is the difference between active duty and Guard/Reserve retirement pay?
+The main difference between active duty and Guard/Reserve retirement pay is the number of qualifying years of service. Active duty members receive retirement pay based on their years of active duty service, while Guard and Reserve members receive retirement pay based on their qualifying years of service, which includes drill periods and active duty time.
Can I increase my military retirement pay?
+Yes, you can increase your military retirement pay by serving more years or advancing in rank. Additionally, cost of living adjustments (COLAs) can increase your retirement pay annually.
Conclusion
The military retirement pay chart can seem complex, but understanding how it works can help you plan for your future. By knowing your final pay grade, years of service, and basic pay, you can calculate your retirement pay and make informed decisions about your military career. Remember to stay up-to-date with changes to the military retirement pay chart and take advantage of opportunities to increase your retirement pay.
