Intro
Discover the wacky world of 7 Quacky Days, a humorous journey filled with duck-themed adventures, quirky escapades, and entertaining stories, perfect for fans of lighthearted comedy and amusing tales.
The world of ducks is a fascinating one, full of interesting behaviors, unique characteristics, and entertaining quirks. For many people, ducks are a source of joy and amusement, whether they're watching them swim in a park pond or learning about their complex social structures. Over the course of 7 quacky days, one can discover a wide range of intriguing facts and insights about these beloved waterfowl. From their remarkable adaptability to their surprising intelligence, ducks are truly one of the most captivating creatures in the animal kingdom.
As we embark on this 7-day journey into the world of ducks, we'll explore their habitats, behaviors, and characteristics in depth. We'll learn about the different species of ducks, their migratory patterns, and their unique communication methods. We'll also examine the importance of conservation efforts and how humans can help protect these amazing birds and their habitats. Whether you're a seasoned bird enthusiast or just starting to learn about ducks, this 7-day adventure is sure to delight and inform.
Ducks have been a part of human culture for thousands of years, featuring in art, literature, and folklore from around the world. From the elegant wood ducks of North America to the colorful mandarin ducks of Asia, these birds have inspired countless stories, poems, and paintings. As we delve into the world of ducks, we'll explore their cultural significance and the impact they've had on human society. We'll also examine the many ways in which ducks have adapted to human environments, from urban parks to agricultural landscapes.
Introduction to Duck Biology

Key Characteristics of Ducks
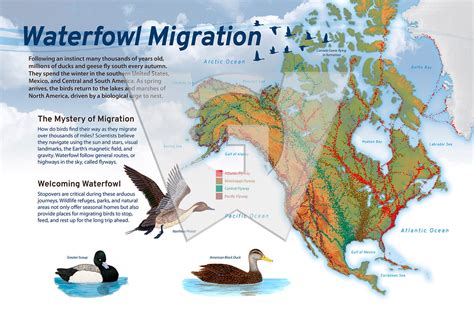
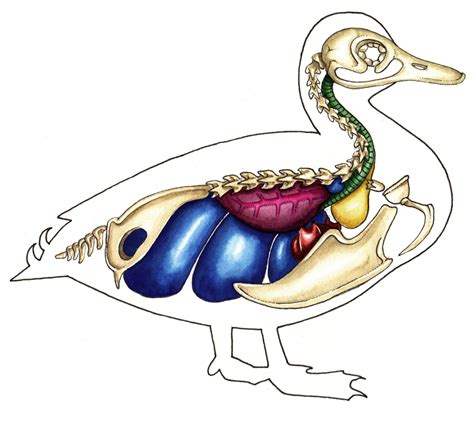
Some of the key characteristics of ducks include their webbed feet, streamlined bodies, and water-repellent feathers. These adaptations enable ducks to swim efficiently, dive to great depths, and survive in a variety of aquatic environments. Ducks are also highly social creatures, often living in large flocks and communicating with each other through a range of quacks, whistles, and body language. By studying the biology and behavior of ducks, we can gain a deeper appreciation for these remarkable birds and the important role they play in ecosystems around the world.Duck Migration Patterns

Conservation Efforts for Duck Migration
Conservation efforts are essential to protect duck migration routes and habitats, which are often threatened by human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and climate change. By preserving wetlands, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable land use practices, we can help ensure the long-term survival of duck populations and the ecosystems they inhabit. Additionally, research and monitoring programs can provide valuable insights into duck migration patterns, helping us to better understand and manage these incredible phenomena.Duck Communication and Social Behavior

Unique Quacking Sounds of Ducks
One of the most distinctive and recognizable sounds in the animal kingdom is the quack of a duck. Different duck species have unique quacking sounds, which can be used for identification and communication. For example, the mallard duck has a loud, nasal quack, while the wood duck has a high-pitched, squeaky call. By listening to and analyzing these quacking sounds, we can learn more about the behavior, social structure, and ecology of ducks, and appreciate the fascinating diversity of these amazing birds.Duck Habitat and Distribution

Importance of Wetlands for Ducks
Wetlands are crucial habitats for ducks, providing them with food, shelter, and breeding grounds. These ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal species, and are essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem health. By conserving and restoring wetlands, we can help protect duck populations and the many other species that depend on these habitats. Additionally, wetlands provide important ecosystem services, such as water filtration, flood control, and carbon sequestration, which benefit both humans and the environment.Duck Diet and Foraging Behavior
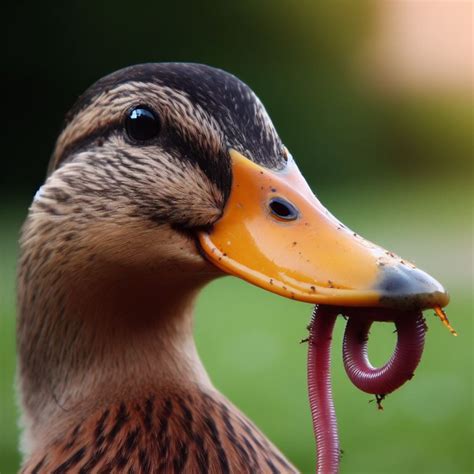

Impact of Food Availability on Duck Populations
The availability of food is a critical factor in determining duck populations and distribution. In areas with abundant food resources, duck populations can thrive, while in areas with limited food availability, populations may decline. By managing food resources, such as aquatic vegetation and invertebrate populations, we can help support duck populations and maintain healthy ecosystems. Additionally, research on duck diet and foraging behavior can provide valuable insights into the ecological role of ducks and the ways in which they interact with their environments.Duck Image Gallery








What is the average lifespan of a duck?
+The average lifespan of a duck is around 2-3 years in the wild, although some species can live up to 5-7 years. In captivity, ducks can live for 10-15 years or more with proper care and management.
What do ducks eat?
+Ducks are omnivorous birds that eat a wide range of plants and animals, including aquatic vegetation, insects, crustaceans, and small fish. They forage for food in a variety of ways, using their beaks to filter small organisms from the water, their feet to stir up sediment, and their eyes to spot prey in the water.
How do ducks communicate?
+Ducks communicate with each other through a range of vocalizations, visual displays, and body language. They use quacks, whistles, and other sounds to convey information about food, predators, and potential mates, and they also use visual cues, such as feather postures and courtship displays, to signal their intentions and status.
Why are ducks important in ecosystems?
+Ducks play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem health and biodiversity. They help to control aquatic vegetation, regulate insect and invertebrate populations, and serve as indicators of environmental quality. Additionally, ducks are an important food source for many predators, including birds of prey, mammals, and fish.
How can we help protect duck populations?
+We can help protect duck populations by conserving and restoring wetlands, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable land use practices. Additionally, research and monitoring programs can provide valuable insights into duck ecology and behavior, helping us to better manage and conserve these amazing birds.
As we conclude our 7-day journey into the world of ducks, we hope that you have gained a deeper appreciation for these fascinating birds and the important role they play in ecosystems around the world. Whether you're a seasoned bird enthusiast or just starting to learn about ducks, we encourage you to continue exploring and learning about these amazing creatures. Share your thoughts and experiences with others, and join us in our efforts to protect and conserve duck populations and their habitats. Together, we can make a difference and ensure the long-term survival of these incredible birds.
