Intro
Russias rising debt-to-GDP ratio sparks economic concerns. Discover the implications of increasing government debt on Russias financial stability, economic growth, and credit rating. Learn how high debt levels can lead to fiscal vulnerabilities, impact investor confidence, and threaten the countrys long-term economic prosperity.
Russia's economy has been facing numerous challenges in recent years, including a decline in oil prices, international sanctions, and a decrease in investor confidence. One of the most pressing concerns is the country's growing debt-to-GDP ratio, which has been increasing steadily over the past few years. In this article, we will explore the causes and consequences of Russia's rising debt-to-GDP ratio and what it means for the country's economic future.
Understanding Russia's Debt-to-GDP Ratio
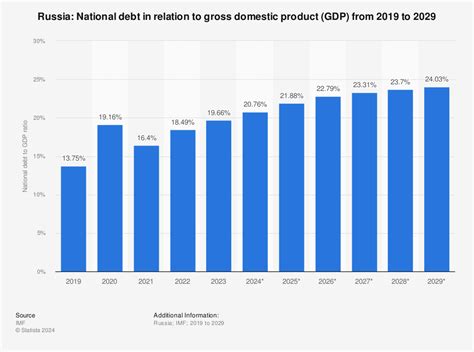
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a widely used indicator of a country's economic health, representing the total amount of debt owed by the government, households, and businesses as a percentage of the country's gross domestic product (GDP). A high debt-to-GDP ratio can indicate a country's vulnerability to economic shocks and its ability to meet its financial obligations.
In Russia's case, the debt-to-GDP ratio has been increasing steadily over the past few years, from around 30% in 2014 to over 70% in 2022. This significant increase is largely due to the government's efforts to stimulate economic growth through fiscal expansion and the impact of international sanctions on the country's economy.
Causes of Russia's Rising Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Several factors have contributed to Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio. Some of the key causes include:
- Fiscal expansion: The Russian government has implemented various fiscal policies aimed at stimulating economic growth, including increased government spending and tax cuts. While these policies have helped to boost economic growth in the short term, they have also led to a significant increase in government debt.
- International sanctions: The imposition of international sanctions on Russia in 2014 has had a significant impact on the country's economy. The sanctions have limited Russia's access to international capital markets, forcing the government to rely on domestic sources of funding, which has contributed to the increase in debt.
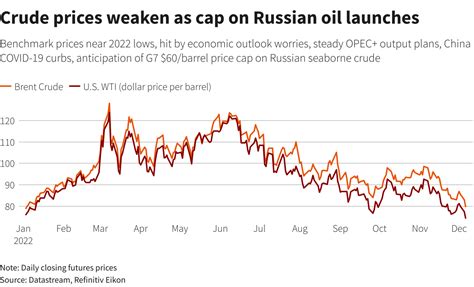
- Decline in oil prices: Russia's economy is heavily dependent on oil exports, and the decline in oil prices in recent years has had a significant impact on government revenue. To compensate for the decline in revenue, the government has increased borrowing, which has contributed to the increase in debt.
Consequences of Russia's Growing Debt-to-GDP Ratio
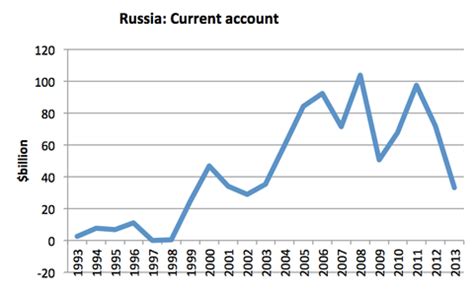
The consequences of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio are far-reaching and can have significant implications for the country's economic future. Some of the key consequences include:
- Increased borrowing costs: A high debt-to-GDP ratio can lead to increased borrowing costs for the government, as investors demand higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk of lending to a country with a high level of debt.
- Reduced investor confidence: A high debt-to-GDP ratio can also reduce investor confidence in the country's economy, making it more difficult for the government to attract foreign investment.
- Limited fiscal space: A high debt-to-GDP ratio can limit the government's ability to implement fiscal policies aimed at stimulating economic growth, as the government may be constrained by its debt obligations.
Steps to Address Russia's Growing Debt-to-GDP Ratio
To address Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio, the government needs to implement a combination of fiscal and structural reforms. Some of the key steps that the government can take include:
- Fiscal consolidation: The government needs to implement a fiscal consolidation program aimed at reducing the budget deficit and stabilizing government debt. This can be achieved through a combination of spending cuts and tax increases.
- Structural reforms: The government needs to implement structural reforms aimed at improving the business environment and increasing economic competitiveness. This can include reforms to the tax code, labor market, and regulatory framework.
- Diversification of the economy: The government needs to implement policies aimed at diversifying the economy and reducing its dependence on oil exports. This can include investments in sectors such as manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
Gallery of Russia's Economic Challenges
Russia's Economic Challenges Image Gallery
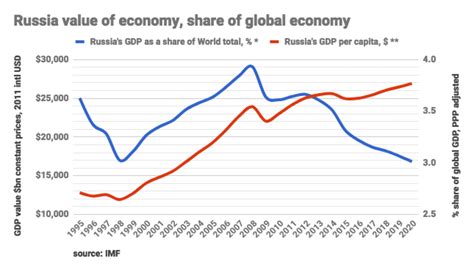


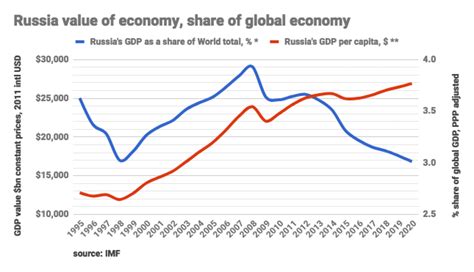





Frequently Asked Questions
What is Russia's current debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Russia's current debt-to-GDP ratio is around 70%.
What are the causes of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio?
+The causes of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio include fiscal expansion, international sanctions, and the decline in oil prices.
What are the consequences of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio?
+The consequences of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio include increased borrowing costs, reduced investor confidence, and limited fiscal space.
What steps can Russia take to address its growing debt-to-GDP ratio?
+Russia can take steps to address its growing debt-to-GDP ratio by implementing fiscal consolidation, structural reforms, and diversifying its economy.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Russia's growing debt-to-GDP ratio and its implications for the country's economic future. We encourage you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic and to stay tuned for further updates on Russia's economic developments.
