Intro
Discover how Army Sergeant salaries vary by rank and experience. From E-5 to E-9, explore the 7 ways sergeant pay differs, including base pay, allowances, and bonuses. Learn about the factors influencing Army Sergeant salaries, including time in service, deployability, and specialization, and how to maximize your earnings.
Understanding the Army Sergeant Salary Structure
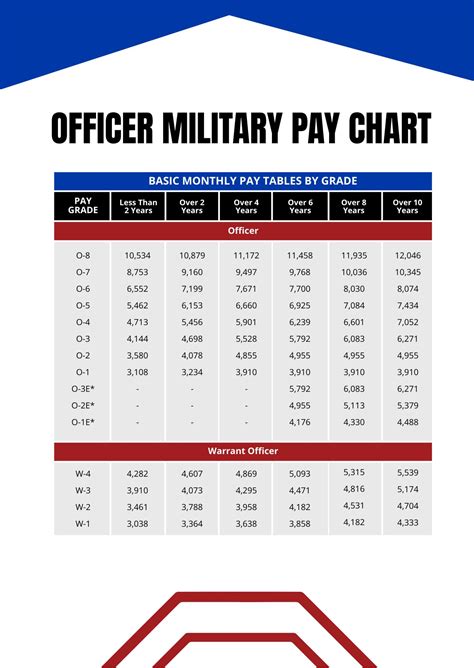
Army sergeants play a crucial role in the United States military, serving as leaders and mentors to junior soldiers. Their salaries, however, vary based on several factors, including rank, time in service, and location. In this article, we'll explore the seven ways army sergeant salaries vary by rank, highlighting the differences and what they mean for those serving in this esteemed position.
The army sergeant salary structure is based on the military's pay grade system, which assigns a specific pay grade to each rank. The higher the pay grade, the higher the salary. Sergeants, who are non-commissioned officers (NCOs), fall into several pay grades, each with its own salary range.
Rank-Based Salary Variations
The army sergeant salary varies significantly based on rank. Here are the seven ways army sergeant salaries vary by rank:
-
Staff Sergeant (E-6): Staff sergeants are senior NCOs who have achieved a high level of expertise in their field. Their salary range is between $2,944.50 and $5,452.90 per month, depending on time in service.
-
Sergeant First Class (E-7): Sergeants first class are advanced NCOs who have demonstrated exceptional leadership skills. Their salary range is between $3,471.30 and $6,269.40 per month, depending on time in service.
-
Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8): Master sergeants and first sergeants are senior NCOs who have achieved the highest level of technical expertise and leadership skills. Their salary range is between $4,247.60 and $7,636.40 per month, depending on time in service.
-
Sergeant Major (E-9): Sergeants major are the highest-ranking NCOs in the army, serving as senior enlisted advisors to senior officers. Their salary range is between $5,174.60 and $8,751.40 per month, depending on time in service.
-
Command Sergeant Major (E-9): Command sergeants major are senior enlisted leaders who serve as command sergeants major for brigades, divisions, and corps. Their salary range is between $5,511.40 and $9,144.90 per month, depending on time in service.
-
Sergeant First Class (E-7) with Special Skills: Sergeants first class with special skills, such as language proficiency or technical expertise, may receive additional pay. Their salary range is between $3,471.30 and $6,269.40 per month, depending on time in service and special skills.
-
Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8) with Special Skills: Master sergeants and first sergeants with special skills, such as language proficiency or technical expertise, may receive additional pay. Their salary range is between $4,247.60 and $7,636.40 per month, depending on time in service and special skills.
Time in Service and Location-Based Salary Variations
In addition to rank-based salary variations, army sergeant salaries also vary based on time in service and location. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Time in Service: The longer an army sergeant serves, the higher their salary will be. For example, a staff sergeant with 10 years of service will earn a higher salary than a staff sergeant with 5 years of service.
- Location: Army sergeants serving in high-cost areas, such as San Francisco or New York City, will receive a higher salary than those serving in lower-cost areas, such as rural areas in the southern United States.
- Hazardous Duty Pay: Army sergeants serving in hazardous duty assignments, such as combat zones or high-risk areas, may receive additional pay.
Benefits and Allowances
Army sergeants receive a range of benefits and allowances in addition to their base salary. These include:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): Army sergeants receive a housing allowance to help cover the cost of housing, whether they live on or off base.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): Army sergeants receive a food allowance to help cover the cost of food, whether they eat on or off base.
- Special Duty Pay: Army sergeants serving in special duty assignments, such as recruiters or drill sergeants, may receive additional pay.
- Jump Pay: Army sergeants who are airborne qualified may receive jump pay, which is a special allowance for serving in airborne units.
Conclusion
The army sergeant salary structure is complex, with salaries varying based on rank, time in service, and location. Understanding these factors can help army sergeants plan their careers and make informed decisions about their service. Whether you're a seasoned veteran or a new recruit, knowing how your salary will vary based on your rank and time in service can help you navigate the army's pay system and achieve your financial goals.
Army Sergeant Salary Gallery






What is the average salary for an army sergeant?
+The average salary for an army sergeant varies based on rank, time in service, and location. However, the average annual salary for an army sergeant is around $50,000.
How does time in service affect army sergeant salaries?
+Time in service is a significant factor in determining army sergeant salaries. The longer an army sergeant serves, the higher their salary will be.
What benefits and allowances do army sergeants receive?
+Army sergeants receive a range of benefits and allowances, including basic allowance for housing, basic allowance for subsistence, special duty pay, and jump pay.
