Intro
Discover the thrill of supersonic flight with our in-depth exploration of Mach 3, a speed that surpasses the sound barrier. Learn about the physics of sonic booms, the challenges of breaking the sound barrier, and the innovative aircraft designs that have achieved this remarkable feat, pushing the boundaries of aerodynamics and aviation technology.
The concept of speed is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of the physical world. From the speed of light to the speed of sound, these concepts have fascinated scientists and engineers for centuries. One term that has captured the imagination of many is Mach 3, a speed that is three times the speed of sound. But what exactly is Mach 3, and what does it mean in practical terms?

To understand Mach 3, we need to first understand the speed of sound. The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). This speed is not constant and can vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure.
What is Mach 3?
Mach 3 is a speed that is three times the speed of sound. This means that an object traveling at Mach 3 is moving at a speed of approximately 2,304 mph (3,708 km/h). To put this in perspective, the fastest military aircraft ever built, the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, has a top speed of around Mach 3.5.
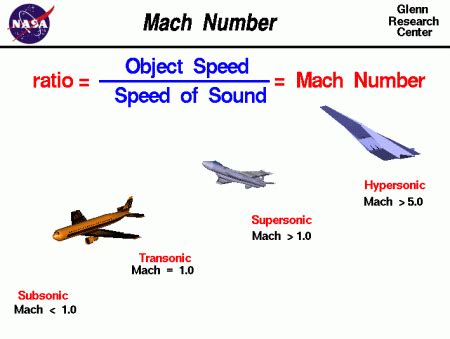
Mach 3 is an incredibly high speed that is rarely achieved in practice. However, it is an important concept in aerodynamics and aerospace engineering, where it is used to describe the performance of high-speed aircraft and spacecraft.
History of Mach 3
The concept of Mach 3 was first explored in the 1940s and 1950s, when the United States military began developing high-speed aircraft. One of the earliest aircraft to achieve Mach 3 was the Bell X-2, a rocket-powered plane that was developed in the 1950s.

Since then, several other aircraft have achieved Mach 3, including the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird and the North American X-15. These aircraft were developed for military and research purposes, and they have played an important role in advancing our understanding of high-speed flight.
Challenges of Mach 3
Achieving Mach 3 is an incredibly challenging task. At such high speeds, the air resistance is so intense that it can cause an aircraft to heat up to extreme temperatures, potentially causing damage to the airframe and engines.

Additionally, the shockwaves generated by an aircraft traveling at Mach 3 can cause sonic booms, which can be disturbing to people on the ground. These challenges make it difficult to design and build aircraft that can safely and efficiently achieve Mach 3.
Applications of Mach 3
Despite the challenges, Mach 3 has several important applications in aerospace and defense. For example, high-speed aircraft can be used for reconnaissance and surveillance, as well as for delivering payloads to space.

Additionally, the technology developed for achieving Mach 3 has spin-off benefits for other industries, such as the development of high-speed transportation systems and advanced materials.
Future of Mach 3
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even faster aircraft and spacecraft in the future. For example, NASA is currently developing a new spacecraft called the X-59 QueSST, which is designed to achieve speeds of up to Mach 1.4.

Private companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin are also working on high-speed spacecraft that could potentially achieve Mach 3 or higher.
Gallery of High-Speed Aircraft
High-Speed Aircraft Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mach 3?
+Mach 3 is a speed that is three times the speed of sound.
What is the speed of sound?
+The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
What are the challenges of achieving Mach 3?
+Achieving Mach 3 is an incredibly challenging task due to the intense air resistance and shockwaves generated at such high speeds.
In conclusion, Mach 3 is an incredibly high speed that is rarely achieved in practice. However, it has several important applications in aerospace and defense, and it continues to inspire innovation and advancement in these fields. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even faster aircraft and spacecraft in the future.
