Intro
Embark on a noble career path with our comprehensive guide on 7 Steps To Join The Army. Learn the requirements, enlistment process, and training procedures to become a proud soldier. Discover the benefits, eligibility criteria, and necessary documents for army recruitment, plus tips on preparing for the ASVAB test and Basic Combat Training.
Joining the army can be a life-changing decision that requires careful consideration, preparation, and dedication. If you're interested in serving your country and pursuing a career in the military, here's a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the process.

The journey to joining the army involves several steps, from meeting the basic requirements to completing the enlistment process. In this article, we'll break down the 7 essential steps to help you get started.
Step 1: Meet the Basic Requirements
Before you begin the enlistment process, it's essential to ensure you meet the army's basic requirements. These include:
- Being a U.S. citizen or national
- Being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Having a high school diploma or equivalent
- Scoring well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Passing a physical fitness test
- Meeting medical and moral standards
Physical Fitness Test Requirements
The army requires you to pass a physical fitness test, which includes:
- 30-40 push-ups in 1 minute
- 30-40 sit-ups in 1 minute
- A 2-mile run in under 16 minutes
Step 2: Choose Your Military Occupational Specialty (MOS)
The army offers a wide range of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS) that cater to different skills and interests. Research and choose an MOS that aligns with your strengths and career goals.

Popular Army MOS
Some popular army MOS include:
- Infantryman (11X)
- Combat Engineer (12B)
- Cyber Operations Specialist (25D)
- Intelligence Analyst (35F)
- Medical Laboratory Specialist (68K)
Step 3: Take the ASVAB Test
The ASVAB test measures your aptitude in various subjects, including math, science, and language. Your test scores will help determine your eligibility for different MOS.
ASVAB Test Sections
The ASVAB test consists of 9 sections:
- General Science (GS)
- Arithmetic Reasoning (AR)
- Word Knowledge (WK)
- Paragraph Comprehension (PC)
- Mathematics Knowledge (MK)
- Electronics Information (EI)
- Auto & Shop Information (AS)
- Mechanical Comprehension (MC)
- Assembling Objects (AO)
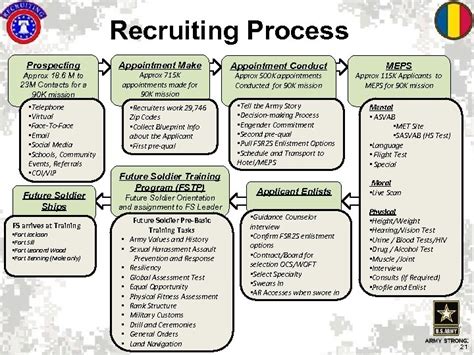
Step 4: Complete the Enlistment Process
Once you've met the basic requirements, chosen your MOS, and taken the ASVAB test, it's time to complete the enlistment process. This includes:
- Meeting with a recruiter to discuss your application
- Completing a background check and medical screening
- Taking the oath of enlistment
- Receiving your enlistment paperwork and orders
Step 5: Attend Basic Combat Training (BCT)
After enlisting, you'll attend Basic Combat Training (BCT) for 10 weeks. BCT is designed to teach you the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the army.
BCT Training Phases
BCT consists of three phases:
- Red Phase (weeks 1-3): Focuses on physical training, first aid, and combat skills
- White Phase (weeks 4-5): Emphasizes marksmanship, map reading, and first aid
- Blue Phase (weeks 6-10): Covers leadership, teamwork, and combat scenarios
Step 6: Attend Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
After completing BCT, you'll attend Advanced Individual Training (AIT) for 14-20 weeks. AIT provides specialized training in your chosen MOS.
AIT Training Objectives
AIT training objectives include:
- Developing technical skills in your MOS
- Learning how to work with others as a team
- Understanding army values and policies
Step 7: Serve and Advance
Once you've completed AIT, you'll be assigned to a unit and begin serving in the army. As you gain experience and complete additional training, you'll have opportunities to advance in rank and take on new challenges.

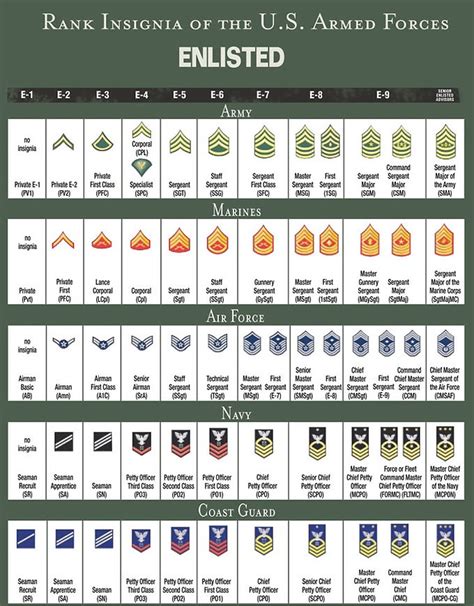
Army Ranks and Promotion
The army offers a clear path for advancement, with opportunities to promote to higher ranks. Here are the army ranks, from lowest to highest:
- Private (E-1)
- Private Second Class (E-2)
- Private First Class (E-3)
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4)
- Sergeant (E-5)
- Staff Sergeant (E-6)
- Sergeant First Class (E-7)
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8)
- Sergeant Major (E-9)
We hope this guide has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the 7 steps to join the army. Remember to stay focused, work hard, and always strive to achieve your goals.
Army Enlistment Gallery









What is the minimum age requirement to join the army?
+The minimum age requirement to join the army is 17 years old. However, you must be at least 18 years old to enlist without parental consent.
How long does the enlistment process take?
+The enlistment process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of your application and the availability of openings in your chosen MOS.
What is the difference between BCT and AIT?
+BCT (Basic Combat Training) is a 10-week training program that teaches you the fundamental skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the army. AIT (Advanced Individual Training) is a specialized training program that teaches you the skills and knowledge specific to your chosen MOS.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and information about the 7 steps to join the army. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask.
