Intro
Explore the cutting-edge world of extreme speed with our in-depth analysis of supersonic vs hypersonic speed. Discover the 5 key differences between these two incredible velocities, including their Mach numbers, propulsion systems, and real-world applications, to gain a deeper understanding of the technology driving innovation in aerospace engineering.
The world of aerospace is constantly evolving, with breakthroughs in technology pushing the boundaries of speed and innovation. Two terms that have gained significant attention in recent years are supersonic and hypersonic. While both refer to speeds beyond the sound barrier, there are distinct differences between the two. In this article, we'll delve into the 5 key differences between supersonic and hypersonic speeds, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and applications.

1. Speed Range
The primary difference between supersonic and hypersonic speeds lies in their speed ranges. Supersonic speeds range from Mach 1 (approximately 768 mph or 1,236 km/h) to Mach 5 (around 3,800 mph or 6,116 km/h). Hypersonic speeds, on the other hand, exceed Mach 5, typically ranging from Mach 5 to Mach 10 (around 12,360 mph or 19,900 km/h) or even higher.
Supersonic Speeds:
- Mach 1-3: Used in military aircraft and some experimental vehicles
- Mach 3-5: Utilized in advanced military aircraft and some space launch vehicles
Hypersonic Speeds:
- Mach 5-10: Currently being researched and developed for future military and space applications
- Mach 10+: Theoretical speeds being explored for advanced space missions and concepts
2. Aerodynamics and Heat
As objects travel at supersonic speeds, they experience intense heat and friction, leading to significant aerodynamic challenges. Hypersonic speeds, however, generate even more extreme heat and friction, requiring specialized materials and designs to withstand these conditions.
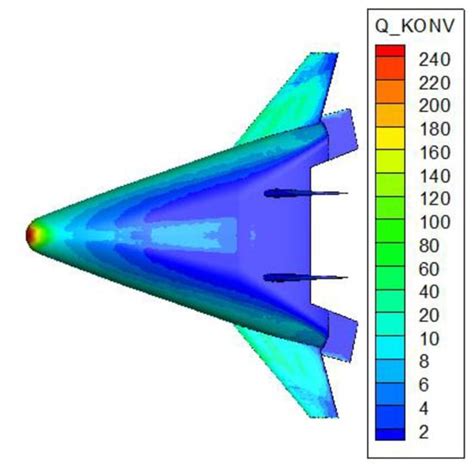
Supersonic Aerodynamics:
- Shockwaves and sonic booms occur as objects break the sound barrier
- Air resistance and friction increase exponentially with speed
Hypersonic Aerodynamics:
- Extreme heat and friction require advanced materials and cooling systems
- Air density and composition change significantly at hypersonic speeds, affecting aerodynamics
3. Propulsion Systems
Supersonic and hypersonic vehicles require distinct propulsion systems to achieve and sustain their respective speeds.

Supersonic Propulsion:
- Conventional jet engines or rocket motors can be used
- Air-breathing engines, like scramjets, are being developed for supersonic applications
Hypersonic Propulsion:
- Advanced rocket motors or air-breathing engines, like hypersonic combustion ramjets, are necessary
- Research focuses on developing efficient and sustainable hypersonic propulsion systems
4. Applications and Missions
Supersonic and hypersonic speeds have different applications and mission profiles.
Supersonic Applications:
- Military aircraft and missiles
- Space launch vehicles and re-entry vehicles
- Experimental vehicles and research platforms
Hypersonic Applications:
- Future military and space missions, such as hypersonic cruise missiles and spaceplanes
- Advanced space exploration and reconnaissance
- Potential for commercial applications, like hypersonic transportation systems
5. Research and Development
Both supersonic and hypersonic speeds are the subject of ongoing research and development, with a focus on advancing materials, propulsion systems, and aerodynamics.

Supersonic Research:
- Focuses on improving aerodynamics, materials, and propulsion systems
- Experimental vehicles and wind tunnel testing drive innovation
Hypersonic Research:
- Investigates advanced materials, propulsion systems, and aerodynamics
- Computational simulations and ground testing support the development of hypersonic technologies
Supersonic and Hypersonic Speed Gallery










What is the main difference between supersonic and hypersonic speeds?
+The primary difference between supersonic and hypersonic speeds lies in their speed ranges. Supersonic speeds range from Mach 1 to Mach 5, while hypersonic speeds exceed Mach 5.
What are the applications of supersonic speeds?
+Supersonic speeds have various applications, including military aircraft and missiles, space launch vehicles and re-entry vehicles, and experimental vehicles and research platforms.
What are the challenges of achieving hypersonic speeds?
+Achieving hypersonic speeds poses significant challenges, including managing extreme heat and friction, developing advanced propulsion systems, and creating materials that can withstand the harsh conditions.
In conclusion, supersonic and hypersonic speeds are distinct regimes with different characteristics, applications, and challenges. As research and development continue to advance, we can expect to see innovative breakthroughs in materials, propulsion systems, and aerodynamics, ultimately pushing the boundaries of speed and innovation. Share your thoughts on the future of supersonic and hypersonic technologies in the comments below!
