Intro
Unlock the power of survey grade mapping with our expert guide. Discover the 5 key facts you need to know about high-accuracy mapping, including RTK GNSS, survey-grade GPS, and precision geospatial data collection. Learn how to achieve centimeter-level accuracy for informed decision-making in industries like construction, mining, and environmental monitoring.
Survey grade mapping is a high-stakes process that requires precision, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the underlying technology. Whether you're a seasoned surveyor or just starting out, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of survey grade mapping to ensure accurate and reliable results. In this article, we'll delve into the world of survey grade mapping, exploring its key facts, benefits, and applications.
What is Survey Grade Mapping?

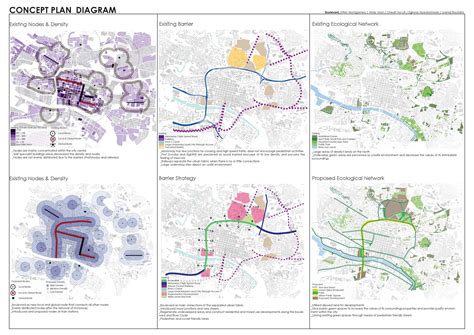
Survey grade mapping refers to the process of creating highly accurate and detailed maps of the Earth's surface using advanced surveying techniques and technologies. This type of mapping is typically used for high-stakes applications, such as construction, engineering, and environmental monitoring, where accuracy and precision are paramount.
Key Fact #1: Survey Grade Mapping Requires High-Accuracy Data
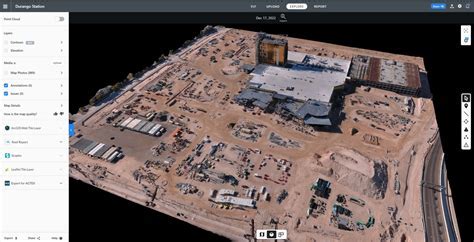
Survey grade mapping relies on high-accuracy data, typically with a precision of 1-2 cm or better. This level of accuracy is achieved through the use of advanced surveying technologies, such as GPS, total stations, and terrestrial LiDAR scanners. These instruments are capable of collecting vast amounts of data, which are then processed and analyzed to create highly detailed maps.
Benefits of Survey Grade Mapping
Survey grade mapping offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved accuracy: Survey grade mapping provides highly accurate data, which is essential for high-stakes applications.
- Enhanced decision-making: With accurate and detailed maps, stakeholders can make informed decisions about construction, engineering, and environmental projects.
- Increased efficiency: Survey grade mapping can streamline the surveying process, reducing the need for manual measurements and minimizing errors.
- Cost savings: By reducing the need for manual measurements and minimizing errors, survey grade mapping can help save costs and reduce project timelines.
Key Fact #2: Survey Grade Mapping is Used in a Variety of Industries
Survey grade mapping is used in a variety of industries, including:
- Construction: Survey grade mapping is used to create accurate maps of construction sites, enabling builders to plan and execute projects with precision.
- Engineering: Survey grade mapping is used to create detailed maps of infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and tunnels.
- Environmental monitoring: Survey grade mapping is used to monitor environmental changes, such as land subsidence, erosion, and climate change.
How Survey Grade Mapping Works

Survey grade mapping involves a multi-step process, including:
- Data collection: Surveyors collect data using advanced surveying technologies, such as GPS, total stations, and terrestrial LiDAR scanners.
- Data processing: Collected data is processed and analyzed to create highly detailed maps.
- Map creation: Maps are created using specialized software, such as geographic information systems (GIS).
- Quality control: Maps are reviewed and verified to ensure accuracy and precision.
Key Fact #3: Survey Grade Mapping Requires Specialized Software
Survey grade mapping requires specialized software, such as GIS, to create and analyze maps. GIS software enables users to manage, analyze, and visualize large datasets, creating highly detailed maps and 3D models.
Applications of Survey Grade Mapping
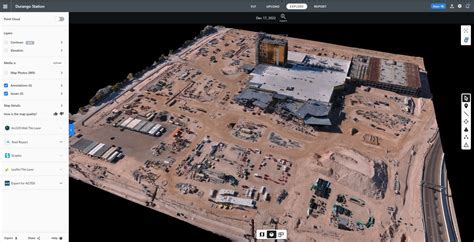
Survey grade mapping has a wide range of applications, including:
- Construction monitoring: Survey grade mapping is used to monitor construction progress, enabling builders to identify potential issues and make adjustments.
- Infrastructure planning: Survey grade mapping is used to plan and design infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and tunnels.
- Environmental monitoring: Survey grade mapping is used to monitor environmental changes, such as land subsidence, erosion, and climate change.
Key Fact #4: Survey Grade Mapping is Used in Urban Planning
Survey grade mapping is used in urban planning to create accurate maps of urban environments, enabling planners to design and develop sustainable and efficient cities.
Best Practices for Survey Grade Mapping

To ensure accurate and reliable results, surveyors should follow best practices for survey grade mapping, including:
- Use high-accuracy data: Use high-accuracy data, typically with a precision of 1-2 cm or better.
- Use specialized software: Use specialized software, such as GIS, to create and analyze maps.
- Conduct regular quality control: Conduct regular quality control checks to ensure accuracy and precision.
Key Fact #5: Survey Grade Mapping is Continuously Evolving
Survey grade mapping is continuously evolving, with advances in technology and software enabling faster, more accurate, and more efficient mapping.
Survey Grade Mapping Image Gallery
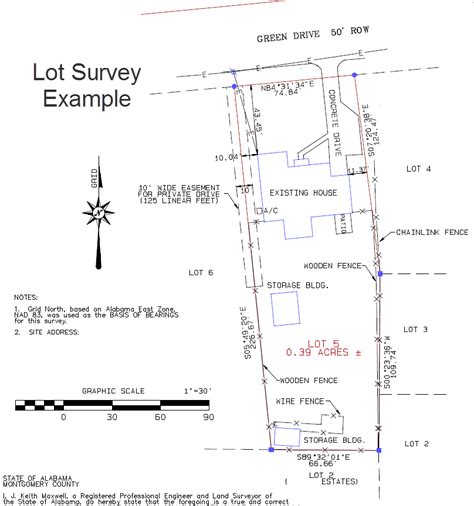

What is survey grade mapping?
+Survey grade mapping is the process of creating highly accurate and detailed maps of the Earth's surface using advanced surveying techniques and technologies.
What are the benefits of survey grade mapping?
+Survey grade mapping offers numerous benefits, including improved accuracy, enhanced decision-making, increased efficiency, and cost savings.
What industries use survey grade mapping?
+Survey grade mapping is used in a variety of industries, including construction, engineering, environmental monitoring, and urban planning.
As we've seen, survey grade mapping is a critical process that requires precision, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the underlying technology. By following best practices and staying up-to-date with the latest advances in technology and software, surveyors can ensure accurate and reliable results that meet the needs of a wide range of industries. Whether you're a seasoned surveyor or just starting out, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of survey grade mapping.
