Intro
Discover the hierarchy of the US Army with our detailed guide to the 10 Army ranks in order of seniority. Learn about the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for each rank, from Private to General. Understand the rank insignia, pay grades, and promotion process to advance your military career or simply broaden your knowledge.
Understanding the hierarchy of the military is essential for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to learn more about the structure and organization of the army. The army ranks are divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and commissioned officers. Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits.
The army ranks are organized in a pyramid structure, with the highest ranks at the top and the lowest ranks at the bottom. The ranks are further divided into two main categories: enlisted personnel and officer personnel. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the army and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. Officer personnel, on the other hand, are responsible for leading and commanding the enlisted personnel.
Here are the 10 army ranks in order of seniority, starting from the lowest:
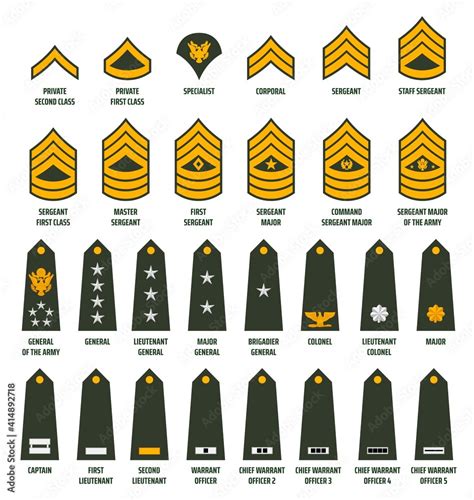

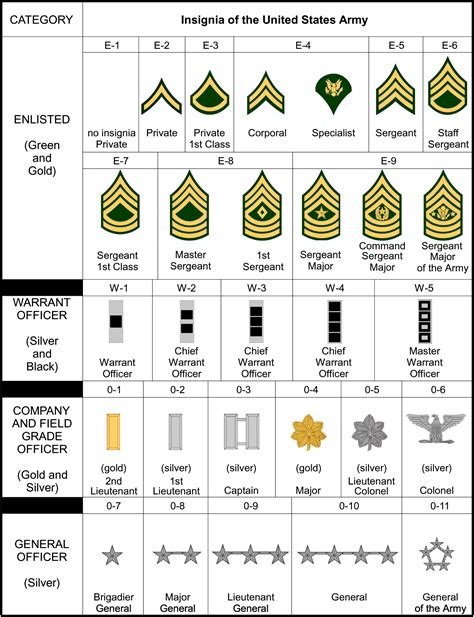
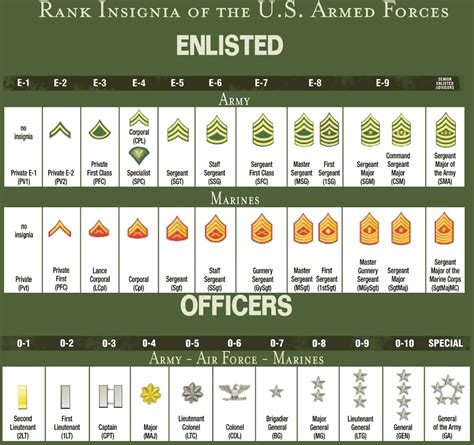
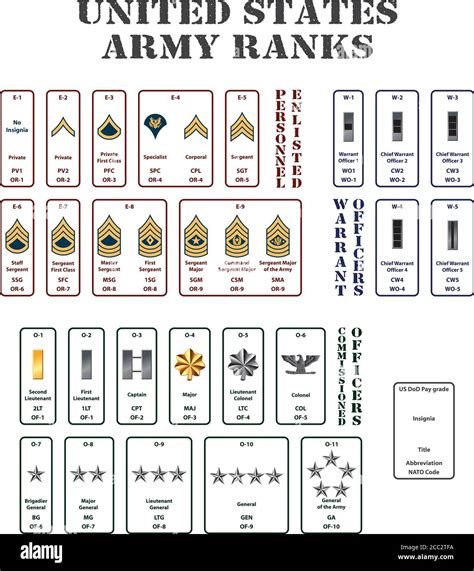
Enlisted Personnel
Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the army, making up the majority of the force. They are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations.
1. Private (PVT)
The lowest rank in the army is the Private (PVT). This rank is typically held by new recruits who have just joined the army. Privates are responsible for carrying out basic tasks and duties, such as cleaning, cooking, and maintaining equipment.
2. Private Second Class (PV2)
The next rank up from Private is the Private Second Class (PV2). This rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their basic training and have been assigned to a unit. Private Second Class soldiers are responsible for carrying out more complex tasks and duties.
3. Private First Class (PFC)
The Private First Class (PFC) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their advanced training and have been assigned to a specialized role. Private First Class soldiers are responsible for carrying out more complex tasks and duties, such as leading teams and operating equipment.

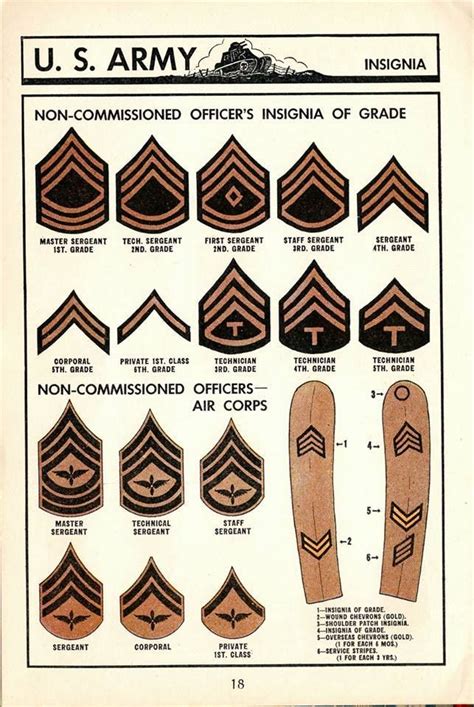
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs)
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) are enlisted personnel who have been promoted to a leadership role. They are responsible for leading and commanding other enlisted personnel.
4. Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL)
The Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their advanced training and have been assigned to a specialized role. Specialist/Corporal soldiers are responsible for leading teams and operating equipment.
5. Sergeant (SGT)
The Sergeant (SGT) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their advanced training and have been assigned to a leadership role. Sergeant soldiers are responsible for leading teams and making tactical decisions.
6. Staff Sergeant (SSG)
The Staff Sergeant (SSG) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their advanced training and have been assigned to a senior leadership role. Staff Sergeant soldiers are responsible for leading teams and making strategic decisions.

Warrant Officers
Warrant Officers are technical experts who have been promoted to a leadership role. They are responsible for providing technical guidance and advice to other soldiers.
7. Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
The Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their technical training and have been assigned to a specialized role. Warrant Officer 1 soldiers are responsible for providing technical guidance and advice to other soldiers.
8. Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
The Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) rank is typically held by soldiers who have completed their technical training and have been assigned to a senior leadership role. Chief Warrant Officer 2 soldiers are responsible for providing technical guidance and advice to other soldiers and making strategic decisions.

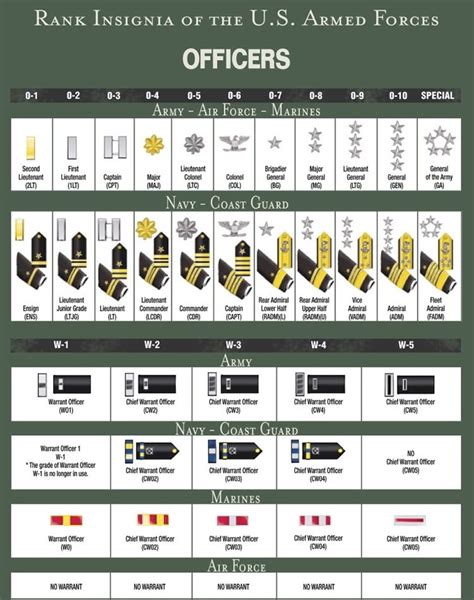
Commissioned Officers
Commissioned Officers are leaders who have been appointed to a command role. They are responsible for leading and commanding other soldiers.
9. Second Lieutenant (2LT)
The Second Lieutenant (2LT) rank is typically held by new officers who have just completed their officer training. Second Lieutenant soldiers are responsible for leading teams and making tactical decisions.
10. First Lieutenant (1LT)
The First Lieutenant (1LT) rank is typically held by officers who have completed their advanced training and have been assigned to a leadership role. First Lieutenant soldiers are responsible for leading teams and making strategic decisions.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the army ranks are organized in a pyramid structure, with the highest ranks at the top and the lowest ranks at the bottom. Understanding the hierarchy of the military is essential for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to learn more about the structure and organization of the army.
Army Ranks Gallery

What is the lowest rank in the army?
+The lowest rank in the army is the Private (PVT).
What is the highest rank in the army?
+The highest rank in the army is the General of the Army (GOA).
What is the difference between an enlisted soldier and an officer?
+Enlisted soldiers are the backbone of the army and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. Officers, on the other hand, are leaders who have been appointed to a command role and are responsible for leading and commanding other soldiers.
