Intro
Discover the 5 types of Sewerulf computing nodes and how they facilitate high-performance computing, edge computing, and IoT device management. Learn about Edge Nodes, Fog Nodes, Cloud Nodes, IoT Nodes, and Micro-Cloud Nodes, and their roles in enabling real-time data processing, reduced latency, and enhanced scalability in computing systems.
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, computing nodes play a crucial role in enabling efficient data processing, storage, and communication. Among the various types of computing nodes, Sewaulf computing nodes have gained significant attention for their robust performance, scalability, and reliability. In this article, we will delve into the world of Sewaulf computing nodes, exploring five distinct types that cater to diverse computing needs.
Sewaulf computing nodes are designed to facilitate seamless data exchange, processing, and storage within distributed computing environments. These nodes serve as the building blocks of complex computing systems, ensuring efficient communication, data processing, and storage. With the increasing demand for high-performance computing, understanding the different types of Sewaulf computing nodes is essential for selecting the right solution for specific computing requirements.
1. Edge Nodes
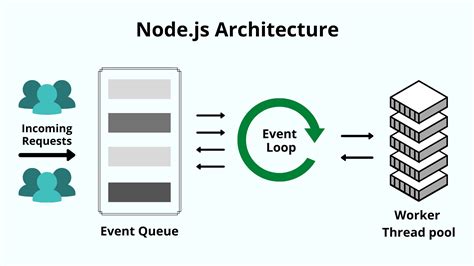
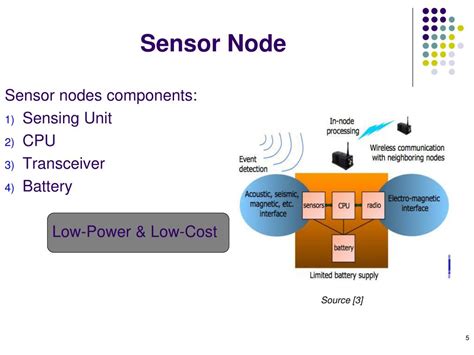
Edge nodes are a type of Sewaulf computing node that operates at the edge of a network, close to the source of data generation. These nodes are designed to process and analyze data in real-time, reducing latency and improving overall system performance. Edge nodes are typically deployed in IoT applications, such as smart homes, cities, and industrial automation, where data needs to be processed and acted upon quickly.
The primary function of edge nodes is to filter, process, and forward relevant data to the central server or cloud for further analysis. By processing data closer to the source, edge nodes minimize the amount of data transmitted over the network, reducing bandwidth requirements and improving overall system efficiency.
2. Storage Nodes
Storage nodes are another type of Sewaulf computing node that focuses on data storage and retrieval. These nodes are designed to provide scalable, high-capacity storage solutions for large-scale computing systems. Storage nodes can be deployed in various configurations, including distributed file systems, object storage, and block storage.
The primary function of storage nodes is to store and retrieve large amounts of data efficiently. These nodes use advanced storage technologies, such as RAID, replication, and erasure coding, to ensure data availability, durability, and scalability.
3. Compute Nodes

Compute nodes are a type of Sewaulf computing node that focuses on data processing and computation. These nodes are designed to execute complex algorithms, simulations, and data analytics workloads. Compute nodes are typically deployed in high-performance computing (HPC) environments, such as scientific research, finance, and machine learning.
The primary function of compute nodes is to execute complex computations efficiently. These nodes use advanced processing technologies, such as multi-core processors, GPUs, and accelerators, to improve processing performance and reduce execution time.
4. Hybrid Nodes

Hybrid nodes are a type of Sewaulf computing node that combines the functions of edge, storage, and compute nodes. These nodes are designed to provide a flexible, multi-functional solution for various computing workloads. Hybrid nodes can be deployed in edge computing environments, where data needs to be processed, stored, and transmitted in real-time.
The primary function of hybrid nodes is to provide a converged infrastructure for computing, storage, and networking. These nodes use advanced technologies, such as hyper-convergence and software-defined infrastructure, to improve system efficiency, scalability, and manageability.
5. Cloud Nodes
Cloud nodes are a type of Sewaulf computing node that operates in cloud computing environments. These nodes are designed to provide scalable, on-demand computing resources for various applications. Cloud nodes can be deployed in public, private, or hybrid cloud environments, where resources need to be dynamically allocated and deallocated.
The primary function of cloud nodes is to provide scalable computing resources on demand. These nodes use advanced cloud computing technologies, such as virtualization, containerization, and serverless computing, to improve resource utilization, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Gallery of Sewaulf Computing Nodes
Sewaulf Computing Nodes Image Gallery
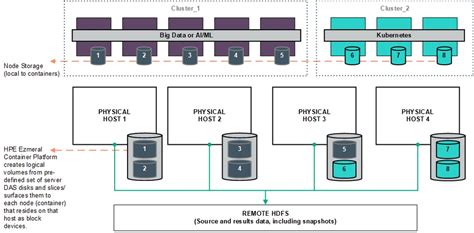
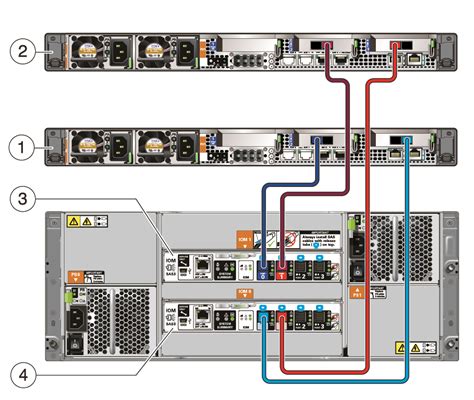
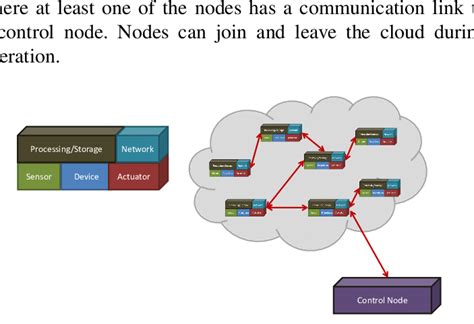

Frequently Asked Questions
What are Sewaulf computing nodes?
+Sewaulf computing nodes are specialized nodes designed to facilitate efficient data processing, storage, and communication within distributed computing environments.
What are the different types of Sewaulf computing nodes?
+There are five main types of Sewaulf computing nodes: Edge Nodes, Storage Nodes, Compute Nodes, Hybrid Nodes, and Cloud Nodes.
What are the primary functions of Sewaulf computing nodes?
+The primary functions of Sewaulf computing nodes vary depending on the node type, but generally include data processing, storage, and communication.
Where are Sewaulf computing nodes typically deployed?
+Sewaulf computing nodes can be deployed in various environments, including edge computing, cloud computing, and high-performance computing (HPC) environments.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of Sewaulf computing nodes. By understanding the different types of nodes and their primary functions, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right solution for your specific computing needs. Whether you're building a high-performance computing system or deploying a cloud-based application, Sewaulf computing nodes can help you achieve your goals.
