Intro
Discover the 5 key U.S. military strengths and weaknesses, from technological advancements and logistical superiority to strategic vulnerabilities and modernization challenges. Explore the complex landscape of American military power, including its global reach, cyber warfare capabilities, and innovative defense systems, to understand the nations defense position in a rapidly changing world.
The United States military is one of the most powerful and technologically advanced armed forces in the world. With a budget of over $700 billion, it is capable of projecting power and defending its interests globally. However, like any other military, it has its strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we will explore five key strengths and weaknesses of the U.S. military.
A Global Reach and Power Projection
The U.S. military has a global reach and power projection capability that is unmatched by any other country. With a network of military bases and installations around the world, the U.S. can deploy its troops and equipment quickly and efficiently to any region. This is made possible by its vast fleet of transport aircraft, ships, and submarines.

The U.S. military's global reach is also facilitated by its network of alliances and partnerships with other countries. This allows it to access military bases and facilities in key regions, such as Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
Technological Superiority
The U.S. military is at the forefront of military technology, with a range of advanced systems and platforms that give it a significant edge over its adversaries. From stealth fighters and bombers to advanced missile defense systems, the U.S. military has invested heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the curve.

The U.S. military's technological superiority is also reflected in its advanced command and control systems, which enable it to coordinate its operations in real-time and respond quickly to emerging threats.
Professional and Well-Trained Personnel
The U.S. military has a highly professional and well-trained personnel, with a strong tradition of leadership and excellence. From the enlisted ranks to the officer corps, U.S. military personnel are known for their skill, dedication, and sacrifice.

The U.S. military's personnel are also supported by a comprehensive system of education and training, which includes some of the world's top military academies and training institutions.
Logistical and Supply Chain Capabilities
The U.S. military has a highly developed logistical and supply chain system, which enables it to deploy and sustain large-scale operations over long distances. From fuel and ammunition to food and medical supplies, the U.S. military has a global network of logistics hubs and supply chains that keep its troops and equipment running.

The U.S. military's logistical capabilities are also supported by a large fleet of cargo ships, aircraft, and trucks, which enable it to transport goods and equipment quickly and efficiently.
Cyber Warfare Capabilities
The U.S. military has a highly developed cyber warfare capability, which enables it to conduct operations in the cyber domain and defend its networks against cyber threats. From hacking and espionage to disruption and destruction, the U.S. military has a range of cyber tools and techniques at its disposal.

However, the U.S. military also faces a number of weaknesses and challenges, including:
Bureaucratic Inefficiencies
The U.S. military is a large and complex organization, with a bureaucratic system that can be slow to respond to changing circumstances. From procurement and acquisition to personnel management and training, the U.S. military's bureaucracy can be a major obstacle to innovation and reform.

High Operating Costs
The U.S. military is a expensive to operate, with a budget of over $700 billion per year. From fuel and ammunition to personnel costs and equipment maintenance, the U.S. military's operating costs are a significant burden on the taxpayer.
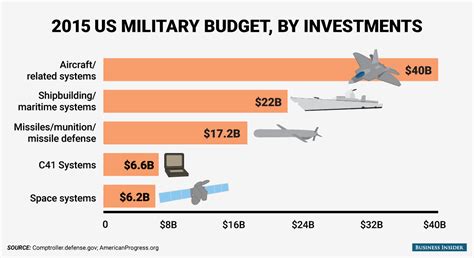
Over-Reliance on Technology
The U.S. military's reliance on advanced technology can be a weakness, as well as a strength. From drones and precision-guided munitions to advanced sensors and communication systems, the U.S. military's technology can be vulnerable to disruption and disablement.

Insufficient Training and Preparation
The U.S. military's personnel are highly trained and professional, but they may not always be prepared for the challenges they face on the battlefield. From counterinsurgency and asymmetric warfare to peacekeeping and humanitarian assistance, the U.S. military's personnel may require specialized training and preparation to operate effectively.

Vulnerability to Emerging Threats
The U.S. military is vulnerable to emerging threats, such as cyber attacks, terrorism, and pandemics. From disruption and disablement to destruction and defeat, the U.S. military must be prepared to respond to a range of emerging threats that can challenge its capabilities and undermine its operations.

In conclusion, the U.S. military is a powerful and technologically advanced armed force, with a range of strengths and weaknesses. From its global reach and power projection capability to its technological superiority and professional personnel, the U.S. military is capable of defending its interests and protecting its allies around the world. However, it also faces a number of challenges and weaknesses, including bureaucratic inefficiencies, high operating costs, over-reliance on technology, insufficient training and preparation, and vulnerability to emerging threats.
U.S. Military Image Gallery










What is the primary mission of the U.S. military?
+The primary mission of the U.S. military is to protect the United States, its citizens, and its interests around the world.
What is the U.S. military's global reach and power projection capability?
+The U.S. military has a global reach and power projection capability that enables it to deploy its troops and equipment quickly and efficiently to any region around the world.
What are some of the U.S. military's key strengths and weaknesses?
+Some of the U.S. military's key strengths include its technological superiority, professional personnel, and logistical capabilities. Some of its key weaknesses include its bureaucratic inefficiencies, high operating costs, over-reliance on technology, insufficient training and preparation, and vulnerability to emerging threats.
