Intro
Discover the US Navy Enlisted Ranks hierarchy, including ratings, pay grades, and insignia, to understand naval career progression and advancement opportunities.
The United States Navy is one of the most prestigious and respected naval forces in the world, with a rich history and a strong tradition of excellence. As a vital part of the US Armed Forces, the Navy plays a critical role in maintaining national security and protecting American interests abroad. For those who serve in the Navy, understanding the enlisted rank structure is essential to navigating the organization and advancing in their careers. In this article, we will delve into the world of US Navy enlisted ranks, exploring the different levels, responsibilities, and requirements for each.
The US Navy enlisted rank structure is designed to provide a clear and logical progression for sailors as they gain experience, develop new skills, and take on additional responsibilities. The ranks are divided into three main categories: junior enlisted, non-commissioned officers (NCOs), and senior enlisted leaders. Each category has its own unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities for advancement. Whether you're just starting out in the Navy or looking to advance to the highest levels of leadership, understanding the enlisted rank structure is crucial to achieving your goals.
As we explore the world of US Navy enlisted ranks, it's essential to recognize the importance of leadership, teamwork, and technical expertise. From the junior enlisted ranks to the senior enlisted leaders, every sailor plays a vital role in the success of the Navy. By understanding the different ranks, responsibilities, and requirements, sailors can better navigate the organization, develop their skills, and achieve their full potential. In the following sections, we will examine each of the US Navy enlisted ranks in detail, providing insights into the roles, responsibilities, and opportunities for advancement.
Junior Enlisted Ranks
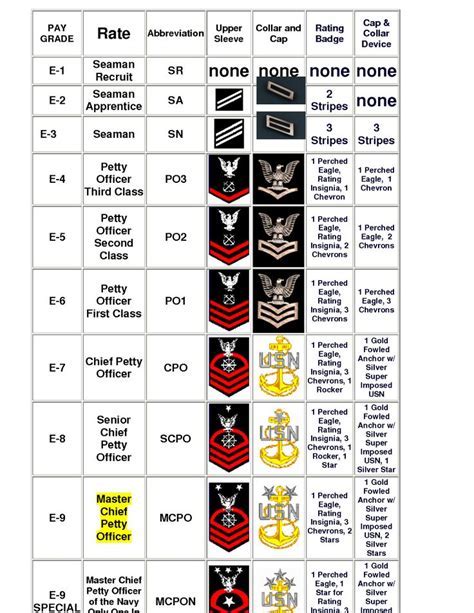
Some of the key responsibilities of junior enlisted sailors include:
- Completing basic training and advanced technical schools
- Learning naval protocols, procedures, and traditions
- Developing technical skills in their chosen rating (job specialty)
- Participating in shipboard operations, maintenance, and repairs
- Collaborating with senior sailors and officers to achieve mission objectives
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs)

Some of the key responsibilities of NCOs include:
- Leading and mentoring junior enlisted sailors
- Developing and implementing training programs
- Providing technical expertise and guidance
- Participating in decision-making processes and problem-solving
- Representing the Navy in official ceremonies and events
Senior Enlisted Leaders

Some of the key responsibilities of senior enlisted leaders include:
- Providing strategic guidance and leadership
- Developing and implementing policies and procedures
- Mentoring and advising junior sailors and officers
- Representing the Navy in high-level meetings and ceremonies
- Participating in decision-making processes at the highest levels
Enlisted Rank Structure
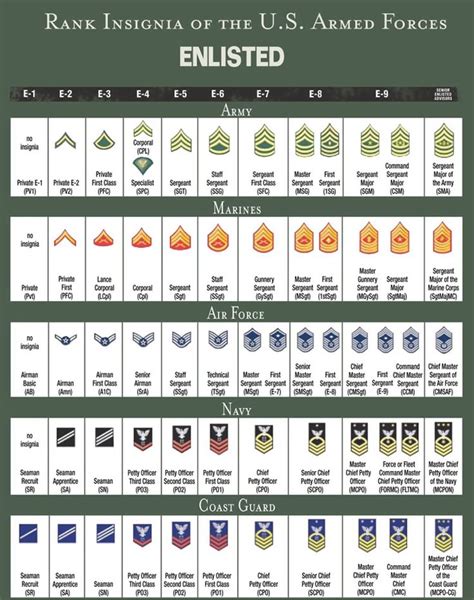
Some of the key factors that influence the enlisted rank structure include:
- Time in service: The amount of time a sailor has served in the Navy
- Time in grade: The amount of time a sailor has spent in their current rank
- Performance evaluations: Regular assessments of a sailor's performance and potential
- Advanced training and education: Completion of specialized courses and degree programs
- Leadership and technical skills: Demonstration of exceptional leadership and technical expertise
Advancement Opportunities

Benefits and Challenges

However, serving in the Navy also comes with challenges, including:
- Deployments and time away from home: Enlisted sailors may be deployed for extended periods, missing important events and milestones with family and friends
- Physical and mental demands: Navy life can be physically and mentally demanding, with sailors facing challenges such as fatigue, stress, and injury
- Limited career flexibility: The Navy's rank structure and career progression can be rigid, limiting flexibility and opportunities for career change
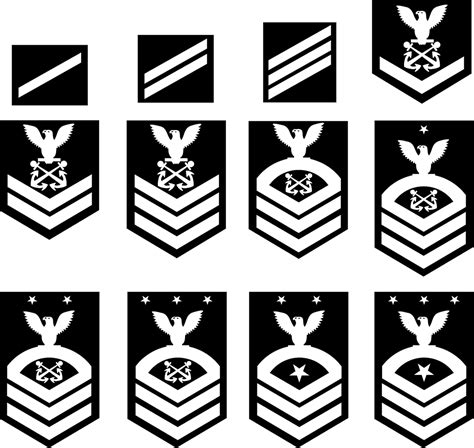
Gallery of US Navy Enlisted Ranks
US Navy Enlisted Ranks Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lowest enlisted rank in the US Navy?
+The lowest enlisted rank in the US Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1).
How do I advance in the US Navy enlisted ranks?
+To advance in the US Navy enlisted ranks, you must meet the requirements for time in service, time in grade, and performance evaluations, and complete advanced training and education.
What is the highest enlisted rank in the US Navy?
+The highest enlisted rank in the US Navy is Command Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
What are the benefits of serving in the US Navy as an enlisted sailor?
+The benefits of serving in the US Navy as an enlisted sailor include competitive pay and benefits, education and training opportunities, travel and adventure, and camaraderie and esprit de corps.
What are the challenges of serving in the US Navy as an enlisted sailor?
+The challenges of serving in the US Navy as an enlisted sailor include deployments and time away from home, physical and mental demands, and limited career flexibility.
As we conclude our exploration of the US Navy enlisted ranks, we hope that you have gained a deeper understanding of the different levels, responsibilities, and requirements for each. Whether you're just starting out in the Navy or looking to advance to the highest levels of leadership, it's essential to recognize the importance of leadership, teamwork, and technical expertise. By understanding the enlisted rank structure and the opportunities and challenges that come with serving in the Navy, you can better navigate the organization, develop your skills, and achieve your full potential. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and explore the many resources available to help you succeed in your Navy career.
