Intro
Discover the pathway to serving your country and community with the US Army National Guard. Learn the 5 ways to join the Army National Guard, including enlistment, officer candidate school, and more. Explore the benefits, requirements, and opportunities for citizenship, education, and career advancement in this esteemed military branch.
Joining the US Army National Guard can be a rewarding and challenging career path for those who want to serve their country while also maintaining a civilian life. With various ways to join, it's essential to understand the different paths to find the one that best suits your needs and goals. In this article, we will explore five ways to join the US Army National Guard.
Why Join the US Army National Guard?
Before we dive into the ways to join, let's take a look at some of the benefits of joining the US Army National Guard:

- Serve your country and community
- Gain valuable skills and training
- Earn education benefits and tuition assistance
- Access to medical and dental care
- Competitive pay and allowances
- Opportunities for advancement and leadership
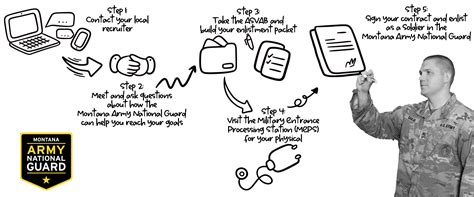
Way 1: Enlist through the National Guard's Enlistment Process
The most common way to join the US Army National Guard is through the enlistment process. To enlist, you must:
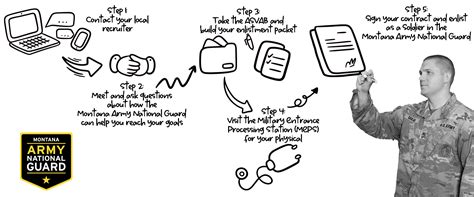
- Meet the eligibility requirements (age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness)
- Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Choose a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS)
- Complete Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
- Sign an enlistment contract
Way 2: Join through the National Guard's Officer Candidate School (OCS)
If you have a bachelor's degree and want to become an officer, you can join the US Army National Guard through the Officer Candidate School (OCS) program:

- Meet the eligibility requirements (age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness)
- Take the ASVAB test
- Apply for OCS
- Complete the OCS program
- Commission as an officer
Way 3: Transfer from Another Military Branch
If you are currently serving in another military branch, you can transfer to the US Army National Guard:

- Meet the eligibility requirements (age, citizenship, and physical fitness)
- Complete the transfer process
- Attend a transfer briefing
- Complete any necessary training
Way 4: Join through the National Guard's Split-Option Program
The Split-Option Program allows high school students to enlist in the US Army National Guard before graduating:
- Meet the eligibility requirements (age, citizenship, and education)
- Take the ASVAB test
- Enlist in the US Army National Guard
- Delay entry into Basic Combat Training (BCT) until after graduation
Way 5: Join through the National Guard's Simultaneous Membership Program (SMP)
The Simultaneous Membership Program (SMP) allows you to join the US Army National Guard while attending college:

- Meet the eligibility requirements (age, citizenship, and education)
- Enlist in the US Army National Guard
- Attend college while serving in the US Army National Guard
- Receive education benefits and tuition assistance
US Army National Guard Image Gallery








What are the eligibility requirements to join the US Army National Guard?
+The eligibility requirements to join the US Army National Guard include age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness requirements.
Can I join the US Army National Guard if I have a felony conviction?
+It is possible to join the US Army National Guard with a felony conviction, but it will depend on the type of conviction and the policies of the state's adjutant general.
How long is the enlistment contract for the US Army National Guard?
+The enlistment contract for the US Army National Guard is typically 6 years, but can vary depending on the type of enlistment and the needs of the National Guard.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the different ways to join the US Army National Guard. Whether you're looking to serve your country, gain valuable skills, or attend college, the US Army National Guard has a path for you.
