Intro
Unlock the requirements for joining the US Army Reserve. Learn about the age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness standards needed to serve. Discover the enlistment process, Military Occupational Specialties, and benefits of reserve service. Get a comprehensive guide to US Army Reserve requirements and start your journey to serving part-time.
The US Army Reserve is a vital part of the country's defense system, providing support to the active Army and responding to domestic emergencies. If you're considering joining the Army Reserve, it's essential to understand the requirements and what to expect from this commitment.
Joining the Army Reserve can be a rewarding experience, offering opportunities for education, training, and personal growth. However, it's crucial to meet the specific requirements and be aware of the responsibilities that come with being a reservist.
Basic Requirements

To be eligible for the Army Reserve, you must meet the following basic requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Be between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Meet the medical and physical fitness standards
- Have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Score a minimum of 31 on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test
- Pass a background check
Physical Fitness Standards
The Army Reserve has strict physical fitness standards, which include:
- Push-ups: 30-40 in 1 minute
- Sit-ups: 30-40 in 1 minute
- 2-mile run: 13-15 minutes
- Body fat percentage: 20-30% for men, 24-36% for women
Enlistment Process
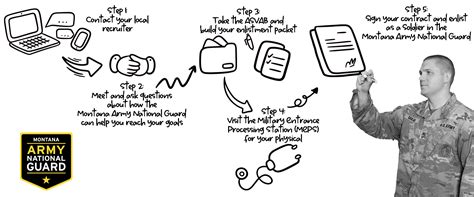
The enlistment process for the Army Reserve involves the following steps:
- Meet with a recruiter: Discuss your qualifications, interests, and career goals with a recruiter to determine the best Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) for you.
- Take the ASVAB test: The ASVAB test measures your aptitude in various subjects, such as math, science, and language.
- Complete the enlistment paperwork: Fill out the necessary forms, including the enlistment contract and medical questionnaire.
- Take the physical fitness test: Demonstrate your physical fitness by completing the push-ups, sit-ups, and 2-mile run.
- Receive a medical examination: A medical professional will evaluate your health and fitness for service.
- Attend Basic Combat Training (BCT): Complete BCT, which includes training in combat skills, first aid, and Army protocol.
- Attend Advanced Individual Training (AIT): Receive specialized training in your chosen MOS.
Training and Drills
As an Army Reserve soldier, you'll be required to attend training and drills regularly. This includes:
- One weekend a month (known as a "drill weekend") for training and exercises
- Two weeks a year (known as "annual training") for more extensive training and exercises
Education Benefits

The Army Reserve offers various education benefits, including:
- Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR): Up to 36 months of education benefits
- Army Reserve Tuition Assistance: Up to 100% tuition assistance for college courses
- Student Loan Repayment Program: Up to $65,000 in student loan repayment
Deployment and Mobilization
As an Army Reserve soldier, you may be deployed or mobilized to support active duty missions or respond to domestic emergencies. This can include:
- Deployment to combat zones or humanitarian missions
- Mobilization to support disaster relief or homeland security
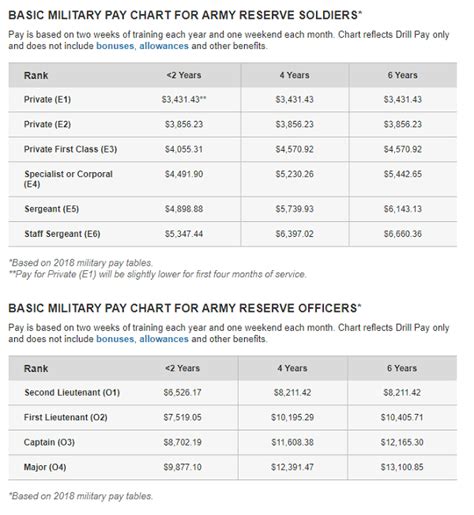
Benefits and Pay

Army Reserve soldiers receive various benefits and pay, including:
- Basic pay: Based on rank and time in service
- Drill pay: For attending drill weekends and annual training
- Special pay: For specialized skills or hazardous duty
- Benefits: Including medical, dental, and vision insurance, as well as access to base facilities and services
Rank Structure
The Army Reserve uses the same rank structure as the active duty Army, with the following ranks:
- Private (E-1) to Private First Class (E-3)
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4) to Sergeant (E-5)
- Staff Sergeant (E-6) to Sergeant First Class (E-7)
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8) to Sergeant Major (E-9)
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1) to Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5)
- Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10)
Conclusion
Joining the Army Reserve requires a significant commitment, but it can also provide valuable skills, education, and personal growth. By understanding the requirements and benefits, you can make an informed decision about serving in the Army Reserve.
Now that you've read this comprehensive guide, take the next step and explore the opportunities available in the Army Reserve.
Gallery of Army Reserve Images
Army Reserve Image Gallery





FAQs
What are the basic requirements for joining the Army Reserve?
+The basic requirements include being a US citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, meeting medical and physical fitness standards, having a high school diploma or equivalent, scoring a minimum of 31 on the ASVAB test, and passing a background check.
What is the enlistment process for the Army Reserve?
+The enlistment process involves meeting with a recruiter, taking the ASVAB test, completing the enlistment paperwork, taking the physical fitness test, receiving a medical examination, attending Basic Combat Training (BCT), and attending Advanced Individual Training (AIT).
What are the education benefits available to Army Reserve soldiers?
+The education benefits include the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR), Army Reserve Tuition Assistance, and the Student Loan Repayment Program.

