Intro
Explore the 7 US Navy ranks, from junior to senior, including enlisted and officer ranks, with details on navy rank structure, insignia, and career progression.
The United States Navy is one of the most prestigious and respected naval forces in the world, with a rich history dating back to 1775. The Navy plays a vital role in protecting American interests and maintaining global security. One of the key factors that contribute to the Navy's success is its well-structured ranking system, which provides a clear hierarchy and chain of command. In this article, we will delve into the world of US Navy ranks, exploring the different levels, responsibilities, and requirements.
The US Navy ranking system is divided into three main categories: enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer. Each category has its own set of ranks, with varying levels of responsibility and authority. Understanding the different Navy ranks is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in the Navy or simply wanting to learn more about this esteemed institution.
The Navy's ranking system is designed to provide a clear and efficient chain of command, with each rank having its own unique responsibilities and duties. From the entry-level ranks to the highest positions of command, every sailor plays a vital role in the Navy's mission to protect and serve. Whether you're interested in becoming a Navy SEAL, a pilot, or a member of the ship's crew, understanding the ranking system is crucial for success.
As we explore the world of US Navy ranks, we will examine the different levels, from the lowest to the highest, and discuss the responsibilities, requirements, and benefits associated with each rank. We will also look at the various career paths available to Navy personnel, including enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer careers. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the US Navy ranking system and the opportunities available to those who serve.
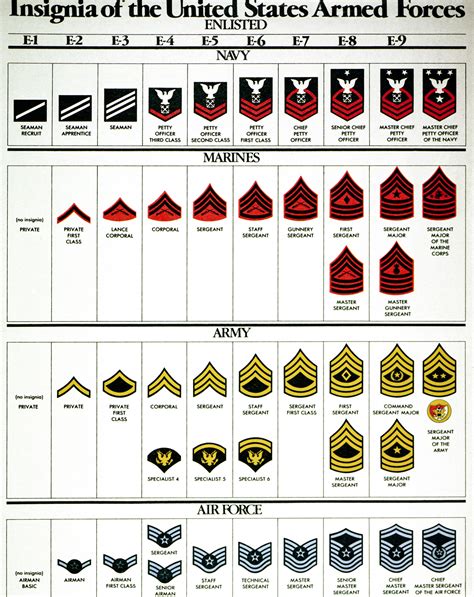
Enlisted Ranks

Some of the key enlisted ranks in the Navy include:
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The entry-level rank for new recruits.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): A junior rank that requires completion of basic training and a certain level of proficiency in their job.
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): A non-commissioned officer rank that requires significant experience and expertise in their field.
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): A senior enlisted rank that requires a high level of leadership and technical expertise.
Warrant Officer Ranks
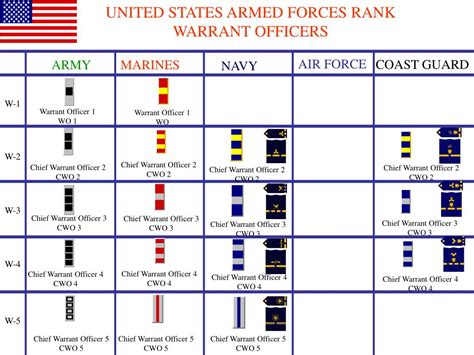
Some of the key warrant officer ranks in the Navy include:
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): The entry-level rank for warrant officers.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): A junior warrant officer rank that requires significant experience and expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): A senior warrant officer rank that requires advanced knowledge and leadership skills.
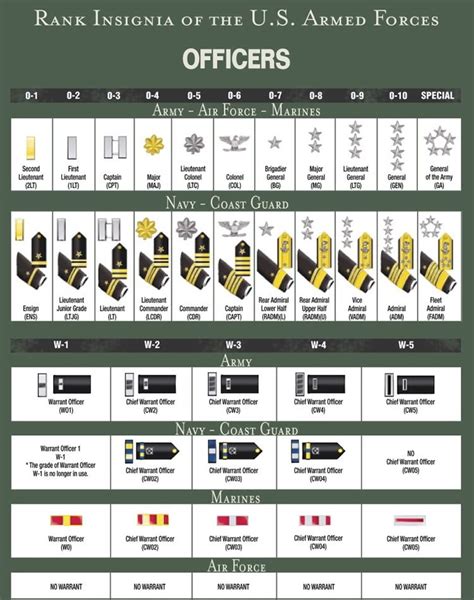
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Some of the key commissioned officer ranks in the Navy include:
- Ensign (O-1): The entry-level rank for commissioned officers.
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2): A junior commissioned officer rank that requires significant experience and leadership skills.
- Captain (O-6): A senior commissioned officer rank that requires advanced knowledge, leadership skills, and strategic thinking.
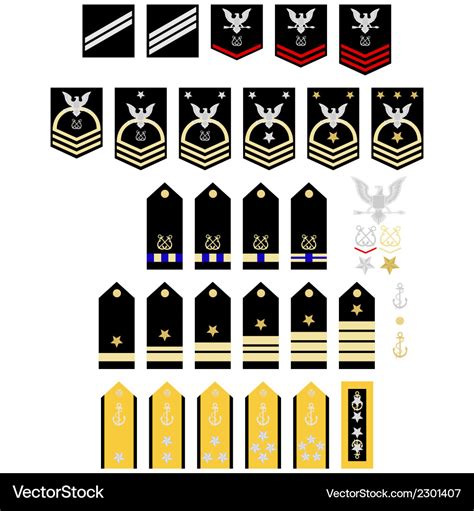
Navy Rank Insignia
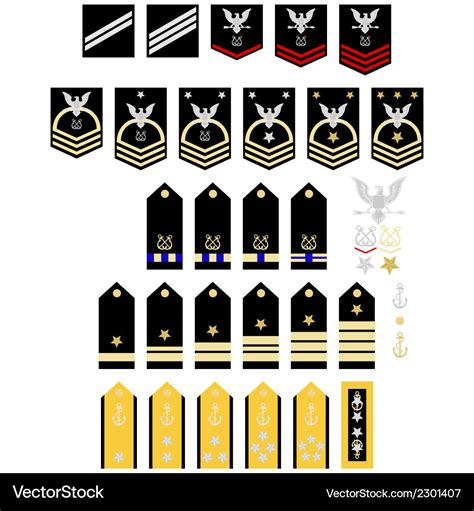
Some of the key Navy rank insignia include:
- Enlisted rank insignia: These are worn by enlisted personnel and reflect their level of experience and expertise.
- Warrant officer rank insignia: These are worn by warrant officers and reflect their technical expertise and authority.
- Commissioned officer rank insignia: These are worn by commissioned officers and reflect their level of responsibility and leadership authority.
Navy Career Paths

Navy Education and Training

Navy Benefits

Navy Ranks Image Gallery







What are the different types of Navy ranks?
+The Navy has three main types of ranks: enlisted, warrant officer, and commissioned officer. Each type of rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements.
What is the highest rank in the Navy?
+The highest rank in the Navy is Admiral (O-10), which is a four-star rank that requires significant experience and leadership skills.
How do I become a Navy officer?
+To become a Navy officer, you must meet the eligibility requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. You must also complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy, and receive a commission as an officer.
What are the benefits of joining the Navy?
+The Navy offers a wide range of benefits, including competitive pay and allowances, comprehensive healthcare and education benefits, and opportunities for career advancement and personal growth.
How long does it take to become a Navy officer?
+The time it takes to become a Navy officer varies depending on the individual's circumstances and the path they choose. Typically, it takes around 4-6 years to complete a bachelor's degree and receive a commission as an officer.
In conclusion, the US Navy ranking system is a complex and fascinating topic that plays a critical role in the Navy's operations and success. Understanding the different ranks, responsibilities, and requirements is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in the Navy or simply wanting to learn more about this esteemed institution. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the US Navy ranking system and the opportunities available to those who serve. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
