Intro
Unveil the mysteries of North Koreas Hermit Kingdom with our in-depth background guide. Explore the countrys isolationist policies, authoritarian regime, and socialist ideology. Discover how its complex history, from Japanese colonial rule to the Korean War, has shaped the nations unique culture and economy, making it one of the most enigmatic states in the world.

North Korea, officially known as the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), has long been a subject of fascination and intrigue for the international community. The country's reclusive nature, authoritarian government, and mysterious policies have led to its nickname, the "Hermit Kingdom." In this article, we will delve into the background of North Korea's isolationist stance, explore the historical events that have shaped the country's current situation, and examine the implications of its policies on the global stage.
Early History and the Korean Peninsula
To understand North Korea's Hermit Kingdom background, it is essential to look at the country's early history and the Korean Peninsula's complex past. The Korean Peninsula has been inhabited since the Paleolithic era, with various dynasties and kingdoms rising and falling over the centuries. In the 20th century, Korea was colonized by Japan from 1910 to 1945, which had a profound impact on the country's development and its people's identity.
After Japan's defeat in World War II, the Korean Peninsula was divided along the 38th parallel, with the Soviet Union occupying the north and the United States occupying the south. This division ultimately led to the establishment of two separate governments: the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) in the north and the Republic of Korea (South Korea) in the south.
Kim Il-sung and the Founding of North Korea
North Korea was founded on September 9, 1948, with Kim Il-sung as its first leader. Kim Il-sung, also known as the "Great Leader," was a key figure in the country's early history and played a crucial role in shaping its ideology and policies. He established a socialist government, aligned with the Soviet Union, and implemented a series of economic and social reforms aimed at rapid industrialization and modernization.
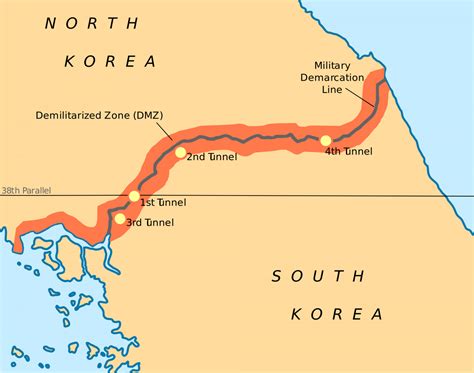
Under Kim Il-sung's leadership, North Korea became increasingly isolated from the rest of the world. The country's government tightly controlled the flow of information, and its citizens were largely cut off from external influences. This isolationist stance was reinforced by the country's geography, with the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) separating North and South Korea and the rugged terrain making it difficult to access.

The Rise of Juche and Self-Reliance
In the 1950s and 1960s, North Korea began to develop its unique ideology, known as Juche, which emphasizes self-reliance and independence. Juche, which translates to "self-reliance" or "independence," became the cornerstone of North Korea's foreign policy and its approach to economic development.
Juche is based on the idea that a country should rely on its own resources and capabilities to achieve prosperity and security, rather than relying on external aid or influence. This ideology has been used to justify North Korea's isolationist stance and its refusal to engage with the international community.
Nuclear Program and International Sanctions
In the 1990s, North Korea began to develop its nuclear program, which has been a major source of tension with the international community. The country's nuclear tests, including the first test in 2006, have led to widespread condemnation and the imposition of international sanctions.
The sanctions, which target North Korea's nuclear program and its leadership, have had a significant impact on the country's economy and its people's standard of living. However, the sanctions have not deterred North Korea from pursuing its nuclear ambitions, and the country remains a major security concern for the region and the world.

Kim Jong-il and the Consolidation of Power
In 1994, Kim Il-sung died, and his son, Kim Jong-il, succeeded him as the leader of North Korea. Kim Jong-il, also known as the "Dear Leader," consolidated power and continued to implement his father's policies.
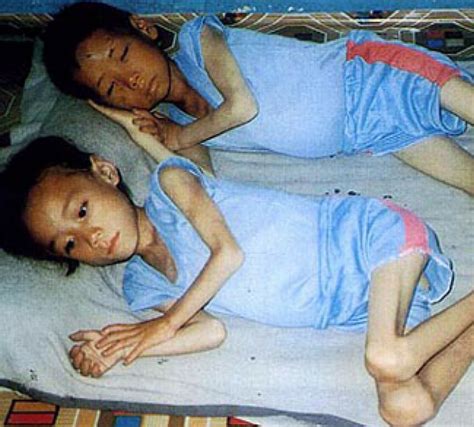
During Kim Jong-il's rule, North Korea's economy continued to decline, and the country faced widespread famine and poverty. However, the country's nuclear program made significant progress, and North Korea became a major security concern for the region and the world.
Kim Jong-un and the Current Situation
In 2011, Kim Jong-il died, and his son, Kim Jong-un, succeeded him as the leader of North Korea. Kim Jong-un, who is still in his 30s, has continued to implement his father's and grandfather's policies, including the development of the country's nuclear program.
Under Kim Jong-un's leadership, North Korea has continued to test its nuclear capabilities, and the country has become increasingly isolated from the rest of the world. The country's economy remains in decline, and its people continue to face widespread poverty and human rights abuses.

Implications and Future Prospects
North Korea's Hermit Kingdom background has significant implications for the international community. The country's nuclear program and its isolationist stance pose a major security concern for the region and the world.
In recent years, there have been efforts to engage with North Korea, including diplomatic efforts by the United States and South Korea. However, these efforts have been met with skepticism, and the country's leadership remains committed to its nuclear program.
As the international community continues to grapple with the challenges posed by North Korea, it is essential to understand the country's history, ideology, and policies. By doing so, we can better appreciate the complexities of the situation and develop effective strategies to address the security concerns posed by the Hermit Kingdom.
North Korea's Hermit Kingdom Image Gallery




What is the origin of the term "Hermit Kingdom"?
+The term "Hermit Kingdom" was first used to describe North Korea's isolationist stance and its refusal to engage with the international community.
Who was Kim Il-sung?
+Kim Il-sung was the founder and first leader of North Korea. He played a crucial role in shaping the country's ideology and policies.
What is Juche?
+Juche is North Korea's unique ideology, which emphasizes self-reliance and independence. It has been used to justify the country's isolationist stance and its refusal to engage with the international community.
As we conclude our exploration of North Korea's Hermit Kingdom background, we hope that you have gained a deeper understanding of the country's complex history, ideology, and policies. We invite you to share your thoughts and insights on this topic and to continue the conversation on the challenges posed by the Hermit Kingdom.
