Intro
Discover the specifications of the 5.56 caliber, a popular rifle cartridge used in firearms like the AR-15. Learn about its origins, dimensions, and ballistic performance, as well as its relationship to the.223 Remington. Understand the differences between 5.56 NATO and.223 Rem, and explore the applications of this versatile caliber.
The 5.56mm cartridge has become one of the most widely used and recognizable ammunition types in the world, primarily due to its adoption by various military forces, particularly in the United States. Its use in the M16 and M4 rifles, among others, has cemented its place in modern firearms. But what exactly is the 5.56mm, and how does it compare to other calibers?
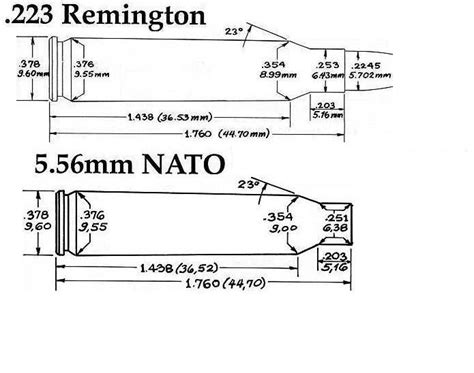
To understand the 5.56mm, it's essential to grasp the basics of firearm calibers and how they're measured. In firearms, caliber refers to the internal diameter of a gun barrel. It's measured in inches or millimeters, with the latter being more common for smaller calibers like the 5.56mm. The 5.56mm is part of the metric system, where the caliber is directly expressed in millimeters. However, it's crucial to note that this measurement doesn't directly reflect the bullet's actual diameter due to the use of rifling in the barrel, which engages the bullet's grooves.
Origins and Development
The 5.56mm cartridge was developed in the 1950s as a smaller and lighter alternative to the 7.62mm NATO cartridge, which was the standard at the time. The initial goal was to create a cartridge that could be fired from a lighter and more compact rifle, allowing soldiers to carry more ammunition without significantly increasing the overall weight of their equipment.

The development of the 5.56mm involved a collaboration between Winchester and the U.S. military. The first commercial version of this cartridge was marketed by Winchester as the.223 Remington, with the ".223" referring to the bullet's diameter in inches. However, the 5.56mm NATO and.223 Remington, while similar, have some key differences, especially in terms of pressure standards.
Key Specifications
-
Bullet Diameter: The bullet diameter of the 5.56mm is actually.224 inches (5.69 mm), not 5.56mm. The difference in naming convention can be confusing, but it reflects the measurements taken at different points along the cartridge.
-
Case Length: The case length of the 5.56mm is 44.70 mm.
-
Rim Diameter: The rim diameter is 9.60 mm.
-
Rifling: The 5.56mm barrel typically has a rifling twist rate of 1:7 to 1:9 inches, which is designed to stabilize the long, lightweight bullets.
Ballistic Performance
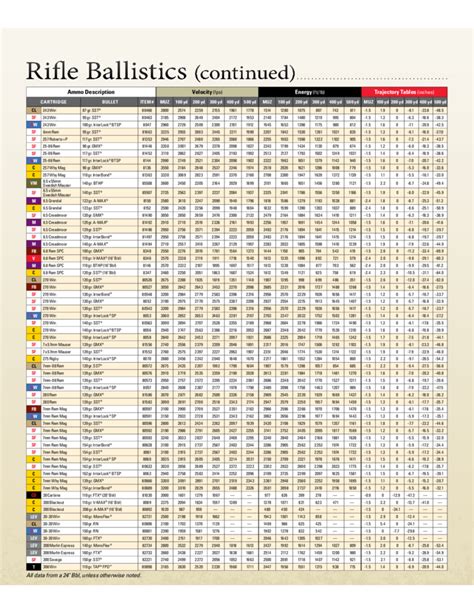
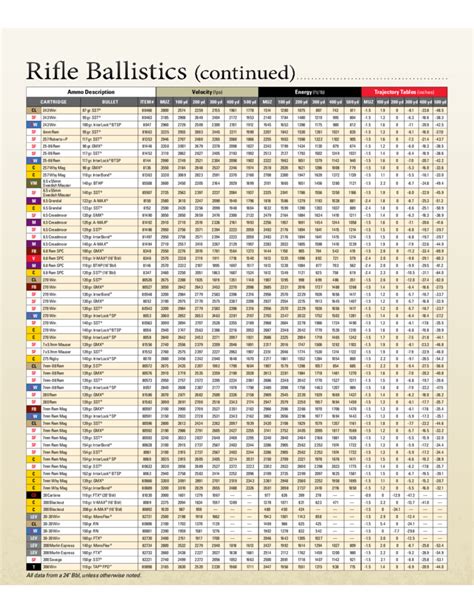
The 5.56mm is known for its flat trajectory and high velocity. When fired from a typical military rifle barrel (about 20 inches long), it achieves muzzle velocities of approximately 3,000 feet per second (914 meters per second). The effective range for a rifle firing 5.56mm ammunition can extend beyond 500 meters, although the practical range for accurate engagement is typically much shorter.
Ammunition Types
The 5.56mm ammunition comes in various types, including:
- Full Metal Jacket (FMJ): FMJ bullets are the most common type and are used for target practice and combat.
- Hollow Point (HP): HP bullets are designed to expand upon impact, increasing stopping power.
- Armor Piercing (AP): AP bullets are hardened to penetrate light armor.
- Tracer: Tracer bullets are tipped with a pyrotechnic material that burns during flight, allowing the trajectory to be seen.
Comparison to Other Calibers

The 5.56mm is often compared to the 7.62mm NATO, its predecessor, and the.300 Blackout, a more recent development designed for use in both rifles and pistols. The.300 Blackout offers better performance at subsonic velocities, making it a favorite among users requiring suppressor capability.
.223 Remington vs. 5.56mm NATO
While the.223 Remington and 5.56mm NATO are similar, they have some differences. The 5.56mm NATO has a slightly longer headspace (the distance from the breech face to where the cartridge headspaces) than the.223 Remington. This means that firearms chambered for 5.56mm can safely fire.223 Remington ammunition, but the reverse is not necessarily true due to potential overpressure issues.
Gallery of 5.56mm Firearms and Ammunition
5.56mm Firearms and Ammunition









What is the effective range of 5.56mm ammunition?
+The effective range for accurate engagement with 5.56mm ammunition can vary depending on the barrel length, rifling twist, and type of ammunition used. Generally, the effective range is considered to be up to 500 meters, but the practical range for most shooters will be much shorter.
Can I fire 5.56mm NATO in a rifle chambered for.223 Remington?
+No, it's not recommended to fire 5.56mm NATO ammunition in a rifle chambered for.223 Remington due to potential overpressure issues. However, rifles chambered for 5.56mm can safely fire.223 Remington ammunition.
What is the difference between FMJ and HP bullets in 5.56mm?
+FMJ (Full Metal Jacket) bullets are completely encased in a copper jacket and are designed for target practice and combat, penetrating deep into the target without expanding. HP (Hollow Point) bullets, on the other hand, have a hollow tip that allows them to expand upon impact, increasing stopping power and reducing the risk of overpenetration.
Whether you're a seasoned veteran or just starting to explore the world of firearms, understanding the specifications and performance of the 5.56mm caliber can enhance your appreciation for the precision and complexity of modern ammunition. With its lightweight and high-velocity characteristics, the 5.56mm has solidified its place in military and civilian use worldwide.
