Intro
Discover the 5 key roles of case workers, from assessment and planning to implementation and evaluation. Learn how case workers navigate complex social situations, collaborate with clients and stakeholders, and prioritize empathy and advocacy. Explore the multifaceted responsibilities of case workers in social services, healthcare, and non-profit sectors.
Case workers play a vital role in various fields, including social work, healthcare, and non-profit organizations. They are the primary point of contact between clients and service providers, ensuring that individuals receive the necessary support and resources to overcome challenges. In this article, we will explore the 5 key roles of case workers, highlighting their responsibilities, skills, and impact on clients' lives.
Understanding the Role of a Case Worker
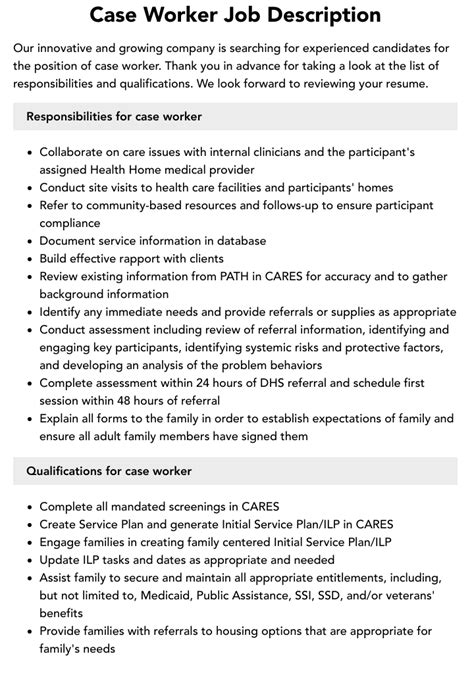
Before diving into the key roles of case workers, it is essential to understand their primary function. Case workers are responsible for assessing clients' needs, developing personalized plans, and connecting them with relevant services and resources. Their ultimate goal is to empower clients to achieve self-sufficiency, stability, and overall well-being.
Role 1: Assessment and Intake
Assessment and Intake
One of the primary roles of case workers is to conduct assessments and intake processes. This involves gathering information about clients' background, needs, and circumstances to determine the best course of action. Case workers use various assessment tools and techniques to identify clients' strengths, weaknesses, and goals.
During the intake process, case workers establish a rapport with clients, build trust, and create a safe and non-judgmental environment. This is crucial in helping clients feel comfortable sharing sensitive information and collaborating with the case worker to develop a personalized plan.
Role 2: Case Planning and Goal Setting
Case Planning and Goal Setting
Once the assessment and intake process are complete, case workers develop a comprehensive case plan that outlines clients' goals, objectives, and strategies for achieving success. This plan is tailored to each client's unique needs and circumstances, taking into account their strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations.
Case workers work closely with clients to set realistic goals, prioritize tasks, and establish a timeline for achieving milestones. This collaborative approach ensures that clients are invested in the planning process and committed to achieving their goals.
Role 3: Service Coordination and Referral
Service Coordination and Referral
Another critical role of case workers is to coordinate services and refer clients to relevant resources. This involves connecting clients with community organizations, healthcare providers, educational institutions, and other service providers that can help them achieve their goals.
Case workers act as liaisons between clients and service providers, ensuring that clients receive seamless and comprehensive support. They also advocate on behalf of clients, helping to overcome barriers and challenges that may hinder their progress.
Role 4: Ongoing Support and Monitoring
Ongoing Support and Monitoring

Case workers provide ongoing support and monitoring to ensure that clients are progressing towards their goals. This involves regular check-ins, progress evaluations, and adjustments to the case plan as needed.
Case workers also help clients develop coping skills, manage stress, and build resilience. They provide emotional support, guidance, and encouragement, empowering clients to take control of their lives and make positive changes.
Role 5: Evaluation and Termination
Evaluation and Termination
The final role of case workers is to evaluate the effectiveness of the case plan and terminate services when clients have achieved their goals. This involves assessing the client's progress, identifying areas for improvement, and determining whether the case plan needs to be revised or terminated.
Case workers also help clients develop a plan for sustaining their progress after services are terminated. This may involve connecting clients with community resources, providing education and training, and offering ongoing support and guidance.
Gallery of Case Worker Roles
Case Worker Roles Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary role of a case worker?
+The primary role of a case worker is to assess clients' needs, develop personalized plans, and connect them with relevant services and resources.
What skills do case workers need to be effective?
+Case workers need strong communication, assessment, and problem-solving skills. They must also be empathetic, non-judgmental, and culturally sensitive.
How do case workers evaluate the effectiveness of their services?
+Case workers evaluate the effectiveness of their services by assessing clients' progress, identifying areas for improvement, and revising the case plan as needed.
In conclusion, case workers play a vital role in supporting clients across various fields. By understanding the 5 key roles of case workers – assessment and intake, case planning and goal setting, service coordination and referral, ongoing support and monitoring, and evaluation and termination – we can appreciate the complexity and importance of their work. If you're interested in learning more about case worker roles and responsibilities, we encourage you to explore our resources and engage with our community.
