Intro
Unlock the secrets of genetic code with a geneticists expertise. Explore the 5 key roles of a geneticist, from diagnosis and treatment to research and development. Discover how geneticists analyze DNA sequences, develop gene therapies, and decode the human genome to combat genetic disorders and improve human health, incorporating genomics, biotechnology, and molecular biology.
Geneticists play a crucial role in understanding the complexities of genetics and its applications in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and research. The field of genetics has grown exponentially over the years, and the demand for skilled geneticists has increased significantly. In this article, we will explore the 5 key roles of a geneticist and the significance of their work.
Understanding Genetics
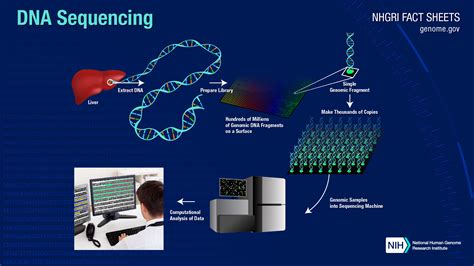
Before we dive into the roles of a geneticist, it's essential to understand what genetics is all about. Genetics is the study of heredity, genes, and variation. It involves the analysis of the structure, function, and evolution of genes and their interactions with the environment. Geneticists use various techniques, including DNA sequencing, genotyping, and gene editing, to understand the genetic basis of traits and diseases.
Role 1: Research and Development

Geneticists play a vital role in research and development, working to understand the genetic basis of various diseases and traits. They design and conduct experiments to identify genetic variants associated with diseases, develop new genetic tests, and create gene therapies. Their work has led to the development of new treatments and therapies for genetic disorders, such as gene editing technologies like CRISPR.
Role 2: Clinical Genetics
Clinical Genetics
Geneticists work in clinical settings, such as hospitals and genetic clinics, to diagnose and manage genetic disorders. They analyze genetic data to identify genetic mutations and interpret the results to provide patients with accurate diagnoses and treatment options. Clinical geneticists also provide genetic counseling to patients and their families, helping them understand the risks and implications of genetic disorders.
Role 3: Genetic Counseling

Genetic counselors work with patients and their families to provide information and support related to genetic disorders. They assess the risk of genetic disorders, provide information on genetic testing, and help patients make informed decisions about their reproductive options. Genetic counselors also provide emotional support and counseling to patients and their families, helping them cope with the diagnosis and management of genetic disorders.
Role 4: Forensic Genetics
Forensic Genetics
Forensic geneticists apply genetic principles to analyze DNA evidence in criminal investigations. They examine DNA samples from crime scenes, victims, and suspects to identify matches and help solve crimes. Forensic geneticists also develop new techniques and methods for DNA analysis, working to improve the accuracy and efficiency of forensic testing.
Role 5: Agricultural Genetics

Agricultural geneticists work to improve crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content. They use genetic techniques, such as gene editing and marker-assisted selection, to develop new crop varieties and improve existing ones. Agricultural geneticists also work to understand the genetic basis of plant traits, such as drought tolerance and pest resistance, to develop more sustainable and resilient crops.
Gallery of Genetics
Genetics Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a geneticist?
+A geneticist is a scientist who studies the structure, function, and evolution of genes and their interactions with the environment. They work in various fields, including research, clinical genetics, genetic counseling, forensic genetics, and agricultural genetics.
What are the different types of geneticists?
+There are several types of geneticists, including research geneticists, clinical geneticists, genetic counselors, forensic geneticists, and agricultural geneticists. Each type of geneticist has a unique role and works in a specific field.
What is the importance of genetics in medicine?
+Genetics plays a crucial role in medicine, as it helps us understand the genetic basis of diseases and develop new treatments and therapies. Genetic testing and counseling also help patients and their families make informed decisions about their health.
In conclusion, geneticists play a vital role in understanding the complexities of genetics and its applications in various fields. Their work has led to significant advances in medicine, agriculture, and forensic science. As the field of genetics continues to evolve, the demand for skilled geneticists will only increase, making it an exciting and rewarding career choice for those passionate about genetics and its applications.
