Intro
Discover the diverse roles and responsibilities of infantry units in modern warfare. Learn about the key duties, skills, and specialties required for success on the battlefield, from combat and tactics to logistics and leadership. Understand the complexities of infantry operations and the crucial contributions they make to military victories.
The infantry is the backbone of any military force, playing a crucial role in ground combat operations. Infantry units are responsible for conducting a wide range of missions, from defensive operations to offensive maneuvers, and from urban warfare to rural patrols. In this article, we will delve into the infantry roles and responsibilities, exploring the various tasks and duties that infantrymen perform.
Infantry Roles and Responsibilities
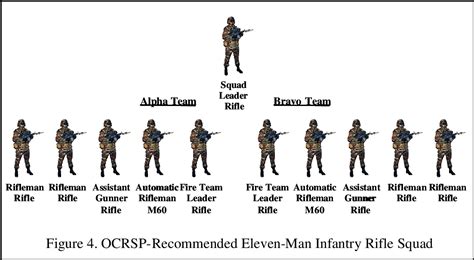
Infantry units are composed of foot soldiers who are trained to engage in close combat with the enemy. Their primary role is to seize and hold territory, conduct patrols, and gather intelligence on enemy forces. Infantrymen are also responsible for conducting urban warfare operations, such as clearing buildings and streets, and conducting counterinsurgency operations.
Combat Operations
Infantry units are trained to conduct a variety of combat operations, including:
- Offensive operations: Infantry units are trained to conduct offensive operations, such as assaults and attacks, to seize key terrain and destroy enemy forces.
- Defensive operations: Infantry units are also trained to conduct defensive operations, such as establishing defensive positions and conducting counterattacks, to protect friendly forces and territory.
- Urban warfare: Infantry units are trained to conduct urban warfare operations, such as clearing buildings and streets, to seize control of urban areas.
- Counterinsurgency operations: Infantry units are trained to conduct counterinsurgency operations, such as conducting patrols and gathering intelligence, to disrupt and defeat insurgent forces.
Infantry Skills and Training

Infantrymen receive extensive training in a variety of skills, including:
- Marksmanship: Infantrymen are trained in marksmanship, including the use of rifles, machine guns, and other small arms.
- First aid: Infantrymen are trained in first aid, including the treatment of wounds and injuries.
- Combat tactics: Infantrymen are trained in combat tactics, including the use of cover and concealment, and the conduct of patrols and ambushes.
- Map reading: Infantrymen are trained in map reading, including the use of maps and compasses to navigate.
- Communication: Infantrymen are trained in communication, including the use of radios and other communication equipment.
Infantry Equipment and Vehicles
Infantry units use a variety of equipment and vehicles, including:
- Small arms: Infantrymen use small arms, such as rifles and machine guns, to engage the enemy.
- Body armor: Infantrymen wear body armor, including helmets and flak jackets, to protect themselves from injury.
- Communication equipment: Infantrymen use communication equipment, such as radios and satellite phones, to communicate with other units.
- Vehicles: Infantry units use vehicles, such as trucks and armored personnel carriers, to transport troops and equipment.
Infantry Unit Structure
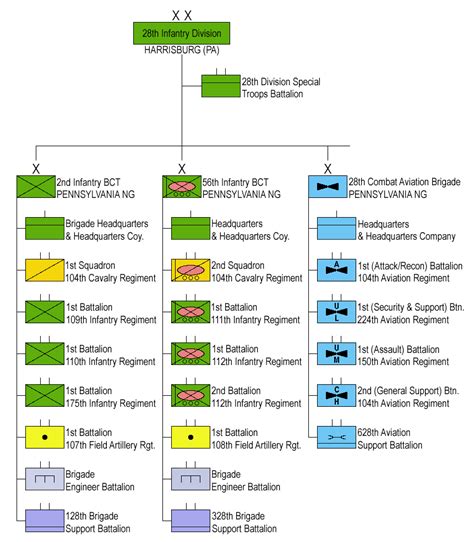
Infantry units are organized into a variety of structures, including:
- Squads: Infantry units are typically organized into squads, which consist of 9-12 soldiers.
- Platoons: Squads are organized into platoons, which consist of 3-4 squads.
- Companies: Platoons are organized into companies, which consist of 3-4 platoons.
- Battalions: Companies are organized into battalions, which consist of 3-4 companies.
Infantry Leadership
Infantry units are led by a variety of leaders, including:
- Squad leaders: Squad leaders are responsible for leading squads and making tactical decisions.
- Platoon leaders: Platoon leaders are responsible for leading platoons and making operational decisions.
- Company commanders: Company commanders are responsible for leading companies and making strategic decisions.
- Battalion commanders: Battalion commanders are responsible for leading battalions and making operational decisions.
Challenges Facing Infantry Units

Infantry units face a variety of challenges, including:
- Urban warfare: Infantry units face unique challenges in urban warfare, including the use of civilians as human shields and the difficulty of navigating complex urban terrain.
- Counterinsurgency operations: Infantry units face challenges in counterinsurgency operations, including the difficulty of distinguishing between friend and foe and the need to win the hearts and minds of local populations.
- Asymmetric warfare: Infantry units face challenges in asymmetric warfare, including the use of unconventional tactics and the difficulty of anticipating enemy actions.
Future of Infantry Units
The future of infantry units is likely to be shaped by a variety of factors, including:
- Technological advancements: Advances in technology, such as the use of drones and robotics, are likely to change the nature of infantry operations.
- Changing nature of warfare: The changing nature of warfare, including the rise of urban warfare and counterinsurgency operations, is likely to require infantry units to adapt and evolve.
- Emerging threats: Emerging threats, such as the use of cyber warfare and electronic warfare, are likely to require infantry units to develop new skills and capabilities.
Infantry Roles and Responsibilities Image Gallery








What is the primary role of infantry units?
+The primary role of infantry units is to seize and hold territory, conduct patrols, and gather intelligence on enemy forces.
What skills do infantrymen receive training in?
+Infantrymen receive training in a variety of skills, including marksmanship, first aid, combat tactics, map reading, and communication.
What are the challenges facing infantry units in urban warfare?
+Infantry units face unique challenges in urban warfare, including the use of civilians as human shields and the difficulty of navigating complex urban terrain.
In conclusion, infantry units play a crucial role in ground combat operations, and their roles and responsibilities are diverse and complex. From conducting combat operations to providing security and support, infantrymen are the backbone of any military force. As the nature of warfare continues to evolve, it is likely that infantry units will continue to adapt and evolve to meet new challenges and threats.
