Intro
Unlock the secrets of military strategy with our in-depth exploration of the 5 roles of military intelligence. From predictive analysis to cyber operations, discover how intel informs decision-making, supports battlefield awareness, and ensures information superiority. Learn how military intelligence agencies leverage human sources, signals intelligence, and more to stay ahead.
The importance of military intelligence cannot be overstated. It is the backbone of any successful military operation, providing critical information that informs strategic decisions and ultimately saves lives. The role of military intelligence is multifaceted, and its impact is felt across various aspects of modern warfare. In this article, we will delve into the five key roles of military intelligence, exploring their significance and the ways in which they contribute to military effectiveness.
Role 1: Information Gathering and Analysis

Military intelligence plays a crucial role in gathering and analyzing information about potential adversaries. This involves collecting data from various sources, including human intelligence (HUMINT), signals intelligence (SIGINT), and geospatial intelligence (GEOINT). The collected data is then analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats. This information is used to inform military planning, identify vulnerabilities, and develop effective countermeasures.
Types of Intelligence Gathering
There are several types of intelligence gathering, including:
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): Gathering information from human sources, such as interviews, interrogations, and surveillance.
- Signals Intelligence (SIGINT): Intercepting and analyzing signals, such as communications and radar emissions.
- Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT): Analyzing satellite and aerial imagery to gather information about terrain, weather, and enemy positions.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): Gathering information from publicly available sources, such as social media and news outlets.
Role 2: Strategic Planning and Decision-Making

Military intelligence plays a critical role in strategic planning and decision-making. The information gathered and analyzed by military intelligence is used to inform military planning, identify potential threats, and develop effective countermeasures. This information is used to support strategic decisions, such as where to deploy troops, how to allocate resources, and when to engage in combat.
The Importance of Accurate Intelligence
Accurate intelligence is essential for effective strategic planning and decision-making. Inaccurate or incomplete intelligence can lead to poor decision-making, which can have disastrous consequences on the battlefield. Military intelligence must be accurate, reliable, and timely to support effective strategic planning and decision-making.
Role 3: Operational Support

Military intelligence provides critical support to military operations. This includes providing real-time intelligence to commanders, identifying potential threats, and developing effective countermeasures. Military intelligence also supports military operations by providing information on enemy positions, movements, and intentions.
Types of Operational Support
There are several types of operational support provided by military intelligence, including:
- Real-time intelligence: Providing real-time information to commanders to support military operations.
- Targeting: Identifying and prioritizing targets for military action.
- Battle damage assessment: Assessing the damage caused by military action to determine the effectiveness of operations.
Role 4: Cybersecurity and Information Assurance

Military intelligence plays a critical role in cybersecurity and information assurance. This includes protecting military computer systems and networks from cyber threats, as well as ensuring the integrity and authenticity of military information. Military intelligence also supports cybersecurity efforts by identifying potential threats and developing effective countermeasures.
The Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is essential for modern military operations. The increasing reliance on computer systems and networks has created new vulnerabilities that must be addressed. Military intelligence must be proactive in identifying and mitigating cyber threats to protect military operations and information.
Role 5: Counterintelligence and Security

Military intelligence plays a critical role in counterintelligence and security. This includes identifying and mitigating potential security threats, such as espionage and sabotage. Military intelligence also supports counterintelligence efforts by identifying and countering enemy intelligence gathering activities.
Types of Counterintelligence
There are several types of counterintelligence, including:
- Counter-HUMINT: Countering enemy human intelligence gathering activities.
- Counter-SIGINT: Countering enemy signals intelligence gathering activities.
- Counter-GEOINT: Countering enemy geospatial intelligence gathering activities.
Military Intelligence Image Gallery








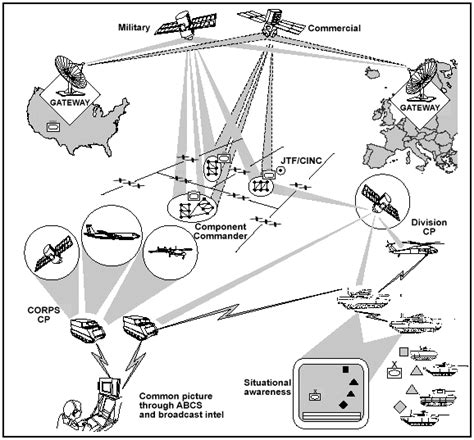
What is the primary role of military intelligence?
+The primary role of military intelligence is to gather and analyze information to support military planning and decision-making.
What are the different types of intelligence gathering?
+There are several types of intelligence gathering, including human intelligence (HUMINT), signals intelligence (SIGINT), and geospatial intelligence (GEOINT).
Why is cybersecurity important for military operations?
+Cybersecurity is essential for modern military operations, as it protects military computer systems and networks from cyber threats and ensures the integrity and authenticity of military information.
In conclusion, the role of military intelligence is multifaceted and critical to modern military operations. From gathering and analyzing information to supporting strategic planning and decision-making, military intelligence plays a vital role in ensuring the success of military operations. By understanding the different roles of military intelligence, we can appreciate the importance of this critical function and its impact on military effectiveness.
