Intro
Discover the vital National Guard roles and responsibilities, from domestic emergency response to overseas deployments. Learn about the different types of National Guard units, their mission, and the skills required for enlistment. Understand the dual mission of the National Guard, supporting both state and federal authorities in times of crisis.
The National Guard is a unique branch of the US military that plays a vital role in the country's defense and domestic security. As a reserve component of the US Armed Forces, the National Guard has a dual mission: to provide support to the federal government during wartime and to assist state governments during times of natural disasters, civil unrest, and other emergencies.
History of the National Guard

The National Guard has its roots in the colonial era, when militias were formed to defend against British rule. After the Revolutionary War, the concept of a citizen-soldier force continued, with state militias playing a key role in the US military. In 1903, the Dick Act established the National Guard as a federal reserve component, and since then, the organization has evolved to become an essential part of the US military.
Mission and Responsibilities

The National Guard has a dual mission:
- Federal Mission: To provide trained and equipped units to support the federal government during wartime, national emergencies, and other crises.
- State Mission: To assist state governments during times of natural disasters, civil unrest, and other emergencies.
In terms of specific responsibilities, National Guard members may be called upon to:
- Participate in combat operations and peacekeeping missions overseas
- Provide humanitarian assistance and disaster relief
- Support law enforcement agencies during civil unrest or other emergencies
- Assist in homeland security operations
- Participate in community outreach and education programs
Structure and Organization
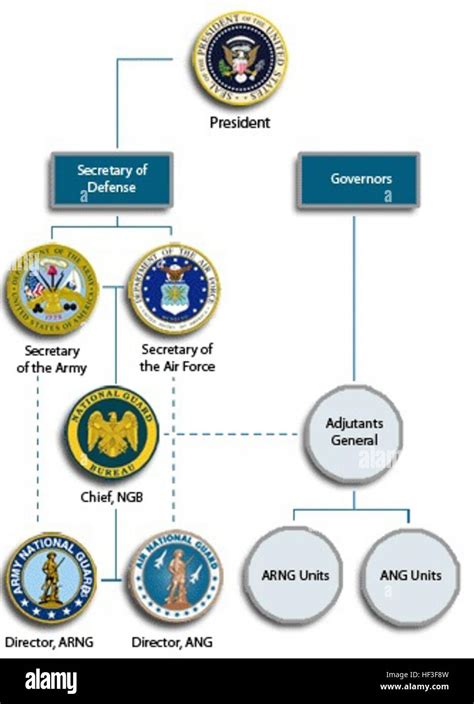
The National Guard is organized into several components:
- Army National Guard (ARNG): The ARNG is the largest component of the National Guard, with over 450,000 soldiers.
- Air National Guard (ANG): The ANG is the air component of the National Guard, with over 100,000 airmen.
- National Guard Bureau (NGB): The NGB is the federal agency responsible for overseeing the National Guard.
The National Guard is also organized into several types of units, including:
- Combat Arms Units: Infantry, armor, artillery, and other units that engage in combat operations.
- Combat Support Units: Units that provide support to combat arms units, such as engineering, signal, and medical units.
- Combat Service Support Units: Units that provide logistical support to combat arms units, such as transportation, supply, and maintenance units.
Leadership and Command Structure
The National Guard is led by the Chief of the National Guard Bureau, who is responsible for overseeing the organization and its operations. The Chief is assisted by several deputy chiefs and other senior leaders.
At the state level, National Guard units are led by adjutants general, who are responsible for overseeing the state's National Guard units and coordinating with state and federal authorities.
Training and Deployment

National Guard members undergo rigorous training to prepare for their dual mission. This training includes:
- Basic Combat Training (BCT): New recruits attend BCT, which provides basic military training and education.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): After BCT, soldiers attend AIT, which provides specialized training in their military occupational specialty (MOS).
- Annual Training (AT): National Guard members attend AT, which provides ongoing training and education in their MOS.
National Guard members may be deployed overseas in support of federal missions or domestically in support of state missions. Deployments can be voluntary or involuntary, and may be for short or extended periods.
Benefits and Incentives
National Guard members receive a range of benefits and incentives, including:
- Education Benefits: National Guard members may be eligible for education benefits, such as the GI Bill.
- Healthcare Benefits: National Guard members may be eligible for healthcare benefits, such as TRICARE.
- Retirement Benefits: National Guard members may be eligible for retirement benefits, such as a pension.
- Pay and Allowances: National Guard members receive pay and allowances for their service.
Challenges and Opportunities
The National Guard faces several challenges, including:
- Budget Constraints: The National Guard faces budget constraints, which can impact its ability to modernize and maintain its equipment and facilities.
- Recruiting and Retention: The National Guard faces challenges in recruiting and retaining members, particularly in certain MOS.
- Deployments: National Guard members may be deployed frequently, which can impact their families and civilian careers.
Despite these challenges, the National Guard also has several opportunities, including:
- Community Outreach: National Guard members may participate in community outreach and education programs, which can help build relationships with local communities.
- Leadership Development: National Guard members may have opportunities for leadership development and advancement.
- Diverse Missions: National Guard members may have the opportunity to participate in a range of missions, from combat operations to humanitarian assistance.
Conclusion
The National Guard is a vital component of the US military, providing a unique blend of federal and state mission capabilities. As a reserve component, the National Guard offers a range of benefits and opportunities for its members, from education benefits to leadership development. However, the National Guard also faces several challenges, including budget constraints and recruiting and retention challenges. Despite these challenges, the National Guard remains an essential part of the US military, providing critical support to both federal and state authorities.
National Guard Image Gallery










What is the National Guard?
+The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces that provides a unique blend of federal and state mission capabilities.
What is the dual mission of the National Guard?
+The National Guard has a dual mission: to provide trained and equipped units to support the federal government during wartime, national emergencies, and other crises, and to assist state governments during times of natural disasters, civil unrest, and other emergencies.
What are the benefits of joining the National Guard?
+National Guard members receive a range of benefits, including education benefits, healthcare benefits, retirement benefits, and pay and allowances.
What are the challenges facing the National Guard?
+The National Guard faces several challenges, including budget constraints, recruiting and retention challenges, and deployments.
What opportunities are available to National Guard members?
+National Guard members may have opportunities for leadership development, community outreach, and participation in diverse missions.
