Intro
Discover the ins and outs of AIT in the Army, from training and duration to job specialties and life after Basic Combat Training. Learn what to expect, how to prepare, and the benefits of Advanced Individual Training, a crucial step in your military career. Get expert insights and insider knowledge to succeed in the Army.
Joining the army can be a life-changing decision that requires careful consideration and preparation. Whether you're looking to serve your country, gain new skills, or find a sense of purpose, the army can be a rewarding and challenging career path. However, it's essential to understand what to expect and what it takes to succeed in the military.
For many, the army is a way of life that provides a sense of belonging, camaraderie, and pride. But it's not without its challenges. The army demands discipline, hard work, and sacrifice. Soldiers must be prepared to face difficult situations, make tough decisions, and put their country's interests above their own.
In this article, we'll explore what it's like to be in the army, the benefits and drawbacks, and what you need to know before making the decision to join.
Benefits of Joining the Army
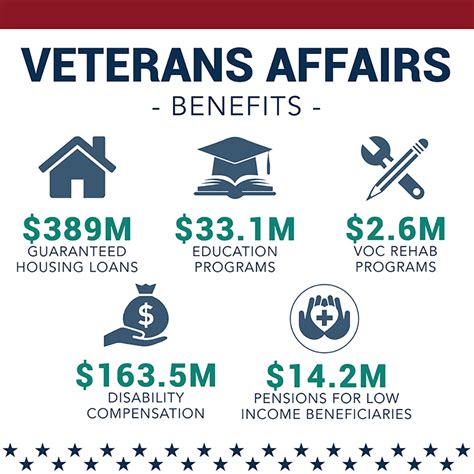
Joining the army can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Education and Training: The army offers various education and training programs, including the GI Bill, which can help you pay for college or vocational school.
- Career Opportunities: The army provides a wide range of career opportunities, from combat roles to administrative and support positions.
- Travel and Adventure: As a soldier, you'll have the opportunity to travel and experience new cultures, both domestically and internationally.
- Camaraderie and Esprit de Corps: The army fosters a sense of belonging and camaraderie among soldiers, which can last a lifetime.
- Leadership and Personal Growth: The army provides opportunities for leadership and personal growth, helping you develop valuable skills and qualities.
Types of Military Service
The army offers various types of military service, including:
- Active Duty: Full-time service, typically for 3-6 years.
- Reserve Duty: Part-time service, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year.
- National Guard: Part-time service, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year, with a focus on state and local emergencies.
- Civilian Service: Working for the army in a civilian capacity, supporting military operations and administration.
Challenges of Army Life

While the army can be a rewarding career path, it's not without its challenges. Some of the difficulties you may face include:
- Deployment and Time Away from Family: Soldiers may be deployed for extended periods, which can be difficult for families and loved ones.
- Physical and Mental Demands: Army life can be physically and mentally demanding, with long hours, intense training, and combat situations.
- Discipline and Structure: The army is a highly structured and disciplined environment, which can be challenging for some individuals.
- Limited Personal Freedom: Soldiers must adhere to strict rules and regulations, which can limit personal freedom and autonomy.
Army Ranks and Pay
The army has a hierarchical rank structure, with various levels of pay and responsibility. Here are some of the main ranks and corresponding pay grades:
- Private (PVT): E-1, $1,733.10 per month
- Private First Class (PFC): E-2, $1,942.50 per month
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): E-4, $2,344.80 per month
- Sergeant (SGT): E-5, $2,684.80 per month
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): E-6, $3,078.60 per month
Army Training and Education

The army provides various training and education programs, including:
- Basic Combat Training (BCT): A 10-week program that teaches basic soldiering skills.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): A program that provides specialized training in a specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
- Officer Candidate School (OCS): A program that commissions officers.
- GI Bill: A program that helps pay for college or vocational school.
Army Careers and MOS
The army offers a wide range of careers and Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), including:
- Combat Arms: Infantry, artillery, armor, and special forces.
- Administration: Human resources, finance, and administration.
- Communications: Communications and information technology.
- Engineer: Engineering and construction.
- Medical: Medical and healthcare.
Gallery of Army Life
Army Life Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average salary for an army soldier?
+The average salary for an army soldier varies depending on rank and time in service. However, the average salary for a private (E-1) is around $1,733.10 per month.
How long does army training last?
+Army training, also known as Basic Combat Training (BCT), typically lasts for 10 weeks. However, some specialized training programs can last longer.
Can I choose my army career?
+Yes, you can choose your army career, but it's subject to availability and your qualifications. You'll take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine your strengths and weaknesses.
In conclusion, joining the army can be a rewarding and challenging career path that provides numerous benefits and opportunities for growth. However, it's essential to understand the challenges and demands of army life and to carefully consider your decision before enlisting. If you're considering a career in the army, we encourage you to do your research, talk to recruiters, and weigh your options carefully.
