Intro
Discover the ins and outs of military reserve life with our expert guide. Learn about the different types of reserve components, including Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, and Air National Guard, and understand the benefits, deployment process, and training requirements. Get insider tips on balancing civilian life with military service.
Understanding the military reserve is crucial for those who are considering joining the military or are already part of it. The military reserve is a component of the armed forces that consists of soldiers who are not on active duty but can be called to serve in times of war or national emergency. Here are five ways to understand the military reserve:
What is the Military Reserve?
The military reserve is a vital part of the armed forces that provides a pool of trained soldiers who can be called to active duty in times of need. The reserve component consists of soldiers who have completed their initial active duty service and have opted to remain in the military as part of the reserve. These soldiers typically drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
Types of Military Reserve
There are several types of military reserve, including:
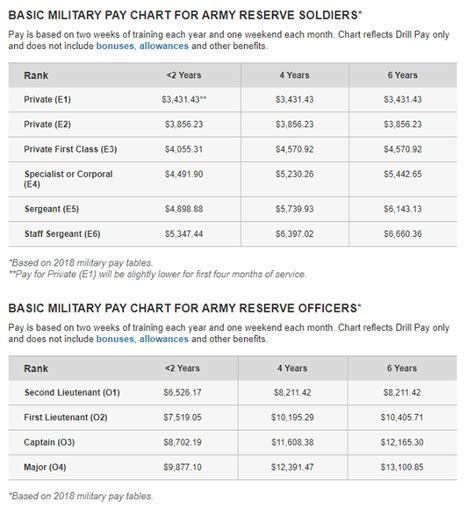
- Army Reserve: The Army Reserve is the largest of the military reserve components, with over 200,000 soldiers. Army Reserve soldiers drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
- Air National Guard: The Air National Guard is a reserve component of the Air Force that consists of over 100,000 airmen. Air National Guard airmen drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
- Navy Reserve: The Navy Reserve is the reserve component of the Navy, with over 50,000 sailors. Navy Reserve sailors drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
- Marine Corps Reserve: The Marine Corps Reserve is the reserve component of the Marine Corps, with over 30,000 Marines. Marine Corps Reserve Marines drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
- Coast Guard Reserve: The Coast Guard Reserve is the reserve component of the Coast Guard, with over 7,000 Coast Guardsmen. Coast Guard Reserve members drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training exercise.
Benefits of Joining the Military Reserve

Joining the military reserve offers numerous benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: The military reserve offers education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Army Reserve Education Assistance Program (AR-EAP).
- Healthcare Benefits: Military reserve members are eligible for healthcare benefits, including medical, dental, and pharmacy coverage.
- Career Advancement: Joining the military reserve can help advance your civilian career, as it provides valuable skills and training.
- Travel Opportunities: Military reserve members have the opportunity to travel and serve in different parts of the world.
- Camaraderie: Joining the military reserve provides the opportunity to be part of a tight-knit community of soldiers who share similar experiences and values.
How to Join the Military Reserve
To join the military reserve, you must meet the eligibility requirements, which include:
- Age: You must be between the ages of 17 and 35 to join the military reserve.
- Citizenship: You must be a U.S. citizen to join the military reserve.
- Education: You must have a high school diploma or equivalent to join the military reserve.
- Physical Fitness: You must meet the physical fitness requirements of the military reserve.
- Background Check: You must undergo a background check to join the military reserve.
Military Reserve Training
Military reserve training is designed to prepare soldiers for their role in the military reserve. The training consists of:
- Basic Training: Basic training is the initial training that all new military reserve soldiers must complete. It provides basic military skills and training.
- Advanced Individual Training (AIT): AIT is specialized training that provides soldiers with the skills and knowledge needed for their specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
- Drill: Drill is the monthly training exercise that military reserve soldiers attend. It provides additional training and preparation for their role in the military reserve.
- Annual Training: Annual training is a two-week training exercise that military reserve soldiers attend. It provides additional training and preparation for their role in the military reserve.
Military Reserve Life
Military reserve life is unique and challenging. Military reserve soldiers must balance their civilian life with their military responsibilities. Here are some tips for making the most of military reserve life:
- Stay Connected: Stay connected with your fellow soldiers and your unit. This will help you stay informed and up-to-date on unit activities and events.
- Attend Drill: Attend drill regularly to stay current with your training and to connect with your fellow soldiers.
- Stay Fit: Stay physically fit by exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. This will help you meet the physical fitness requirements of the military reserve.
- Pursue Education: Pursue education and training to advance your civilian career and to stay current with your military skills.
Challenges of Military Reserve Life

Military reserve life can be challenging, but there are several challenges that military reserve soldiers may face. Here are some of the most common challenges:
- Balancing Civilian and Military Life: Military reserve soldiers must balance their civilian life with their military responsibilities. This can be challenging, especially for those with families or demanding civilian careers.
- Staying Connected: Military reserve soldiers may struggle to stay connected with their fellow soldiers and their unit. This can make it difficult to stay informed and up-to-date on unit activities and events.
- Meeting Physical Fitness Requirements: Military reserve soldiers must meet the physical fitness requirements of the military reserve. This can be challenging, especially for those who are new to the military or who have not exercised regularly.
- Dealing with Deployment: Military reserve soldiers may be deployed in times of war or national emergency. This can be challenging for those with families or civilian careers.
Conclusion
Understanding the military reserve is crucial for those who are considering joining the military or are already part of it. The military reserve is a vital part of the armed forces that provides a pool of trained soldiers who can be called to active duty in times of need. By understanding the types of military reserve, the benefits of joining, and the challenges of military reserve life, individuals can make informed decisions about their future.
Military Reserve Image Gallery








What is the military reserve?
+The military reserve is a component of the armed forces that consists of soldiers who are not on active duty but can be called to serve in times of war or national emergency.
What are the benefits of joining the military reserve?
+The benefits of joining the military reserve include education benefits, healthcare benefits, career advancement, travel opportunities, and camaraderie.
How do I join the military reserve?
+To join the military reserve, you must meet the eligibility requirements, which include age, citizenship, education, physical fitness, and background check.
What is military reserve training?
+Military reserve training is designed to prepare soldiers for their role in the military reserve. The training consists of basic training, advanced individual training, drill, and annual training.
What are the challenges of military reserve life?
+The challenges of military reserve life include balancing civilian and military life, staying connected, meeting physical fitness requirements, and dealing with deployment.
