Intro
Discover the ins and outs of the Reserve Military with our expert guide. Learn about the different types of reserve components, deployment frequency, drill weekends, and more. From training requirements to benefits and pay, well cover the top 7 things to know about serving in the Reserve Military, including Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, and Air National Guard.
The reserve military is a vital component of a country's defense system, providing a crucial link between the active-duty military and civilian life. For those considering a career in the reserve military or wanting to learn more about this unique institution, here are seven key things to know.
What is the Reserve Military?

The reserve military is a part-time military force that supplements the active-duty military in times of war or national emergency. Reserve personnel typically drill one weekend a month and attend an annual two-week training period, known as annual training (AT). This structure allows reserve personnel to maintain their civilian careers and lives while also serving their country.
Types of Reserve Components
There are several types of reserve components, each with its own unique characteristics and responsibilities. These include:
- Army Reserve (USAR)
- Navy Reserve (USNR)
- Air National Guard (ANG)
- Air Force Reserve (AFR)
- Marine Corps Reserve (USMCR)
- Coast Guard Reserve (USCGR)
Each reserve component has its own specific mission and responsibilities, but all share the common goal of supporting the active-duty military and defending the nation.
Benefits of Serving in the Reserve Military

Serving in the reserve military offers a range of benefits, including:
- Education benefits: The reserve military offers education assistance, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Post-9/11 GI Bill.
- Career advancement: Reserve service can provide valuable skills and experience, which can be applied to civilian careers.
- Leadership development: Reserve personnel have opportunities to develop leadership skills, which can benefit both military and civilian careers.
- Camaraderie: Serving in the reserve military provides a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps, which can be a lifelong source of pride and fulfillment.
Reserve Military vs. Active-Duty Military
While both the reserve military and active-duty military are essential components of a country's defense system, there are key differences between the two. Active-duty personnel serve full-time, typically for 3-6 years, and are subject to deployment and other military requirements. Reserve personnel, on the other hand, serve part-time and typically have more control over their military commitments.
Reserve Military Training and Deployment
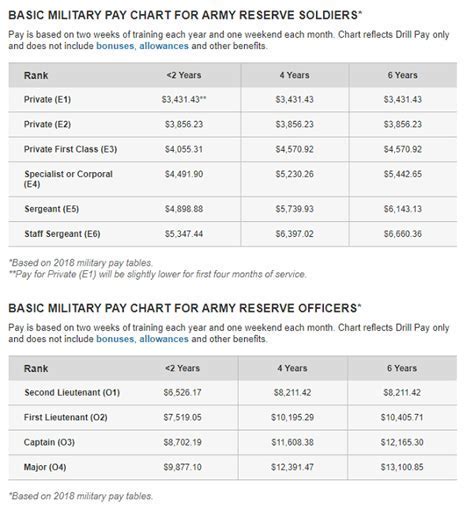
Reserve military training and deployment can vary depending on the specific component and unit. Reserve personnel typically attend annual training (AT) for two weeks, during which they participate in military training and exercises. They may also be subject to deployment, either domestically or internationally, in support of military operations.
Reserve Military Deployment Statistics
According to the Defense Manpower Data Center, in 2020:
- 24% of reserve personnel were deployed in support of military operations.
- The average length of deployment for reserve personnel was 9 months.
- 45% of reserve personnel reported being deployed in the past 5 years.
Reserve Military and Civilian Life

Reserve military personnel often balance their military commitments with civilian careers and family life. This can be challenging, but many reserve personnel find that their military service enhances their civilian lives and careers.
Employer Support for Reserve Military Personnel
Many employers offer support for reserve military personnel, including:
- Paid time off for military training and deployment.
- Continued pay and benefits during deployment.
- Support for military-related education and training.
Conclusion
The reserve military is a vital component of a country's defense system, providing a unique blend of military and civilian life. With its part-time structure and range of benefits, the reserve military offers a rewarding and challenging career path for those who want to serve their country while also pursuing civilian careers and lives.
Reserve Military Image Gallery






What is the difference between the reserve military and active-duty military?
+The main difference between the reserve military and active-duty military is the level of commitment. Active-duty personnel serve full-time, typically for 3-6 years, while reserve personnel serve part-time and typically have more control over their military commitments.
Can I still pursue a civilian career while serving in the reserve military?
+Yes, many reserve military personnel balance their military commitments with civilian careers and family life. In fact, the reserve military offers a range of benefits, including education assistance and career advancement opportunities, that can enhance civilian careers.
How often do reserve military personnel deploy?
+Reserve military personnel may be subject to deployment, either domestically or internationally, in support of military operations. However, the frequency and length of deployment vary depending on the specific component and unit.
