Intro
Discover the meaning behind Mach speed, a fundamental concept in aerodynamics and physics. Learn how Mach numbers relate to the speed of sound, sonic booms, and supersonic flight. Understand the significance of Mach 1, Mach 2, and beyond in aerospace engineering, aircraft design, and high-speed travel.
Speed is a fundamental concept in physics, and it's essential to understand the different ways to measure and express it. One such way is through the concept of Mach speed, which is a critical idea in aerodynamics and aerospace engineering.
The term "Mach speed" is named after Austrian physicist Ernst Mach, who first introduced the concept in the late 19th century. In essence, Mach speed is a measure of an object's speed relative to the speed of sound in a given medium, such as air. This speed is a critical factor in determining the behavior of objects in motion, particularly at high speeds.
To understand Mach speed, let's first consider the speed of sound. The speed of sound is the distance traveled by a sound wave per unit time, typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or miles per hour (mph). In dry air at room temperature, the speed of sound is approximately 343 m/s (768 mph). However, this speed can vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure.
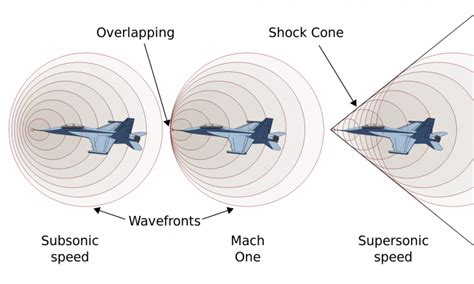
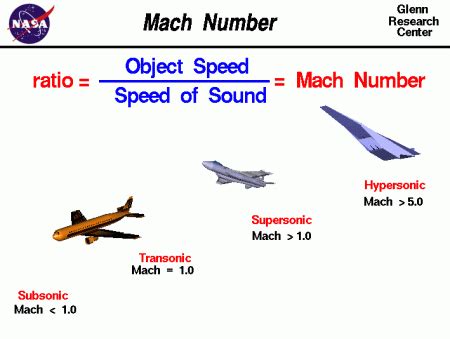
Now, let's define Mach speed. Mach speed is the ratio of an object's speed to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. This ratio is typically denoted by the symbol M and is expressed as a decimal value. For example, an object traveling at Mach 1 is moving at the same speed as the speed of sound, while an object traveling at Mach 2 is moving at twice the speed of sound.
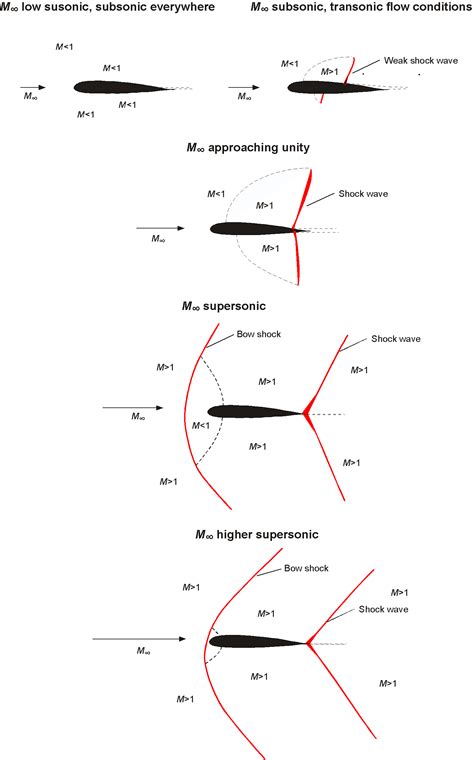
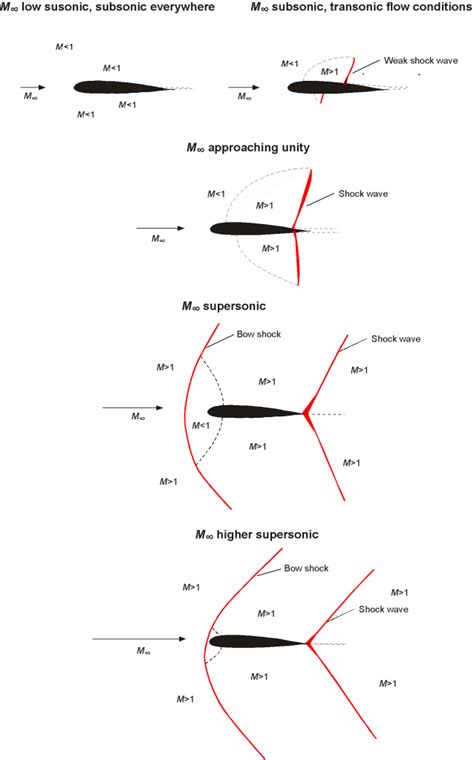
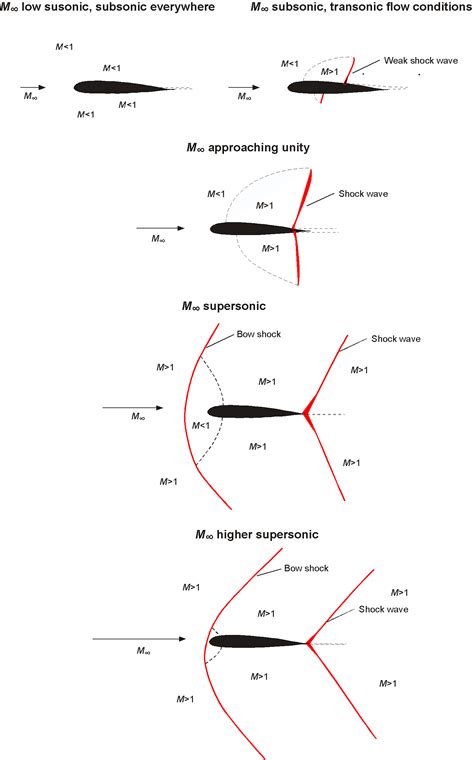
Mach speed is a critical concept in aerodynamics because it helps predict the behavior of objects in motion, particularly when they approach or exceed the speed of sound. At low Mach numbers (M < 0.8), the airflow around an object is typically smooth and continuous. However, as the Mach number increases (M > 0.8), the airflow can become turbulent, leading to shock waves, sonic booms, and other complex phenomena.
Here are some examples of different Mach speeds and their corresponding effects:
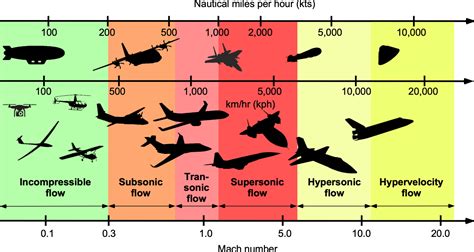
- Subsonic (M < 0.8): Airflow is smooth and continuous. Most commercial airliners cruise at subsonic speeds, typically around Mach 0.8.
- Transonic (M = 0.8-1.2): Airflow is transitional, with some turbulence and shock waves. Military aircraft often operate in this regime.
- Supersonic (M > 1.2): Airflow is turbulent, with shock waves and sonic booms. Fighter jets and spacecraft often operate at supersonic speeds.
- Hypersonic (M > 5): Airflow is extremely turbulent, with intense heat generation and shock waves. Some spacecraft and missiles operate at hypersonic speeds.
Mach speed has numerous practical applications in various fields, including aerospace engineering, military aviation, and even medical research. Understanding Mach speed is crucial for designing and operating high-speed vehicles, such as aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles.
In conclusion, Mach speed is a fundamental concept in physics that measures an object's speed relative to the speed of sound in a given medium. Understanding Mach speed is essential for predicting the behavior of objects in motion, particularly at high speeds. The concept of Mach speed has numerous practical applications in various fields, from aerospace engineering to medical research.
How Is Mach Speed Calculated?
Calculating Mach speed is relatively straightforward, but it requires knowledge of the object's speed and the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. The formula for calculating Mach speed is:
M = v / c
where:
- M is the Mach number
- v is the object's speed (in m/s or mph)
- c is the speed of sound (in m/s or mph)
For example, let's calculate the Mach speed of an aircraft traveling at 600 mph (965 km/h) in dry air at room temperature, where the speed of sound is approximately 768 mph (1,236 km/h).
M = 600 mph / 768 mph ≈ 0.78
This means the aircraft is traveling at approximately Mach 0.78, which is a subsonic speed.

What Are the Limitations of Mach Speed?
While Mach speed is a useful concept for predicting the behavior of objects in motion, it has several limitations. Here are some of the key limitations:
- Assumes ideal gas behavior: Mach speed calculations assume that the surrounding medium behaves as an ideal gas, which may not always be the case. In reality, gases can exhibit complex behavior, such as non-ideal gas effects and turbulence.
- Ignores other factors: Mach speed only accounts for the speed of sound and the object's speed. It ignores other factors that can affect the behavior of objects in motion, such as air density, temperature, and humidity.
- Limited to specific regimes: Mach speed is primarily useful for predicting the behavior of objects in specific regimes, such as subsonic, transonic, supersonic, and hypersonic. It may not be applicable to other regimes, such as low-speed flows or high-speed flows in rarefied gases.
Real-World Applications of Mach Speed
Mach speed has numerous real-world applications in various fields, including:
- Aerospace engineering: Mach speed is critical for designing and operating high-speed aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles.
- Military aviation: Mach speed is used to predict the performance of military aircraft, including fighter jets and bombers.
- Medical research: Mach speed is used in medical research to study the behavior of high-speed particles and their effects on human tissue.
- Wind tunnel testing: Mach speed is used to design and operate wind tunnels, which are used to test the aerodynamic properties of objects.
Gallery of Mach Speed
Mach Speed Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Mach speed?
+Mach speed is a measure of an object's speed relative to the speed of sound in a given medium.
How is Mach speed calculated?
+Mach speed is calculated using the formula M = v / c, where M is the Mach number, v is the object's speed, and c is the speed of sound.
What are the limitations of Mach speed?
+Mach speed has several limitations, including assuming ideal gas behavior, ignoring other factors, and being limited to specific regimes.
We hope this article has helped you understand the concept of Mach speed and its importance in various fields. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please feel free to ask!
