Intro
Discover the fulfillment of serving with purpose and pride in the US Army. Learn why joining the army offers a unique opportunity for personal growth, career development, and service to country. Explore the benefits, career options, and sense of camaraderie that come with being part of the army community.
The decision to join the army is a significant one, marked by a desire to serve a higher purpose and contribute to the greater good. For many, the army represents a unique opportunity to make a difference, to be part of a brotherhood that transcends personal interests and forges bonds that last a lifetime. But what is it about joining the army that sparks such profound commitment and dedication?

Benefits of Joining the Army
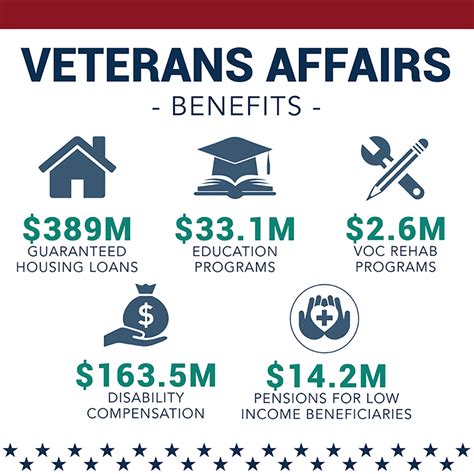
Joining the army offers a wide range of benefits that cater to different aspects of an individual's life. From education and career advancement to personal growth and development, the army provides a platform for individuals to excel in various fields. Some of the key benefits of joining the army include:
- Education Benefits: The army offers various education programs, including the GI Bill, which helps soldiers pay for college. Additionally, the army provides training and certification in specialized skills, which can be valuable in both military and civilian careers.
- Career Advancement: The army offers a clear career path, with opportunities for advancement and promotion. Soldiers can choose from a variety of Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), each with its own unique challenges and rewards.
- Personal Growth: Joining the army can be a transformative experience that helps individuals develop valuable skills, such as leadership, teamwork, and problem-solving. The army also provides opportunities for personal growth, including training in areas such as physical fitness, first aid, and emergency response.
Education Benefits
The army's education benefits are designed to help soldiers pursue higher education and achieve their career goals. Some of the key education benefits include:
- GI Bill: The GI Bill provides financial assistance to soldiers who want to attend college or vocational school. The bill can help pay for tuition, fees, and other education-related expenses.
- Tuition Assistance: The army offers tuition assistance to soldiers who want to pursue higher education while serving in the military. This benefit can help pay for tuition and fees at accredited colleges and universities.
- Certification and Training: The army provides training and certification in specialized skills, which can be valuable in both military and civilian careers. Soldiers can choose from a variety of training programs, including aviation, engineering, and healthcare.

Types of Military Service
There are several types of military service, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements. Some of the main types of military service include:
- Active Duty: Active duty soldiers serve full-time in the military, typically for a period of 2-6 years. Active duty soldiers are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and housing allowances.
- Reserve Duty: Reserve soldiers serve part-time in the military, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year. Reserve soldiers are eligible for some benefits, including education assistance and healthcare.
- National Guard: National Guard soldiers serve part-time in the military, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year. National Guard soldiers are eligible for some benefits, including education assistance and healthcare.
Types of Military Careers
There are many different types of military careers, each with its own unique challenges and rewards. Some of the main types of military careers include:
- Combat Careers: Combat careers involve serving in combat roles, such as infantry, artillery, or special operations. Combat careers require soldiers to be physically fit, mentally tough, and willing to serve in high-stress environments.
- Support Careers: Support careers involve providing support to combat units, such as logistics, intelligence, or communications. Support careers require soldiers to be skilled in areas such as problem-solving, leadership, and teamwork.
- Medical Careers: Medical careers involve providing medical care to soldiers and civilians, such as nursing, medicine, or dentistry. Medical careers require soldiers to be skilled in areas such as patient care, diagnosis, and treatment.

Training and Preparation
Before joining the army, it's essential to prepare physically, mentally, and emotionally. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
- Physical Fitness: Start a physical fitness program to improve your endurance, strength, and agility. Focus on exercises such as push-ups, sit-ups, and running.
- Mental Preparation: Start practicing mental preparation techniques, such as meditation, mindfulness, and visualization. Focus on building your confidence, resilience, and focus.
- Education and Training: Research the army's education and training programs, including the types of skills and knowledge you'll need to succeed.
Basic Training
Basic training, also known as boot camp, is the initial training program for new recruits. Basic training typically lasts 10-12 weeks and involves physical fitness, combat training, and education in areas such as first aid, map reading, and military protocol.

Army Culture and Traditions
The army has a rich culture and tradition, shaped by its history, values, and mission. Some of the key aspects of army culture and tradition include:
- Honor and Integrity: The army values honor and integrity, emphasizing the importance of honesty, fairness, and respect for others.
- Esprit de Corps: The army has a strong sense of esprit de corps, emphasizing the importance of teamwork, camaraderie, and shared purpose.
- Traditions and Rituals: The army has many traditions and rituals, such as the changing of the guard, the presentation of colors, and the singing of the national anthem.
Army Values
The army has seven core values, which are:
- Loyalty: Loyalty to the army, to fellow soldiers, and to the nation.
- Duty: Duty to serve, to protect, and to defend.
- Respect: Respect for others, including fellow soldiers, civilians, and the enemy.
- Selfless Service: Selfless service, putting the needs of others before one's own needs.
- Honor: Honor, integrity, and honesty in all actions.
- Integrity: Integrity, adhering to moral and ethical principles.
- Personal Courage: Personal courage, facing challenges and overcoming fears.

Conclusion
Joining the army is a significant decision, marked by a desire to serve, to contribute, and to make a difference. The army offers a wide range of benefits, including education assistance, career advancement, and personal growth. Whether you're interested in combat, support, or medical careers, the army has a place for you. By preparing physically, mentally, and emotionally, and by understanding the army's culture and traditions, you can succeed in your military career and serve with purpose and pride.
Army Image Gallery









What are the benefits of joining the army?
+The benefits of joining the army include education assistance, career advancement, personal growth, and a range of other benefits.
What types of military careers are available?
+The army offers a wide range of military careers, including combat, support, and medical careers.
What is basic training like?
+Basic training, also known as boot camp, is the initial training program for new recruits. It typically lasts 10-12 weeks and involves physical fitness, combat training, and education in areas such as first aid, map reading, and military protocol.
