Intro
Discover the cutting-edge technology and mighty power of World War 1 destroyers. Explore the evolution of these naval vessels, from their humble beginnings to their crucial role in the Great War. Learn about their design, armament, and capabilities, and how they revolutionized naval warfare with advanced propulsion systems and torpedo technology.
The onset of World War I marked a significant turning point in the history of naval warfare. The introduction of destroyers, small and agile warships, revolutionized the way navies operated at sea. These vessels played a crucial role in the conflict, serving as escorts, torpedo boats, and anti-submarine warfare platforms. In this article, we will explore the power and technology of World War I destroyers, highlighting their development, design, and impact on the war.
Early Development of Destroyers

The concept of destroyers dates back to the late 19th century, when navies began to recognize the need for fast and maneuverable vessels to counter the growing threat of torpedo boats. The first destroyers were developed in the 1890s, with the British Royal Navy's HMS Havock and HMS Hornet being among the earliest examples. These early destroyers were essentially enlarged torpedo boats, with a focus on speed and agility rather than firepower or endurance.
Design and Characteristics
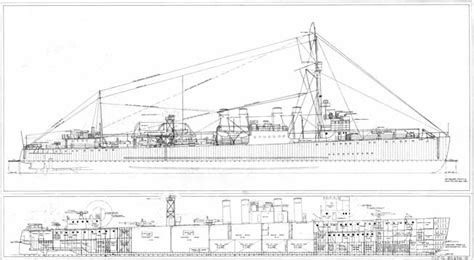
World War I destroyers were designed to be fast and maneuverable, with a typical length of around 250-300 feet (76-91 meters) and a displacement of 700-1,000 tons. They were powered by steam turbines or reciprocating engines, which provided a top speed of around 25-30 knots (46-56 km/h). Armament consisted of a combination of guns, torpedoes, and depth charges, with the primary focus being on torpedo warfare.
Some notable design features of World War I destroyers include:
- High-speed propulsion systems, allowing them to keep pace with faster enemy vessels
- Maneuverable hull designs, enabling them to make sharp turns and evade enemy fire
- Lightweight construction, minimizing their visibility and making them harder to hit
- Limited armor plating, prioritizing speed and agility over protection
Technological Advancements

The development of destroyers during World War I was marked by significant technological advancements, including:
- Improved propulsion systems, such as geared turbines and high-pressure boilers
- Enhanced armament, including larger guns and more advanced torpedo systems
- Increased use of wireless telegraphy and radio communication, allowing for more effective coordination and command
- Development of anti-submarine warfare technologies, including depth charges and hydrophones
These advancements played a crucial role in the effectiveness of destroyers during the war, enabling them to perform a range of tasks with greater efficiency and accuracy.
Roles and Operations

Destroyers played a variety of roles during World War I, including:
- Escort duties, protecting larger vessels from enemy submarines and torpedo boats
- Torpedo warfare, attacking enemy ships with torpedoes and mines
- Anti-submarine warfare, using depth charges and other technologies to counter enemy submarines
- Patrol duties, monitoring enemy movements and providing intelligence to commanders
These roles were critical to the war effort, as destroyers helped to safeguard convoys, protect naval bases, and disrupt enemy supply lines.
Notable Examples

Some notable examples of World War I destroyers include:
- HMS Grafton (British Royal Navy): A G-class destroyer that served as a convoy escort and anti-submarine warfare platform
- USS Cassin (United States Navy): A Cassin-class destroyer that participated in the Battle of the Atlantic and was involved in several notable engagements
- SMS V25 (German Imperial Navy): A V25-class destroyer that saw action at the Battle of Jutland and was sunk in 1916
These vessels, among many others, played important roles in the war and helped to shape the development of destroyers in the years that followed.
Legacy of World War I Destroyers

The destroyers of World War I left a lasting legacy in naval warfare, paving the way for the development of modern destroyers and frigates. Their innovative designs, technological advancements, and varied roles helped to shape the course of the war and influenced the construction of warships in the decades that followed.
In conclusion, World War I destroyers were a critical component of naval warfare during the conflict, playing a range of roles and utilizing cutting-edge technologies to achieve their objectives. Their impact on the war and their legacy in naval design and operations continue to be felt today.
Gallery of World War 1 Destroyers
World War 1 Destroyers Image Gallery










What were the primary roles of destroyers during World War I?
+Destroyers played a variety of roles during World War I, including escort duties, torpedo warfare, anti-submarine warfare, and patrol duties.
What technological advancements were made in destroyers during World War I?
+Significant technological advancements were made in destroyers during World War I, including improved propulsion systems, enhanced armament, and increased use of wireless telegraphy and radio communication.
What was the impact of destroyers on the outcome of World War I?
+Destroyers played a crucial role in the outcome of World War I, helping to safeguard convoys, protect naval bases, and disrupt enemy supply lines.
What was the legacy of World War I destroyers?
+The destroyers of World War I left a lasting legacy in naval warfare, paving the way for the development of modern destroyers and frigates.
What were some notable examples of World War I destroyers?
+Some notable examples of World War I destroyers include HMS Grafton, USS Cassin, and SMS V25.

