Intro
Convert 1.42 meters to feet with ease! Learn how to make quick conversions using simple formulas and charts. Understand the metric system and imperial system equivalencies, including meter to feet and inches calculations. Get instant results and master unit conversions with our easy-to-follow guide.
Converting meters to feet can be a bit of a challenge, but don't worry, we've got you covered. In this article, we'll break down the process of converting 1.42 meters to feet in a simple and easy-to-follow way. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just someone who needs to make conversions, this article is for you.
Understanding the Conversion Process
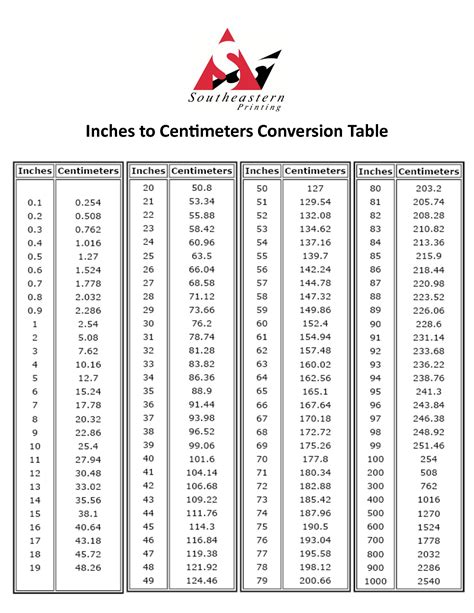
Before we dive into the conversion process, let's take a look at the relationship between meters and feet. The metric system uses meters as the base unit of length, while the imperial system uses feet. To convert between the two, we need to use a conversion factor. One meter is equal to 3.2808 feet.
Converting 1.42 Meters to Feet
Now that we know the conversion factor, let's use it to convert 1.42 meters to feet. We can do this by multiplying the number of meters by the conversion factor.
1.42 meters x 3.2808 feet/meter = 4.66 feet
So, 1.42 meters is equal to 4.66 feet.
Why Accurate Conversions Matter
Accurate conversions are crucial in a variety of fields, including science, engineering, and construction. In science, accurate conversions are necessary to ensure that experimental results are reliable and consistent. In engineering, conversions are used to design and build structures, such as bridges and buildings. In construction, conversions are used to ensure that buildings are built to the correct specifications.
Common Conversion Errors
Despite the importance of accurate conversions, errors can still occur. Some common conversion errors include:
- Rounding errors: Rounding numbers can lead to small errors that can add up over time.
- Unit errors: Using the wrong unit of measurement can lead to significant errors.
- Calculation errors: Mistakes in calculation can also lead to errors.
To avoid these errors, it's essential to double-check your work and use precise calculations.
Real-World Applications of Conversions
Conversions are used in a wide range of real-world applications, including:
- Building design and construction
- Scientific research
- Engineering
- Navigation
In building design and construction, conversions are used to ensure that buildings are built to the correct specifications. In scientific research, conversions are used to ensure that experimental results are reliable and consistent. In engineering, conversions are used to design and build structures, such as bridges and buildings. In navigation, conversions are used to determine distances and directions.

Tools and Resources for Conversions
There are many tools and resources available to help with conversions, including:
- Online conversion calculators
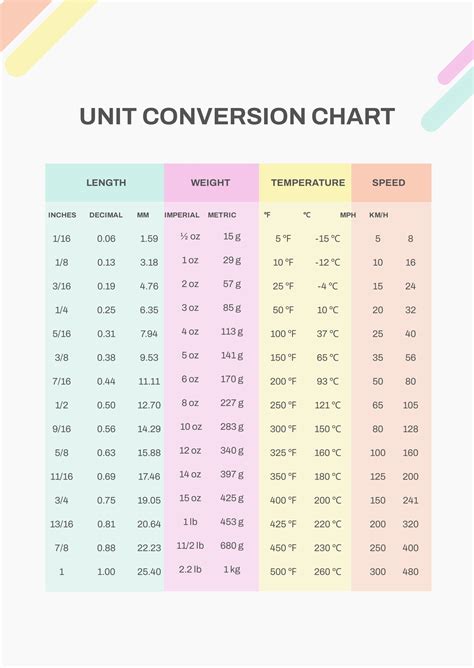
- Conversion charts and tables
- Scientific calculators
Online conversion calculators can be used to quickly and easily make conversions. Conversion charts and tables can be used to look up conversions. Scientific calculators can be used to make precise calculations.
Conclusion
Converting 1.42 meters to feet is a simple process that requires a basic understanding of the conversion factor. By using the conversion factor and double-checking your work, you can ensure accurate conversions. Accurate conversions are crucial in a variety of fields, and there are many tools and resources available to help. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just someone who needs to make conversions, we hope this article has been helpful.
Conversion Image Gallery


What is the conversion factor for meters to feet?
+The conversion factor for meters to feet is 3.2808 feet/meter.
Why are accurate conversions important?
+Accurate conversions are crucial in a variety of fields, including science, engineering, and construction, to ensure reliable and consistent results.
What are some common conversion errors?
+Common conversion errors include rounding errors, unit errors, and calculation errors.

