Intro
Uncover the 5 types of warfare acronyms and understand their significance in modern combat. Learn about C4ISR, UW, IO, PSYOP, and EBO, and how they enhance military operations, information operations, and cyber warfare. Discover how these acronyms impact command and control, special operations, and electronic warfare, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of modern warfare.
The world of warfare acronyms can be overwhelming, with a multitude of terms and abbreviations that can leave even the most seasoned military professionals scratching their heads. In this article, we'll delve into five types of warfare acronyms, exploring their meanings, applications, and significance in modern military operations.
1. C2: Command and Control

Command and Control (C2) refers to the exercise of authority and direction by a commander over assigned forces in the accomplishment of a mission. C2 is a critical component of modern warfare, enabling commanders to make informed decisions, coordinate efforts, and adapt to changing circumstances. Effective C2 systems rely on advanced technologies, such as communication networks, sensors, and data analytics, to provide real-time situational awareness and facilitate decision-making.
Key Characteristics of C2:
- Decentralized decision-making
- Real-time situational awareness
- Advanced communication networks
- Integrated sensor systems
- Data-driven decision-making
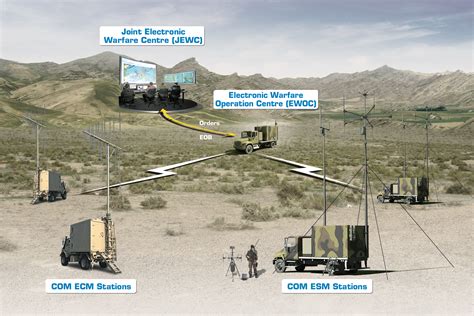
2. EW: Electronic Warfare

Electronic Warfare (EW) involves the use of electromagnetic energy to disrupt, neutralize, or destroy an adversary's ability to use the electromagnetic spectrum. EW encompasses a range of activities, including electronic attack, electronic protection, and electronic support. These operations can be conducted to disrupt communication systems, radar systems, or other electronic systems, providing a strategic advantage on the battlefield.
Types of EW Operations:
- Electronic Attack (EA): Disrupting or destroying an adversary's electronic systems
- Electronic Protection (EP): Protecting friendly electronic systems from EW attacks
- Electronic Support (ES): Intercepting and analyzing an adversary's electronic emissions
3. IO: Information Operations

Information Operations (IO) involve the use of information-related capabilities to achieve strategic objectives. IO encompasses a range of activities, including cyber operations, electronic warfare, psychological operations, and military information support operations. These operations can be conducted to disrupt an adversary's command and control systems, influence public opinion, or support military operations.
Key Components of IO:
- Cyber operations
- Electronic warfare
- Psychological operations
- Military information support operations
4. PSYOP: Psychological Operations

Psychological Operations (PSYOP) involve the use of planned operations to convey selected information and indicators to foreign audiences. PSYOP can be conducted to influence the perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors of an adversary's military forces, government officials, or civilian populations. These operations can be used to support military operations, promote stability, or counter ideological threats.
Types of PSYOP:
- White propaganda: Overtly attributed to the US military
- Gray propaganda: Attribution is ambiguous or unclear
- Black propaganda: Attributed to a false source
5. CBRN: Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear

Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN) warfare involves the use of weapons that can cause mass casualties or widespread destruction. CBRN weapons can be used to attack military forces, civilians, or critical infrastructure, posing a significant threat to national security. Military forces must be prepared to operate in CBRN environments, using protective equipment, detection systems, and decontamination procedures to mitigate the risks.
Types of CBRN Threats:
- Chemical agents: Toxic substances that can cause harm or death
- Biological agents: Pathogens or toxins that can cause disease or death
- Radiological agents: Radioactive materials that can cause harm or death
- Nuclear agents: Nuclear explosives that can cause widespread destruction
Gallery of Modern Warfare





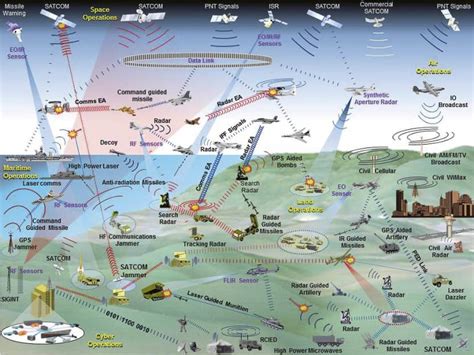
What is the primary goal of C2 in modern warfare?
+The primary goal of C2 is to provide commanders with the ability to make informed decisions, coordinate efforts, and adapt to changing circumstances in real-time.
What is the difference between EW and IO?
+EW involves the use of electromagnetic energy to disrupt, neutralize, or destroy an adversary's electronic systems, while IO encompasses a broader range of activities, including cyber operations, electronic warfare, psychological operations, and military information support operations.
What is the purpose of PSYOP in modern warfare?
+The purpose of PSYOP is to influence the perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors of an adversary's military forces, government officials, or civilian populations, in order to support military operations, promote stability, or counter ideological threats.
What are the key components of CBRN warfare?
+The key components of CBRN warfare include chemical agents, biological agents, radiological agents, and nuclear agents, which can be used to attack military forces, civilians, or critical infrastructure.
How do modern military forces protect themselves from CBRN threats?
+Modern military forces protect themselves from CBRN threats by using protective equipment, detection systems, and decontamination procedures, in addition to conducting regular training exercises and maintaining a high level of situational awareness.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the five types of warfare acronyms, highlighting their significance and applications in modern military operations. By understanding these concepts, military professionals and civilians alike can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of modern warfare and the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in this field.

