Intro
Discover the key differences between the Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve. Learn about the distinct roles, benefits, and requirements of each, including deployment, training, and career opportunities. Understand the unique aspects of each branch and make an informed decision about your military service.
When considering a career in the military, specifically in the Air Force, two options often come to mind: the Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve. While both branches share some similarities, they also have distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial in making an informed decision about which path to take.
For those who are eager to serve their country while maintaining a civilian life, both the Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve offer a unique opportunity to do so. However, the way they operate, their requirements, and the benefits they provide are distinct. In this article, we will delve into the details of each branch, exploring their differences, benefits, and what it takes to join.
Understanding the Air National Guard

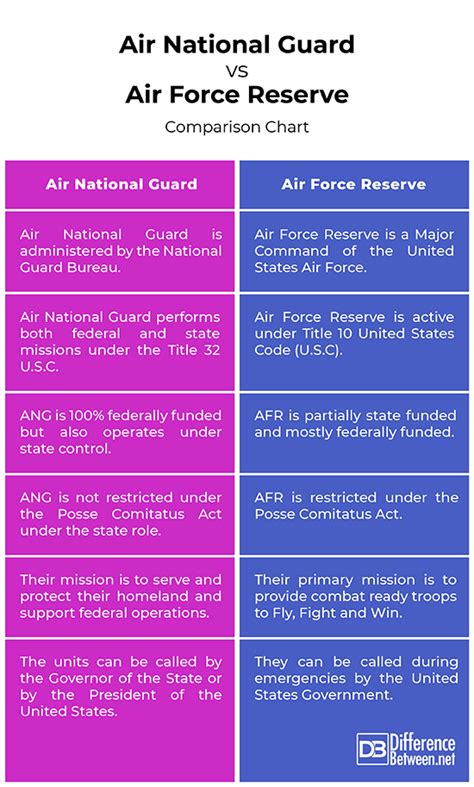
The Air National Guard (ANG) is a reserve component of the United States Air Force. It is unique in that it is a dual-status organization, meaning it can be called upon to serve both the state and federal governments. This dual status is what sets the ANG apart from the Air Force Reserve.
The ANG is composed of citizen airmen who can be deployed in support of state emergencies, such as natural disasters, as well as federal missions. ANG units are typically located in specific states and are responsible for defending their respective areas.
Benefits of Joining the Air National Guard
- Education Benefits: The ANG offers education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Tuition Assistance Program.
- Career Advancement: Serving in the ANG can provide valuable skills and experience, enhancing career advancement opportunities in both military and civilian life.
- Community Involvement: As a member of the ANG, you will have the opportunity to serve your community and state, making a positive impact on the lives of those around you.
Understanding the Air Force Reserve

The Air Force Reserve (AFR) is a federal force that provides operational capability to the United States Air Force. Unlike the ANG, the AFR is strictly a federal organization and does not have a dual status.
Members of the AFR can be deployed in support of federal missions, both domestically and internationally. The AFR is designed to augment the active duty Air Force, providing additional manpower and resources as needed.
Benefits of Joining the Air Force Reserve
- Education Benefits: The AFR offers education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Tuition Assistance Program.
- Healthcare Benefits: As a member of the AFR, you will be eligible for TRICARE, a comprehensive healthcare program.
- Career Opportunities: Serving in the AFR can provide valuable skills and experience, enhancing career advancement opportunities in both military and civilian life.
Key Differences Between the Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve
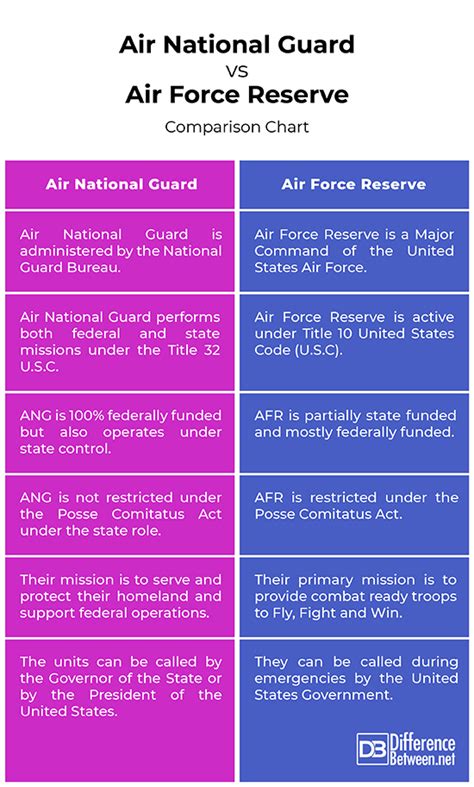
- Dual Status: The ANG has a dual status, serving both the state and federal governments, whereas the AFR is strictly a federal organization.
- Deployment: ANG members can be deployed in support of state emergencies, whereas AFR members are typically deployed in support of federal missions.
- Training: ANG and AFR members receive similar training, but ANG members may also participate in state-specific training exercises.
How to Join the Air National Guard or the Air Force Reserve
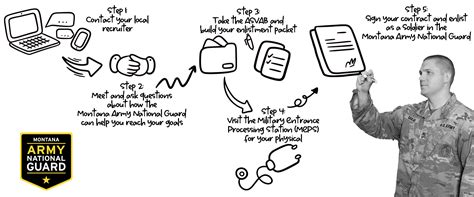
To join the ANG or AFR, you must meet specific requirements, including:
- Age: Be between the ages of 17 and 39 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Education: Have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Physical Fitness: Meet physical fitness standards
- Background Check: Pass a background check
Once you have met these requirements, you can begin the enlistment process, which includes:
- Talking to a Recruiter: Discuss your options with a recruiter to determine which branch is best for you.
- Taking the ASVAB: Complete the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine your qualifications for different career fields.
- Physical Exam: Complete a physical exam to ensure you meet the physical fitness standards.
- Background Check: Pass a background check to ensure you are eligible to serve.
Conclusion
The Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve offer unique opportunities for those who want to serve their country while maintaining a civilian life. Understanding the differences between these two branches is crucial in making an informed decision about which path to take.
Whether you choose to join the ANG or AFR, you will be part of a proud tradition of service and sacrifice. By serving in one of these branches, you will have the opportunity to develop valuable skills, advance your career, and make a positive impact on the lives of those around you.
Air Guard vs Air Reserve Image Gallery








What is the main difference between the Air National Guard and the Air Force Reserve?
+The main difference is the dual status of the Air National Guard, which serves both the state and federal governments, whereas the Air Force Reserve is strictly a federal organization.
Can I join the Air National Guard or Air Force Reserve if I have a felony conviction?
+It is unlikely that you will be eligible to join the Air National Guard or Air Force Reserve with a felony conviction. However, it is best to consult with a recruiter to discuss your individual circumstances.
How long is the enlistment contract for the Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve?
+The enlistment contract for the Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve is typically 6 years.
