Intro
Explore the iconic American World War 2 bombers, specifically the B-17 Flying Fortress, a legendary aircraft that dominated the skies during WWII. Learn about its design, capabilities, and historic missions, as well as its significance in the Allied victory, and discover why it remains an enduring symbol of American aviation ingenuity.
The United States' involvement in World War 2 marked a significant turning point in the country's history, and one of the key factors that contributed to the Allied victory was the development and deployment of American World War 2 bombers. Among the most iconic and revered of these bombers was the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, a behemoth of a plane that earned its nickname due to its durability and formidable defensive capabilities.

The B-17 Flying Fortress was a four-engine heavy bomber designed to provide long-range, high-altitude bombing capabilities. With a crew of ten, the B-17 was equipped with a range of defensive armaments, including machine guns and cannons, making it a formidable opponent in the skies. Its robust design and redundant systems allowed the plane to sustain significant damage and continue flying, earning it a reputation for reliability and toughness.
Design and Development
The B-17 was designed in response to a 1934 United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) request for a new multi-engine bomber. Boeing, along with two other manufacturers, submitted proposals for the project, with Boeing's design ultimately being selected. The first B-17 prototype made its maiden flight in July 1935, and after several iterations and improvements, the B-17B entered production in 1939.
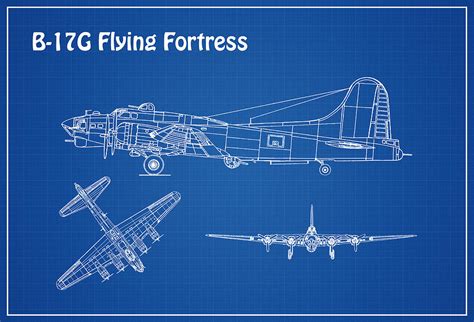
Key Features and Innovations
The B-17 Flying Fortress boasted several innovative features and design elements that set it apart from other bombers of its time. Some of the key features included:
- Four Wright R-1820 radial engines, providing a combined 4,800 horsepower
- A robust airframe designed to withstand significant damage and continue flying
- Redundant systems, including duplicate engines, fuel tanks, and control surfaces
- A crew of ten, including pilots, navigators, gunners, and bombardiers
- A range of defensive armaments, including machine guns and cannons
Operational History
The B-17 Flying Fortress saw extensive service during World War 2, participating in numerous campaigns and battles. The plane's first combat deployment was in 1941, when a squadron of B-17s was sent to the Philippines to bolster the country's defenses against Japanese aggression.

The B-17 played a significant role in the Allied bombing campaign against Germany, participating in numerous raids against key industrial and military targets. The plane's ability to fly at high altitudes and withstand significant damage made it an ideal platform for daylight bombing missions.
Notable Missions and Incidents
The B-17 Flying Fortress was involved in several notable missions and incidents during World War 2. Some of the most significant include:
- The Doolittle Raid: A squadron of B-17s, led by Lieutenant Colonel James H. Doolittle, launched a surprise attack on Tokyo in April 1942, striking key industrial and military targets.
- The Schweinfurt-Regensburg Mission: In August 1943, a large formation of B-17s launched a daring daylight raid against key industrial targets in Germany, including the Schweinfurt ball bearing factory and the Regensburg aircraft factory.
- The Memphis Belle: A B-17 nicknamed the Memphis Belle became the first heavy bomber to complete 25 missions over Europe, earning its crew significant recognition and accolades.
Legacy and Impact
The B-17 Flying Fortress played a significant role in the Allied victory in World War 2, contributing to the destruction of key industrial and military targets in Germany and Japan. The plane's durability, reliability, and defensive capabilities made it a formidable opponent in the skies, earning it a reputation as one of the greatest bombers in history.

The B-17 also played a significant role in the development of modern bomber design, influencing the creation of later planes such as the Boeing B-29 Superfortress and the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress.
Preservation and Restoration
Several B-17 Flying Fortresses have been preserved and restored, with many on display in museums and airshows around the world. Some of the most notable include:
- The National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio
- The National World War II Museum in New Orleans, Louisiana
- The Boeing Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington
American World War 2 Bombers Image Gallery






What was the B-17 Flying Fortress's primary role in World War 2?
+The B-17 Flying Fortress was a heavy bomber, used primarily for daylight bombing missions against industrial and military targets in Germany and Japan.
What were some of the B-17's key features and innovations?
+The B-17 boasted a robust airframe, redundant systems, and a range of defensive armaments, including machine guns and cannons.
What was the significance of the Memphis Belle?
+The Memphis Belle was a B-17 that became the first heavy bomber to complete 25 missions over Europe, earning its crew significant recognition and accolades.
The B-17 Flying Fortress remains one of the most iconic and revered planes in history, a testament to American ingenuity and determination. Its legacy continues to inspire and educate, serving as a reminder of the significant contributions made by the United States during World War 2.
