Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the armed forces with our comprehensive guide to Army and Navy ranks. Discover the meanings behind 20 insignias and roles, from enlisted personnel to high-ranking officers. Learn about the different ranks, responsibilities, and insignia for each branch, including enlisted, warrant, and commissioned officers, and understand the promotions and requirements for advancement.
The military is a cornerstone of any country's defense and security, and understanding its organizational structure is essential for appreciating the roles and responsibilities of its personnel. At the heart of this structure are the ranks, which serve as a hierarchical system defining authority, responsibility, and level of expertise. The army and navy, two of the primary branches of the military, have their own unique set of ranks, each with distinct insignias and roles.
In this article, we will delve into the world of army and navy ranks, exploring 20 insignias and roles that define the chain of command and operational responsibilities within these two branches. Understanding these ranks not only provides insight into the military's organizational complexity but also sheds light on the dedication, hard work, and sacrifices made by those who serve.
Understanding Military Ranks
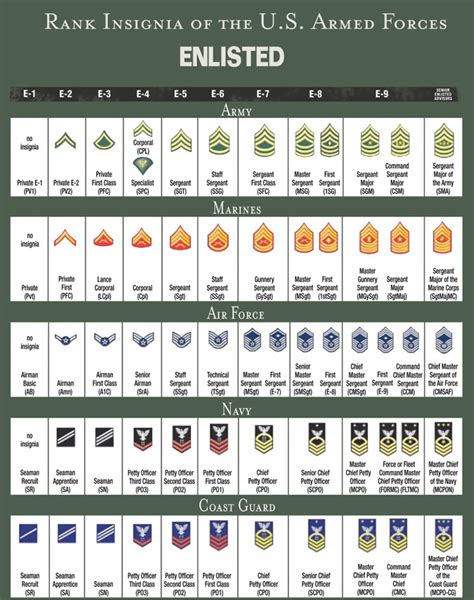
Military ranks are not merely symbols of authority; they signify the level of expertise, experience, and responsibility an individual has within the military. These ranks are divided into two primary categories: enlisted personnel and officers. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the military and are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations, while officers are leaders who have completed a higher level of education and training, commanding and directing operations.
Enlisted Personnel vs. Officers
- Enlisted Personnel: These are individuals who have enlisted in the military without a college degree. They undergo basic training and specialize in a specific skill or Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
- Officers: Officers are leaders who have a college degree and have completed Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy. They hold positions of authority and are responsible for strategic planning and decision-making.
Army Ranks Explained

The army's rank structure is a complex system that defines the level of authority, responsibility, and pay grade of its personnel. It is divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and officers.
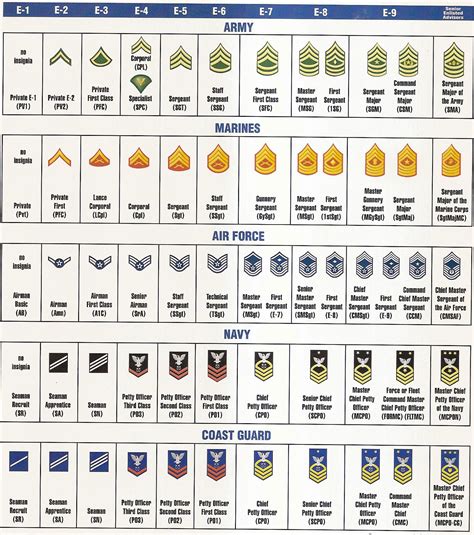
Enlisted Personnel
-
Private (PVT) - E-1
- The lowest rank in the army, privates are in the initial stages of their military career.
- Insignia: None
-
Private Second Class (PV2) - E-2
- Above private, this rank requires more time in service and demonstrates a level of responsibility.
- Insignia: One chevron
-
Private First Class (PFC) - E-3
- A higher rank than private second class, privates first class are more experienced and skilled.
- Insignia: One chevron with a rocker underneath
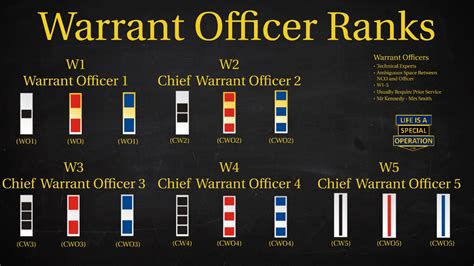
Warrant Officers
-
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) - W-1
- Warrant officers are technical experts in their field and serve as advisors to commanders.
- Insignia: A silver bar with a black square in the center
-
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) - W-2
- Above warrant officer 1, chief warrant officer 2s are more experienced and have more responsibility.
- Insignia: A silver bar with a black square in the center and a leaf
-
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) - W-3
- A higher rank than chief warrant officer 2, chief warrant officer 3s are specialists in their field.
- Insignia: A silver bar with a black square in the center and two leaves
-
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) - W-4
- Chief warrant officer 4s are experienced leaders and technical experts.
- Insignia: A silver bar with a black square in the center and three leaves
-
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) - W-5
- The highest rank for warrant officers, chief warrant officer 5s are highly respected for their expertise.
- Insignia: A silver bar with a black square in the center and four leaves
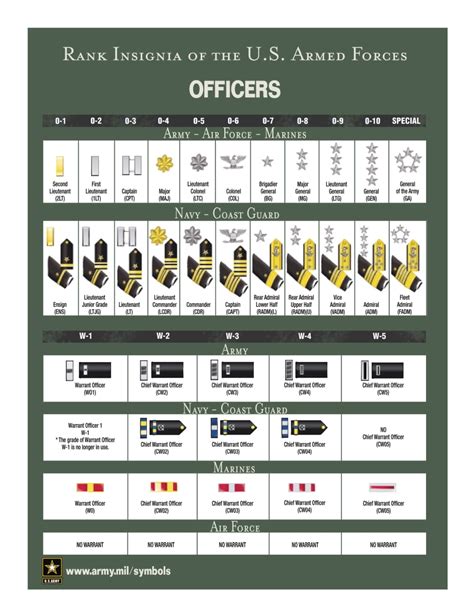
Officers
-
Second Lieutenant (2LT) - O-1
- The lowest officer rank, second lieutenants are recent graduates of the service academy or OCS.
- Insignia: One gold bar
-
First Lieutenant (1LT) - O-2
- Above second lieutenant, first lieutenants are more experienced and responsible for leading platoons.
- Insignia: One gold bar with a silver oak leaf
-
Captain (CPT) - O-3
- Captains are company commanders and are responsible for leading companies.
- Insignia: Two gold bars
-
Major (MAJ) - O-4
- Majors are field-grade officers who serve as battalion or brigade executive officers.
- Insignia: A gold oak leaf
-
Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) - O-5
- Lieutenant colonels are battalion commanders and have significant leadership responsibilities.
- Insignia: A silver oak leaf
-
Colonel (COL) - O-6
- Colonels are brigade commanders and have a high level of authority and responsibility.
- Insignia: An eagle
-
Brigadier General (BG) - O-7
- Brigadier generals are one-star generals and serve as assistant division commanders.
- Insignia: One star
-
Major General (MG) - O-8
- Major generals are two-star generals and serve as division commanders.
- Insignia: Two stars
-
Lieutenant General (LTG) - O-9
- Lieutenant generals are three-star generals and serve as corps commanders.
- Insignia: Three stars
-
General (GEN) - O-10
- Generals are four-star generals and serve as the highest-ranking officers in the army.
- Insignia: Four stars
Navy Ranks Explained

The navy's rank structure is similar to the army's but has some key differences. It is also divided into enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and officers.
Enlisted Personnel
-
Seaman Recruit (SR) - E-1
- The lowest rank in the navy, seaman recruits are in the initial stages of their military career.
- Insignia: None
-
Seaman Apprentice (SA) - E-2
- Above seaman recruit, seaman apprentices are more experienced and skilled.
- Insignia: One diagonal stripe
-
Seaman (SN) - E-3
- Seamen are experienced sailors who have specialized in a particular skill.
- Insignia: Two diagonal stripes
Warrant Officers
-
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) - W-1
- Warrant officers in the navy are technical experts in their field.
- Insignia: A fouled anchor
-
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) - W-2
- Above warrant officer 1, chief warrant officer 2s are more experienced.
- Insignia: A fouled anchor with a gold leaf
-
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) - W-3
- Chief warrant officer 3s are specialists in their field.
- Insignia: A fouled anchor with two gold leaves
-
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) - W-4
- Chief warrant officer 4s are experienced leaders and technical experts.
- Insignia: A fouled anchor with three gold leaves
-
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) - W-5
- The highest rank for warrant officers in the navy, chief warrant officer 5s are highly respected.
- Insignia: A fouled anchor with four gold leaves
Officers
-
Ensign (ENS) - O-1
- The lowest officer rank in the navy, ensigns are recent graduates of the service academy or OCS.
- Insignia: One gold bar
-
Lieutenant Junior Grade (LTJG) - O-2
- Above ensign, lieutenant junior grades are more experienced and responsible for leading divisions.
- Insignia: One gold bar with a silver oak leaf
-
Lieutenant (LT) - O-3
- Lieutenants are experienced officers who serve as department heads on ships.
- Insignia: Two gold bars
-
Lieutenant Commander (LCDR) - O-4
- Lieutenant commanders are experienced leaders who serve as executive officers on ships.
- Insignia: A gold oak leaf
-
Commander (CDR) - O-5
- Commanders are experienced officers who command ships and shore-based activities.
- Insignia: A silver oak leaf
-
Captain (CAPT) - O-6
- Captains are experienced leaders who command large ships and shore-based activities.
- Insignia: An eagle
-
Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (RDML) - O-7
- Rear admirals are one-star admirals and serve as assistants to fleet commanders.
- Insignia: One star
-
Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (RADM) - O-8
- Rear admirals are two-star admirals and serve as fleet commanders.
- Insignia: Two stars
-
Vice Admiral (VA) - O-9
- Vice admirals are three-star admirals and serve as deputy commanders of fleets.
- Insignia: Three stars
-
Admiral (ADM) - O-10
- Admirals are four-star admirals and serve as the highest-ranking officers in the navy.
- Insignia: Four stars
Gallery of Army and Navy Ranks
Army and Navy Ranks Image Gallery
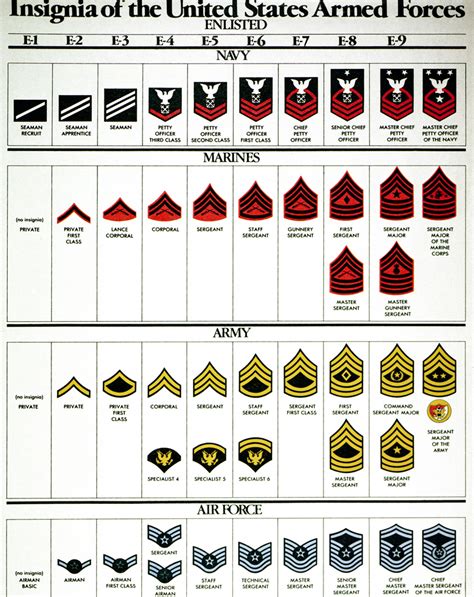
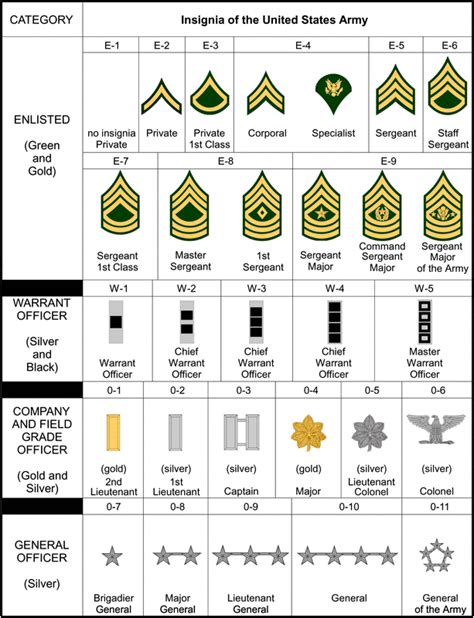


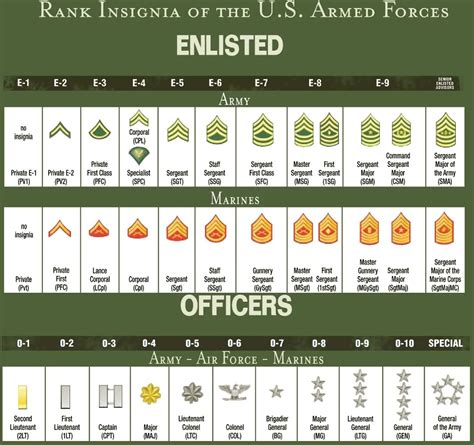
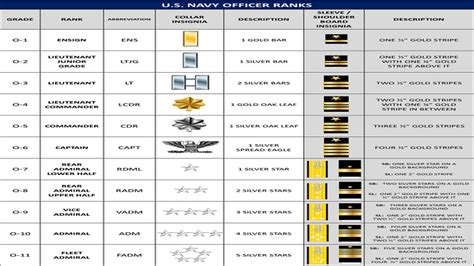

What are the differences between army and navy ranks?
+The primary difference between army and navy ranks lies in their insignias and the responsibilities associated with each rank. While both branches follow a similar hierarchical structure, their roles and insignias are unique to their branch of service.
What are the highest ranks in the army and navy?
+The highest rank in the army is General (GEN), and in the navy, it is Admiral (ADM). Both are four-star ranks and signify the highest level of authority and responsibility within their respective branches.
How do enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and officers differ?
+Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the military, carrying out day-to-day operations. Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, serving as advisors to commanders. Officers are leaders who have completed a higher level of education and training, commanding and directing operations.
Understanding the complexities of army and navy ranks not only provides insight into the military's organizational structure but also highlights the dedication and sacrifices made by those who serve. Whether enlisted personnel, warrant officers, or officers, each rank plays a crucial role in maintaining national defense and security.
