Intro
Discover 5 ways to implement Kanban, a lean methodology, to boost agile project management, workflow visualization, and team collaboration, enhancing productivity and efficiency with continuous improvement and iterative development.
The world of project management and workflow optimization is vast and diverse, with numerous methodologies and tools designed to help teams and individuals work more efficiently. Among these, Kanban has emerged as a popular and highly effective approach, emphasizing continuous improvement, flexibility, and visualization of work. Kanban, which translates to "visual board" in Japanese, originated in the manufacturing industry but has since been widely adopted across various sectors, including software development, marketing, and beyond. At its core, Kanban is about managing work by balancing demands with available capacity, and continuous improvement. Here, we'll delve into five ways to implement Kanban, exploring its principles, benefits, and practical applications.
Kanban's appeal lies in its simplicity and adaptability. Unlike some other project management methodologies that require strict adherence to specific practices or roles, Kanban can be tailored to fit the unique needs and culture of any team. It focuses on visualizing the workflow, limiting work in progress, and enhancing flow. This means teams can see their work, understand the workflow, and make informed decisions about how to manage their tasks and projects more effectively. Whether you're looking to improve team collaboration, reduce project delivery times, or simply make your work processes more transparent and manageable, Kanban offers a flexible framework that can be applied in various ways.
One of the key reasons Kanban has gained such widespread acceptance is its ability to promote continuous improvement. By visualizing the workflow and analyzing the flow of work, teams can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This leads to a culture of ongoing learning and adaptation, where processes are regularly reviewed and refined to better meet the needs of the team and the organization as a whole. Moreover, Kanban's emphasis on limiting work in progress helps prevent overcommitting and reduces the stress associated with trying to manage too many tasks simultaneously. This approach not only improves productivity but also enhances job satisfaction, as team members feel more in control of their work and are better able to manage their workload.
Understanding Kanban Basics
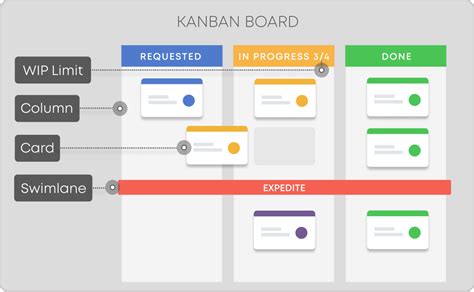
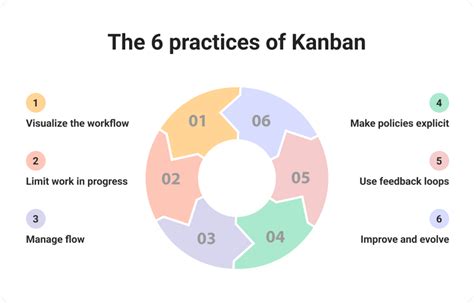
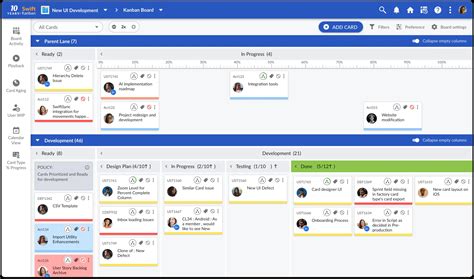
To apply Kanban effectively, it's essential to understand its core principles. These include visualization, limiting work in progress, focus on flow, continuous improvement, and lead time reduction. Visualization involves creating a clear and concise representation of the workflow, often using a Kanban board, which can be physical or digital. Limiting work in progress means setting boundaries on how much work can be in each stage of the workflow at any given time, preventing overload and promoting focus. The focus on flow encourages teams to prioritize moving work through the system efficiently, rather than maximizing individual productivity. Continuous improvement involves regularly assessing and refining the workflow to eliminate waste and improve delivery times. Finally, reducing lead time—the time it takes for work to go from start to finish—is a key metric for measuring the effectiveness of a Kanban system.
Implementing Kanban in Software Development
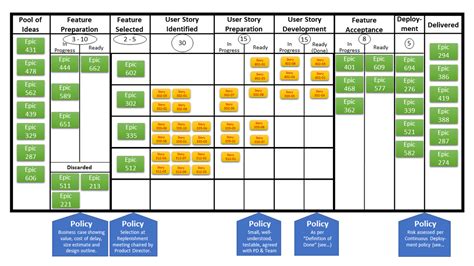
In software development, Kanban can be particularly beneficial, allowing teams to manage complex projects with multiple stakeholders and dependencies. By visualizing the development workflow, teams can better understand the status of features, identify potential bottlenecks early, and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation. Kanban also facilitates continuous integration and delivery, enabling teams to release software updates more frequently and respond quickly to customer feedback. Moreover, its emphasis on limiting work in progress helps development teams avoid context switching and reduce the complexity associated with managing numerous tasks simultaneously.
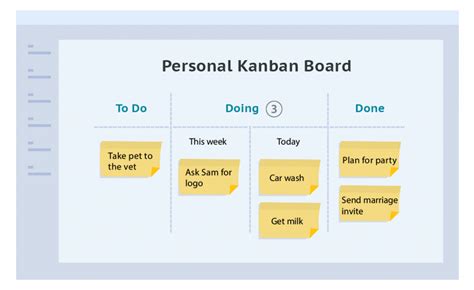
Kanban for Personal Productivity
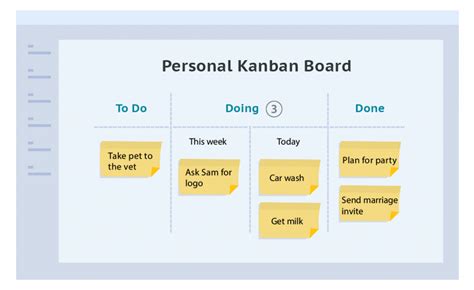
Beyond team and project management, Kanban can also be applied to personal productivity. Individuals can use Kanban boards to visualize their tasks and projects, prioritize work based on importance and deadlines, and limit their work in progress to focus on the most critical tasks. This approach helps in avoiding multitasking, which can lead to divided attention and reduced productivity. By applying Kanban principles, individuals can better manage their time, reduce stress, and achieve a more balanced work-life integration. Personal Kanban boards can be as simple as sticky notes on a wall or as sophisticated as digital tools designed specifically for Kanban.
Scaling Kanban Across Organizations

As organizations grow, scaling Kanban to meet the needs of multiple teams and departments becomes essential. This involves creating a system that allows different teams to work together seamlessly, sharing knowledge, and aligning their workflows to achieve common goals. Scaling Kanban requires a deep understanding of the organization's overall strategy and objectives, as well as the unique challenges and opportunities faced by each team. It's about creating a culture of transparency, collaboration, and continuous improvement that permeates every level of the organization. By doing so, organizations can enhance their agility, improve customer satisfaction, and stay competitive in rapidly changing markets.
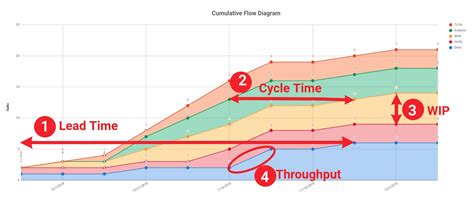
Measuring Kanban Success

Measuring the success of a Kanban implementation is crucial for understanding its impact and identifying areas for further improvement. Key metrics include lead time, cycle time, throughput, and work in progress. Lead time measures how long it takes for work to go from request to delivery, while cycle time focuses on the time work spends in the development stage. Throughput refers to the amount of work completed over a set period, and work in progress (WIP) limits are essential for maintaining flow and preventing overloading. By tracking these metrics, teams and organizations can assess the effectiveness of their Kanban system, make informed decisions about process improvements, and ultimately deliver value to customers more efficiently.
Kanban Implementation Gallery




What are the core principles of Kanban?
+The core principles of Kanban include visualization, limiting work in progress, focus on flow, continuous improvement, and lead time reduction. These principles work together to create a system that is efficient, adaptable, and focused on delivering value.
How does Kanban differ from other project management methodologies?
+Kanban differs from other methodologies like Scrum or Agile in its flexibility and lack of rigid roles or ceremonies. It focuses on workflow visualization and continuous improvement, making it highly adaptable to different teams and projects.
Can Kanban be applied to personal productivity?
+Yes, Kanban can be applied to personal productivity. By using a personal Kanban board, individuals can visualize their tasks, limit their work in progress, and focus on delivering value in their personal and professional lives.
What metrics are used to measure the success of a Kanban implementation?
+Key metrics for measuring Kanban success include lead time, cycle time, throughput, and work in progress. These metrics help teams understand the efficiency of their workflow and identify areas for improvement.
How can teams scale Kanban across an organization?
+Scaling Kanban involves creating a culture of transparency, collaboration, and continuous improvement that aligns with the organization's overall strategy. It requires understanding the unique needs of each team and department, and implementing a system that allows for seamless collaboration and workflow alignment.
In conclusion, Kanban offers a versatile and effective approach to managing work, whether at the team, project, or personal level. Its emphasis on visualization, limiting work in progress, and continuous improvement makes it an attractive methodology for those seeking to enhance productivity, reduce stress, and deliver value more efficiently. By understanding and applying the principles of Kanban, individuals and teams can unlock new levels of performance and achieve their goals with greater ease and agility. We invite you to share your experiences with Kanban, ask questions, and explore how this powerful methodology can transform your work and personal projects. Whether you're just starting out or are a seasoned practitioner, the journey to mastering Kanban is one of continuous learning and improvement, and we're excited to be a part of it.
