Intro
Discover how soldiers get paid while serving in the military. Learn about the 5 ways service members receive compensation, including base pay, allowances, special pays, and bonuses. Understand the military pay chart and how factors like rank, time in service, and family size impact earnings. Get insight into military pay benefits.
Being a soldier can be a challenging yet rewarding career, offering a range of benefits and compensation. One of the most significant advantages of serving in the military is the financial support provided to soldiers and their families. From basic pay to specialized allowances, soldiers receive various forms of compensation that help them support themselves and their loved ones. In this article, we will explore the different ways soldiers get paid while serving, highlighting the various forms of compensation and benefits they receive.
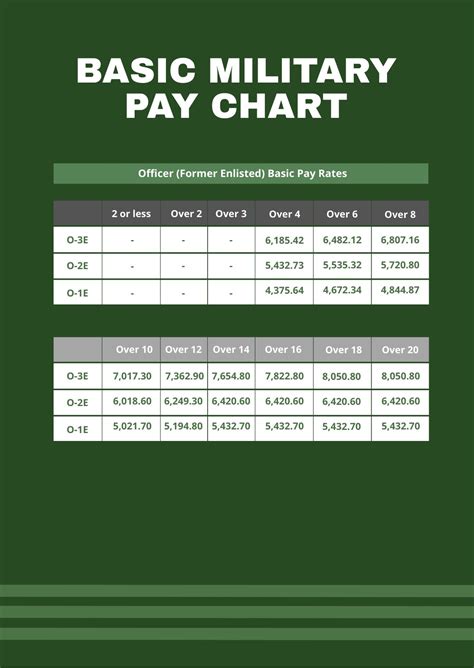
Basic Pay
Basic pay is the fundamental form of compensation for soldiers, providing a steady income that reflects their rank and time in service. The amount of basic pay varies based on the soldier's pay grade, which is determined by their rank and time in service. The higher the rank and the longer the time in service, the higher the basic pay. Basic pay is tax-free, and soldiers can expect to receive their pay bi-weekly.
Pay Grades and Ranks
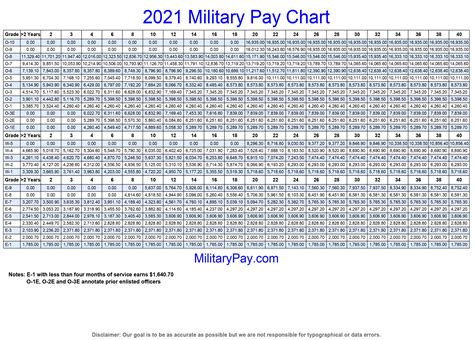
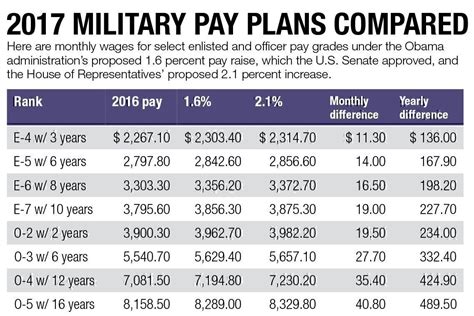
The military uses a pay grade system to determine the basic pay for soldiers. There are nine pay grades, ranging from E-1 (Private) to E-9 (Sergeant Major). Each pay grade corresponds to a specific rank, and the pay increases as the soldier advances in rank. For example, a Private (E-1) with less than two years of service can expect to earn around $1,733 per month, while a Sergeant Major (E-9) with over 20 years of service can earn up to $8,498 per month.

Allowances
In addition to basic pay, soldiers receive various allowances that help cover living expenses, food, and housing. These allowances are tax-free and can vary based on the soldier's location, rank, and family size.
Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH)
The Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) is a monthly allowance that helps soldiers pay for housing expenses. The amount of BAH varies based on the soldier's location, rank, and family size. For example, a soldier stationed in New York City can expect to receive a higher BAH than a soldier stationed in a smaller town.
Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS)
The Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS) is a monthly allowance that helps soldiers pay for food expenses. The amount of BAS is the same for all soldiers, regardless of rank or location.

Special Duty Pay
Soldiers who perform specialized duties, such as flying or diving, may receive special duty pay. This pay is in addition to their basic pay and allowances and is designed to compensate soldiers for the unique challenges and risks associated with their duties.
Flight Pay
Soldiers who fly aircraft, such as pilots or navigators, may receive flight pay. The amount of flight pay varies based on the soldier's rank, time in service, and flying experience.
Diving Duty Pay
Soldiers who perform diving duties, such as Navy SEALs or Army Rangers, may receive diving duty pay. The amount of diving duty pay varies based on the soldier's rank, time in service, and diving experience.

Bonuses
Soldiers may receive bonuses for various reasons, such as enlisting, reenlisting, or performing hazardous duties. These bonuses are one-time payments that can provide a significant financial boost.
Enlistment Bonus
Soldiers who enlist in the military may receive an enlistment bonus. The amount of the bonus varies based on the soldier's Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) and the length of their enlistment contract.
Reenlistment Bonus
Soldiers who reenlist in the military may receive a reenlistment bonus. The amount of the bonus varies based on the soldier's rank, time in service, and the length of their reenlistment contract.

Education Benefits
Soldiers may receive education benefits, such as the GI Bill, to help pay for college or vocational training. These benefits can provide significant financial assistance and can be used to pursue higher education or career advancement.
GI Bill
The GI Bill is a popular education benefit that provides soldiers with financial assistance to pursue higher education or vocational training. The bill can be used to cover tuition, fees, and living expenses, and can be transferred to dependents.

Military Pay and Benefits Image Gallery







How much do soldiers get paid?
+Soldiers' pay varies based on their rank, time in service, and location. Basic pay ranges from around $1,733 per month for a Private (E-1) to over $8,498 per month for a Sergeant Major (E-9).
What are military allowances?
+Military allowances are tax-free payments that help soldiers cover living expenses, food, and housing. The most common allowances are Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS).
Can soldiers receive education benefits?
+Yes, soldiers can receive education benefits, such as the GI Bill, to help pay for college or vocational training. These benefits can provide significant financial assistance and can be transferred to dependents.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the various ways soldiers get paid while serving. From basic pay to specialized allowances and education benefits, soldiers receive a range of compensation and benefits that help support themselves and their families.
